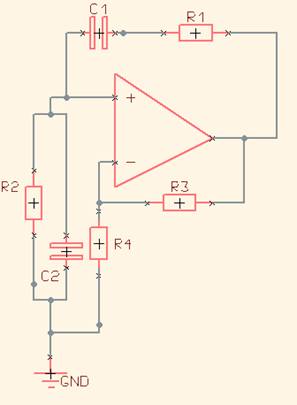
Wein bridge oscillator again
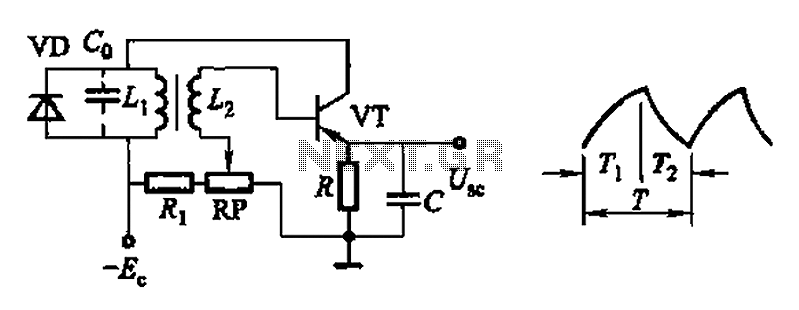
The objective is to test a Wien bridge oscillator and ensure its proper functionality. There is a study of relevant material, but some concepts remain unclear.
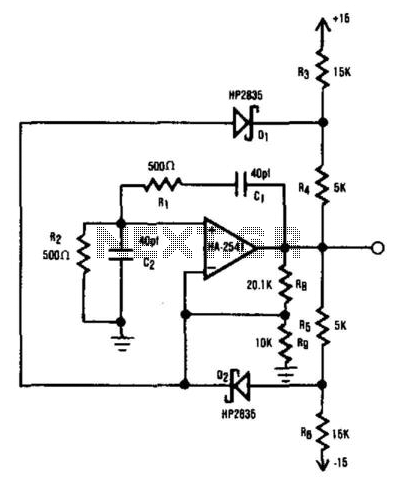
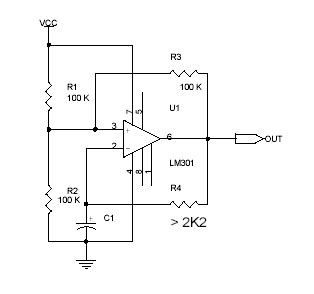
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It utilizes a bridge circuit, which consists of resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration to create a feedback loop. The oscillator operates based on the principle of positive and negative feedback, where the gain of the amplifier is adjusted to maintain oscillation.
To construct a Wien bridge oscillator, the following components are typically required: an operational amplifier (op-amp), four resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4), and two capacitors (C1 and C2). The resistors R1 and R2 are typically equal, and capacitors C1 and C2 are also equal, which establishes the frequency of oscillation. The frequency (f) of the output sine wave can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance value and C is the capacitance value used in the circuit.
The circuit configuration involves connecting the resistors and capacitors in a bridge arrangement. The output of the op-amp is connected to the junction of R1 and R2, while the feedback loop is established through R3 and R4. The gain of the op-amp is adjusted using a variable resistor or a thermistor, which helps stabilize the amplitude of the oscillation.
In operation, the Wien bridge oscillator begins to oscillate when powered on, provided that the gain of the amplifier is set correctly. If the gain is too high, the output will clip, leading to distortion. Conversely, if the gain is too low, oscillations may cease. Therefore, a balance must be achieved for the oscillator to function effectively.
To troubleshoot any issues, it is essential to verify the values of the resistors and capacitors, ensure proper connections, and check the power supply voltage. Additionally, an oscilloscope can be used to visualize the output waveform, aiding in diagnosing any problems with the circuit's performance.Hi I am testing wein bridge oscillator and I looking to make it work. I have study the page below, but there are some concept i do not understand.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It utilizes a bridge circuit, which consists of resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration to create a feedback loop. The oscillator operates based on the principle of positive and negative feedback, where the gain of the amplifier is adjusted to maintain oscillation.
To construct a Wien bridge oscillator, the following components are typically required: an operational amplifier (op-amp), four resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4), and two capacitors (C1 and C2). The resistors R1 and R2 are typically equal, and capacitors C1 and C2 are also equal, which establishes the frequency of oscillation. The frequency (f) of the output sine wave can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance value and C is the capacitance value used in the circuit.
The circuit configuration involves connecting the resistors and capacitors in a bridge arrangement. The output of the op-amp is connected to the junction of R1 and R2, while the feedback loop is established through R3 and R4. The gain of the op-amp is adjusted using a variable resistor or a thermistor, which helps stabilize the amplitude of the oscillation.
In operation, the Wien bridge oscillator begins to oscillate when powered on, provided that the gain of the amplifier is set correctly. If the gain is too high, the output will clip, leading to distortion. Conversely, if the gain is too low, oscillations may cease. Therefore, a balance must be achieved for the oscillator to function effectively.
To troubleshoot any issues, it is essential to verify the values of the resistors and capacitors, ensure proper connections, and check the power supply voltage. Additionally, an oscilloscope can be used to visualize the output waveform, aiding in diagnosing any problems with the circuit's performance.Hi I am testing wein bridge oscillator and I looking to make it work. I have study the page below, but there are some concept i do not understand.. 🔗 External reference