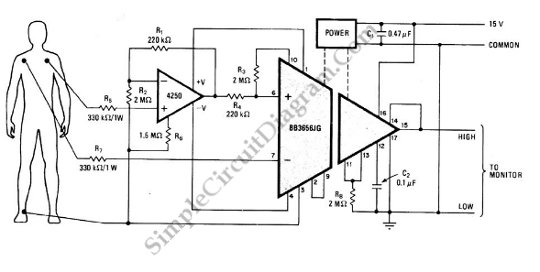
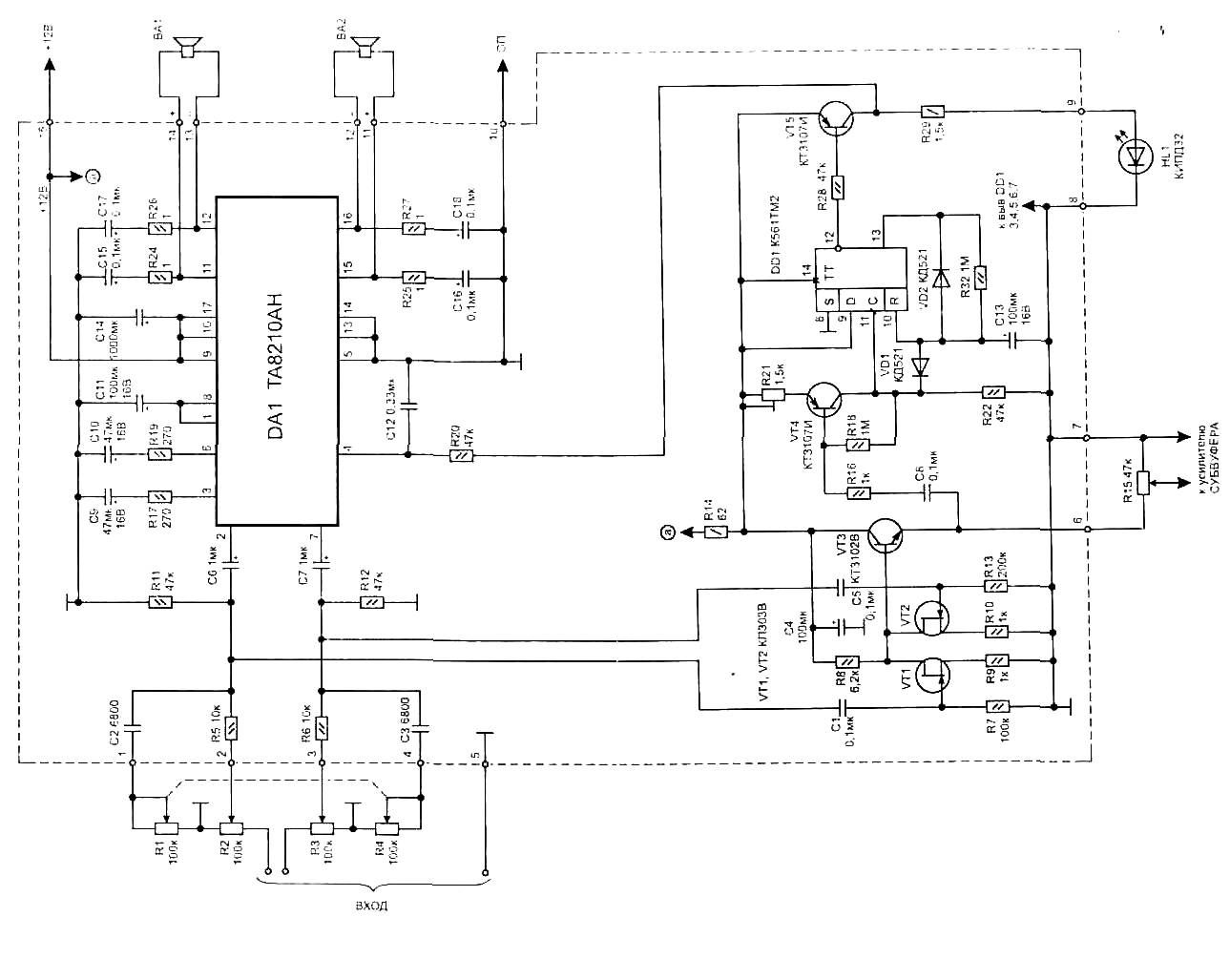
A Hiqh Quality Headphone Amplifier
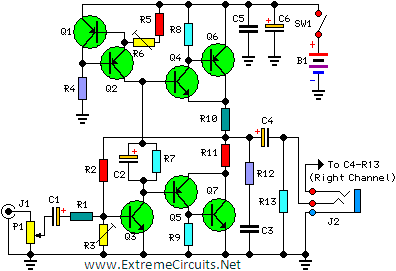
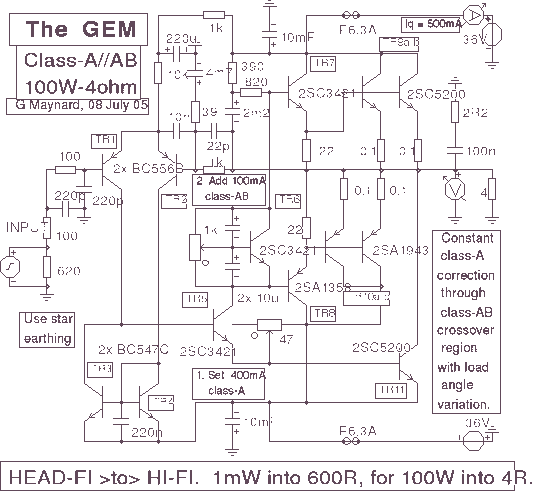
Enthusiasts of high-fidelity headphone listening often favor battery-powered headphone amplifiers for both portable and home use. This design aims to meet those preferences. By utilizing a push-pull Class-B configuration, the output driving capability is enhanced. The amplifier can deliver up to 100mW RMS into a 16 Ohm load at a 6V supply, maintaining low standing and average current consumption, which extends battery life.
The described headphone amplifier circuit employs a push-pull Class-B topology, which is characterized by its ability to efficiently drive headphones while minimizing distortion. In this configuration, two transistors are used: one for the positive half of the audio signal and the other for the negative half. This arrangement allows for a more effective use of the power supply, particularly when driving low-impedance loads such as 16 Ohm headphones.
The design operates at a supply voltage of 6V, which is suitable for battery operation, making it ideal for portable applications. The output power of 100mW RMS indicates that the amplifier can deliver sufficient volume levels for most headphones without introducing significant distortion, a crucial factor for high-fidelity listening.
The low standing and average current consumption are essential features of this amplifier design, as they contribute to the longevity of the battery life. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for users who prefer to use the amplifier in portable settings, where battery replacement or recharging can be inconvenient.
In terms of circuit implementation, the input stage typically consists of a differential amplifier configuration to provide high input impedance and low noise. The output stage, being push-pull, utilizes complementary transistors to enhance linearity and reduce crossover distortion. Proper biasing of the transistors is critical to ensure that they operate in their linear regions for the entire audio signal cycle.
Overall, this headphone amplifier design not only caters to the needs of high-fidelity enthusiasts but also emphasizes efficiency, making it a practical choice for both home and portable applications.Some lovers of High Fidelity headphone listening prefer the use of battery powered headphone amplifiers, not only for portable units but also for home "table" applications. This design is intended to fulfill their needs. An improved output driving capability is gained by making this a push-pull Class-B arrangement. Output power can reach 100mW RMS into a 16 Ohm load at 6V supply with low standing and mean current consumption, allowing long battery duration..
