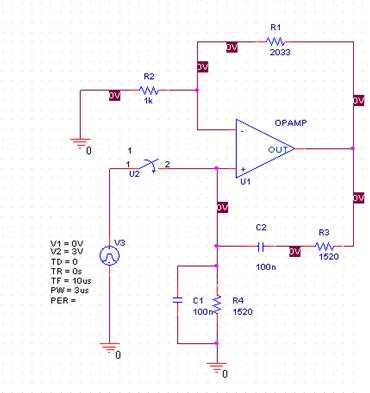
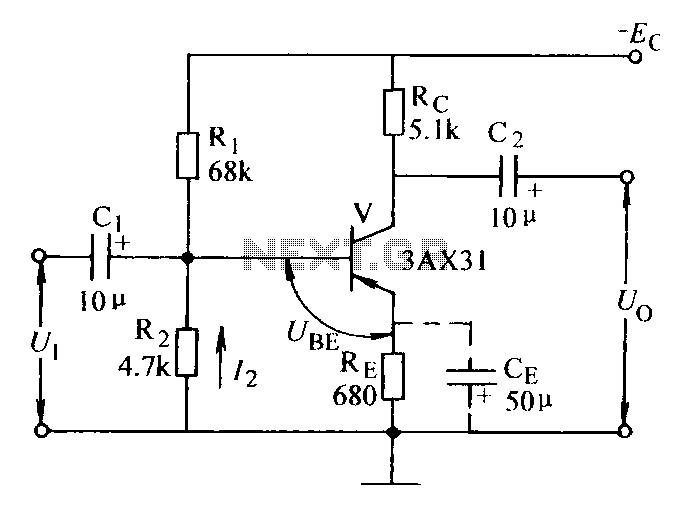
A hydraulic circuit diagram showing
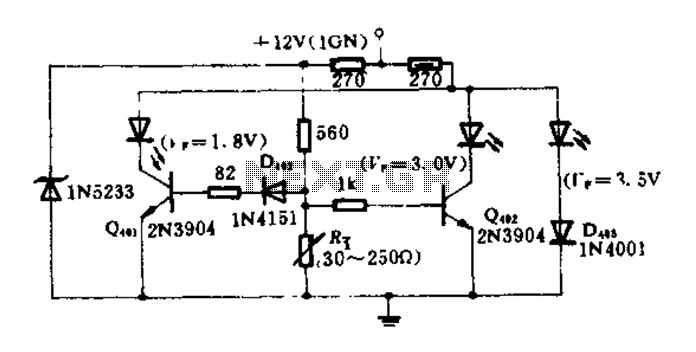
The circuit diagram illustrates how an oil pressure sensor is transformed into a variable resistor, denoted as Rt. Variations in Rt lead to changes in the biasing of each transistor, which in turn controls three LEDs (red, yellow, and green) that illuminate under forward bias at different intensities. By selecting the bias resistor correctly, it is possible to ensure that only one light-emitting diode activates to indicate the corresponding hydraulic pressure.
The circuit operates on the principle of using an oil pressure sensor that functions as a variable resistor, Rt. As the oil pressure in the system changes, the resistance value of Rt also changes correspondingly. This variation in resistance influences the biasing conditions of three transistors arranged in a configuration that allows them to control the current flowing to three different LEDs, each representing a specific pressure range.
The transistors are configured such that they are biased differently based on the resistance value of Rt. When the oil pressure is low, Rt increases, causing the first transistor to turn on, which in turn activates the red LED, signaling low pressure. As the pressure increases and Rt decreases, the biasing condition shifts, leading to the activation of the yellow LED at an intermediate pressure level. Finally, when the pressure reaches a certain threshold, the green LED is illuminated, indicating a safe operating pressure.
The selection of the bias resistor is critical in this design. It must be chosen to ensure that the transistors switch on and off at the correct thresholds corresponding to the desired pressure levels. This ensures that only one LED lights up at any given time, providing a clear and unambiguous indication of the hydraulic pressure status. The circuit provides a simple yet effective visual representation of pressure levels, enhancing the monitoring capabilities in hydraulic systems.FIG circuit, the oil pressure sensor is converted into a variable resistor Rt. Due to changes in Rt, changing the size of each transistor is biased, three LEDs (red, yellow, gr een) under forward bias in a different light. Therefore, as long as the bias resistor is appropriately selected, it can ensure that only one light emitting diode, to indicate the corresponding hydraulic pressure.
The circuit operates on the principle of using an oil pressure sensor that functions as a variable resistor, Rt. As the oil pressure in the system changes, the resistance value of Rt also changes correspondingly. This variation in resistance influences the biasing conditions of three transistors arranged in a configuration that allows them to control the current flowing to three different LEDs, each representing a specific pressure range.
The transistors are configured such that they are biased differently based on the resistance value of Rt. When the oil pressure is low, Rt increases, causing the first transistor to turn on, which in turn activates the red LED, signaling low pressure. As the pressure increases and Rt decreases, the biasing condition shifts, leading to the activation of the yellow LED at an intermediate pressure level. Finally, when the pressure reaches a certain threshold, the green LED is illuminated, indicating a safe operating pressure.
The selection of the bias resistor is critical in this design. It must be chosen to ensure that the transistors switch on and off at the correct thresholds corresponding to the desired pressure levels. This ensures that only one LED lights up at any given time, providing a clear and unambiguous indication of the hydraulic pressure status. The circuit provides a simple yet effective visual representation of pressure levels, enhancing the monitoring capabilities in hydraulic systems.FIG circuit, the oil pressure sensor is converted into a variable resistor Rt. Due to changes in Rt, changing the size of each transistor is biased, three LEDs (red, yellow, gr een) under forward bias in a different light. Therefore, as long as the bias resistor is appropriately selected, it can ensure that only one light emitting diode, to indicate the corresponding hydraulic pressure.