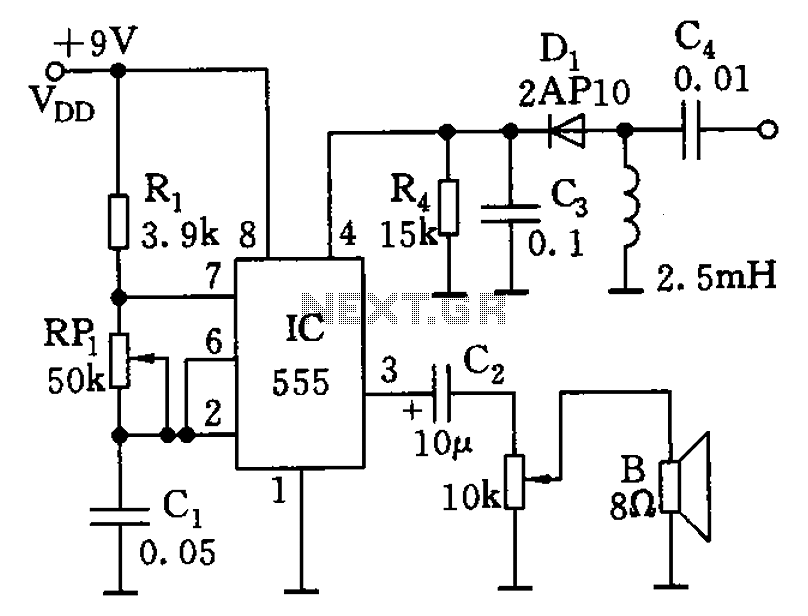
96Mhz crystal oscillator
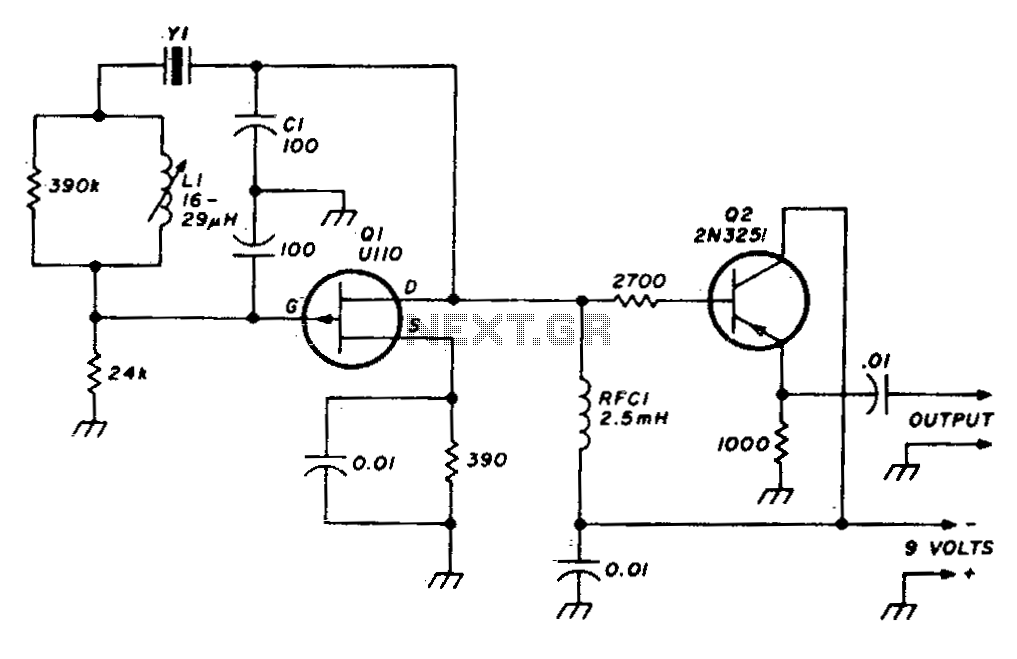
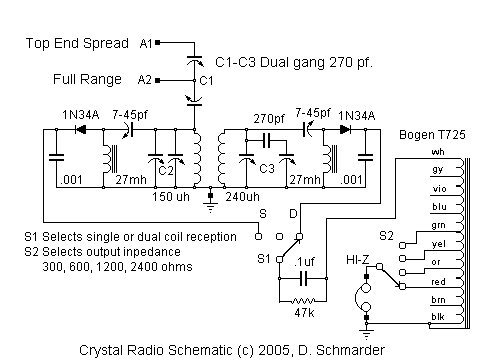
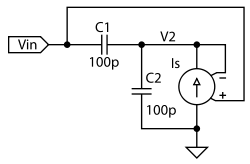
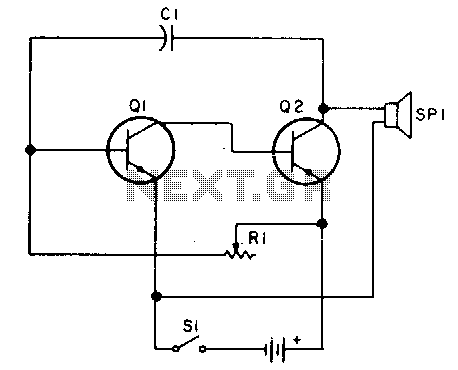
A stable variable crystal oscillator (VXO) utilizing 6- or 8-MHz crystals employs a capacitor and an inductor to facilitate frequency pulling on either side of series resonance.
The described circuit operates as a variable crystal oscillator, which is crucial in applications requiring precise frequency control. The oscillator employs a fundamental frequency set by the crystal, which serves as a frequency reference. The inclusion of a capacitor and an inductor allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency through a technique known as frequency pulling.
In this configuration, the crystal is connected in series with the inductor and capacitor, forming a resonant circuit. The resonant frequency of this LC circuit can be adjusted by varying the capacitance or inductance, which alters the effective load on the crystal. When the frequency is adjusted slightly above or below the crystal's natural frequency, the circuit can pull the frequency in either direction, thus providing a range of output frequencies.
The stability of the oscillator is primarily determined by the quality factors of the inductor and capacitor, as well as the crystal itself. A high-quality crystal will exhibit low phase noise and minimal drift, making it suitable for applications such as RF transmission, where precision is paramount. Additionally, the choice of inductor and capacitor values must be carefully calculated to ensure that the circuit operates within the desired frequency range without compromising stability.
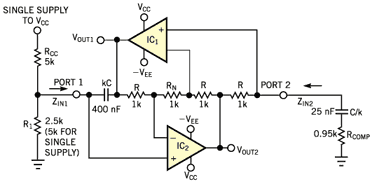