🔗 External reference
The described headphone amplifier circuit employs a push-pull Class-B topology, which is characterized by its ability to efficiently drive headphones while minimizing distortion. In this configuration, two transistors are used: one for the positive half of the audio signal and the other for the negative half. This arrangement allows for a more effective use of the power supply, particularly when driving low-impedance loads such as 16 Ohm headphones.
The design operates at a supply voltage of 6V, which is suitable for battery operation, making it ideal for portable applications. The output power of 100mW RMS indicates that the amplifier can deliver sufficient volume levels for most headphones without introducing significant distortion, a crucial factor for high-fidelity listening.
The low standing and average current consumption are essential features of this amplifier design, as they contribute to the longevity of the battery life. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for users who prefer to use the amplifier in portable settings, where battery replacement or recharging can be inconvenient.
In terms of circuit implementation, the input stage typically consists of a differential amplifier configuration to provide high input impedance and low noise. The output stage, being push-pull, utilizes complementary transistors to enhance linearity and reduce crossover distortion. Proper biasing of the transistors is critical to ensure that they operate in their linear regions for the entire audio signal cycle.
Overall, this headphone amplifier design not only caters to the needs of high-fidelity enthusiasts but also emphasizes efficiency, making it a practical choice for both home and portable applications.Some lovers of High Fidelity headphone listening prefer the use of battery powered headphone amplifiers, not only for portable units but also for home "table" applications. This design is intended to fulfill their needs. An improved output driving capability is gained by making this a push-pull Class-B arrangement. Output power can reach 100mW RMS into a 16 Ohm load at 6V supply with low standing and mean current consumption, allowing long battery duration..
🔗 External reference