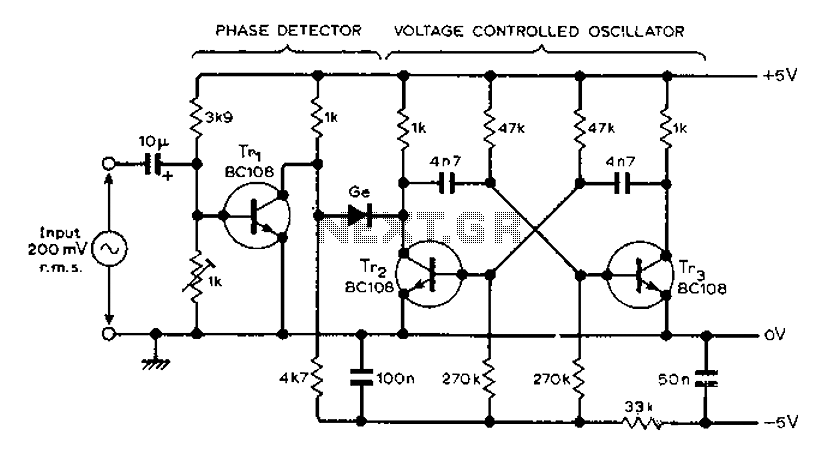
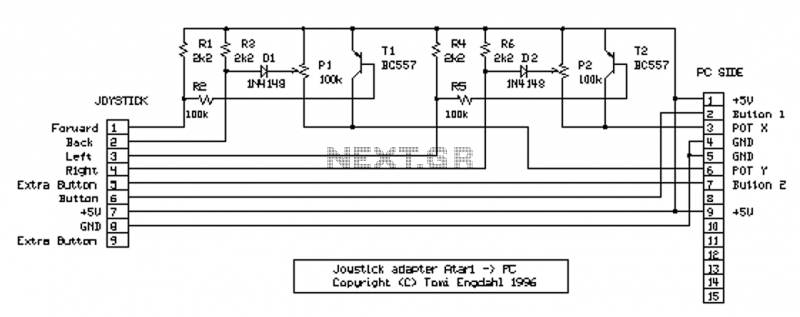
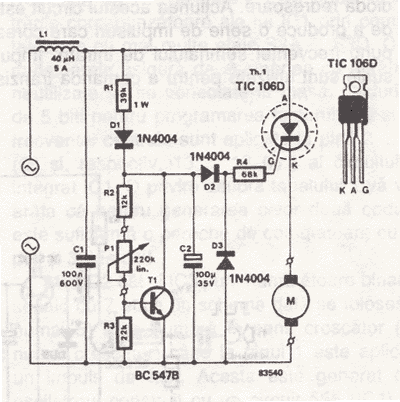
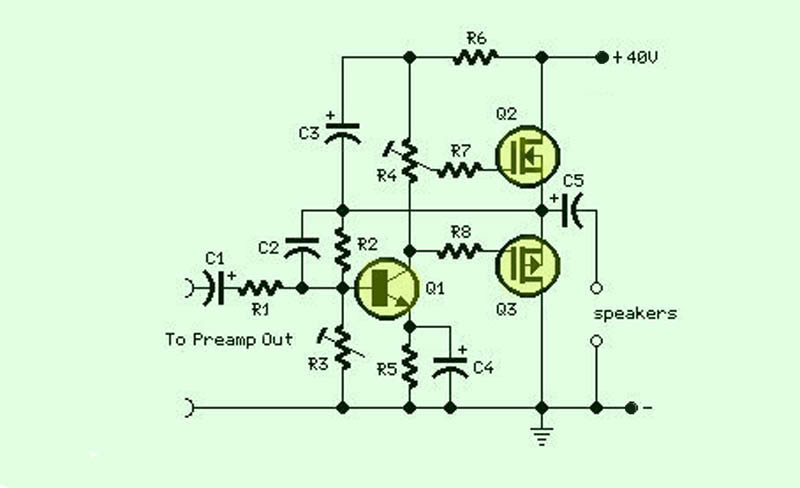
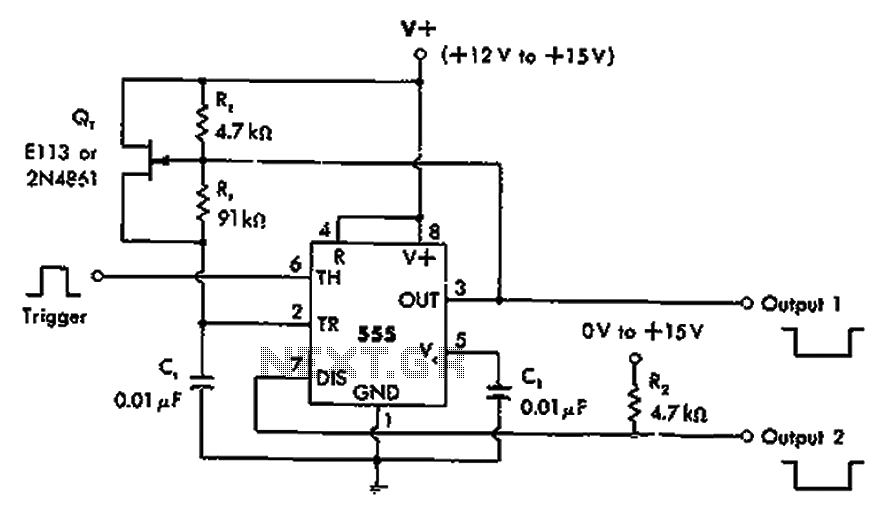
A differential input differential output amplifying circuit diagram
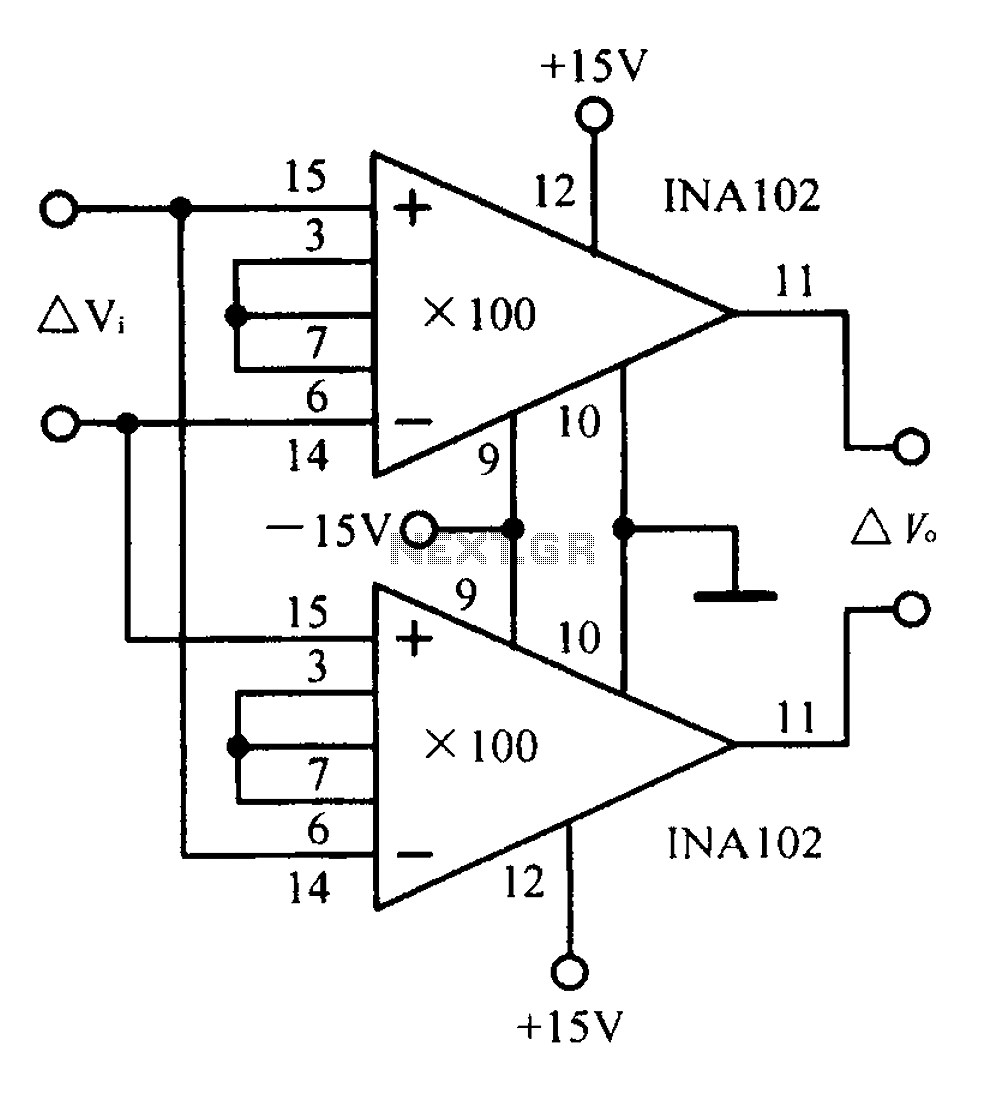
A differential input differential output amplifying circuit diagram.
A differential input differential output (DIDO) amplifier is a type of operational amplifier configuration that is designed to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This characteristic makes DIDO amplifiers particularly useful in applications where noise reduction and signal integrity are critical, such as in instrumentation and audio processing.
In a typical DIDO amplifier circuit, two input terminals (often labeled as V+ and V-) receive the differential signals. The output is taken from two output terminals, which provide the amplified difference. The circuit often employs resistors to set the gain, which can be adjusted by changing the resistor values. Feedback loops are commonly utilized to stabilize the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier, ensuring reliable performance over a range of frequencies.
The configuration may include additional components such as capacitors for frequency compensation, which helps to prevent oscillations and improve transient response. Power supply considerations are also important; the amplifier typically requires dual power supplies (positive and negative) to accommodate the full range of input signal variations.
Overall, the DIDO amplifier circuit is a versatile tool in electronic design, capable of delivering high precision and low distortion in various applications. Proper understanding of its design and implementation is essential for achieving optimal performance in specific use cases.A differential input differential output amplifying circuit diagram:
A differential input differential output (DIDO) amplifier is a type of operational amplifier configuration that is designed to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. This characteristic makes DIDO amplifiers particularly useful in applications where noise reduction and signal integrity are critical, such as in instrumentation and audio processing.
In a typical DIDO amplifier circuit, two input terminals (often labeled as V+ and V-) receive the differential signals. The output is taken from two output terminals, which provide the amplified difference. The circuit often employs resistors to set the gain, which can be adjusted by changing the resistor values. Feedback loops are commonly utilized to stabilize the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier, ensuring reliable performance over a range of frequencies.
The configuration may include additional components such as capacitors for frequency compensation, which helps to prevent oscillations and improve transient response. Power supply considerations are also important; the amplifier typically requires dual power supplies (positive and negative) to accommodate the full range of input signal variations.
Overall, the DIDO amplifier circuit is a versatile tool in electronic design, capable of delivering high precision and low distortion in various applications. Proper understanding of its design and implementation is essential for achieving optimal performance in specific use cases.A differential input differential output amplifying circuit diagram:
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713