The output of the VXO can be further processed or amplified, depending on the specific application requirements. This flexibility makes the VXO a valuable component in various electronic systems, including communication devices, signal generators, and frequency synthesizers.Stable VXO using 6- or 8-MHz crystals uses a capacitor and an inductor to achieve frequency pulling on either side of series resonance. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a variable crystal oscillator, which is crucial in applications requiring precise frequency control. The oscillator employs a fundamental frequency set by the crystal, which serves as a frequency reference. The inclusion of a capacitor and an inductor allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency through a technique known as frequency pulling.
In this configuration, the crystal is connected in series with the inductor and capacitor, forming a resonant circuit. The resonant frequency of this LC circuit can be adjusted by varying the capacitance or inductance, which alters the effective load on the crystal. When the frequency is adjusted slightly above or below the crystal's natural frequency, the circuit can pull the frequency in either direction, thus providing a range of output frequencies.
The stability of the oscillator is primarily determined by the quality factors of the inductor and capacitor, as well as the crystal itself. A high-quality crystal will exhibit low phase noise and minimal drift, making it suitable for applications such as RF transmission, where precision is paramount. Additionally, the choice of inductor and capacitor values must be carefully calculated to ensure that the circuit operates within the desired frequency range without compromising stability.
The output of the VXO can be further processed or amplified, depending on the specific application requirements. This flexibility makes the VXO a valuable component in various electronic systems, including communication devices, signal generators, and frequency synthesizers.Stable VXO using 6- or 8-MHz crystals uses a capacitor and an inductor to achieve frequency pulling on either side of series resonance. 🔗 External reference