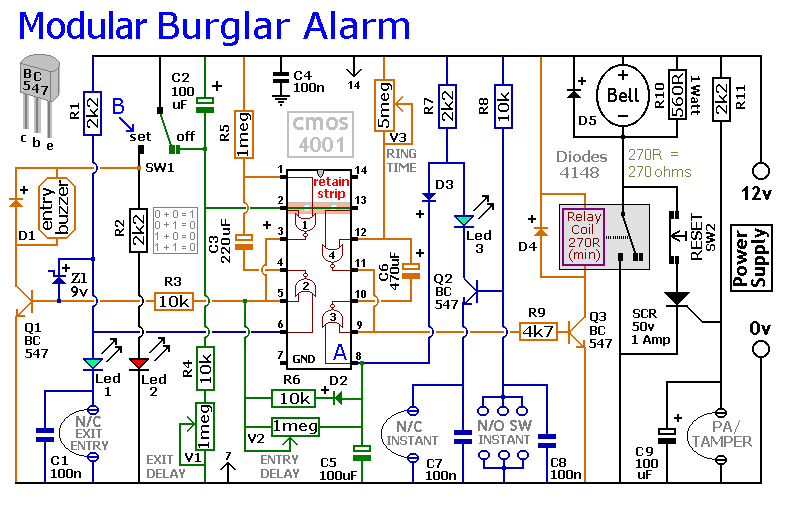
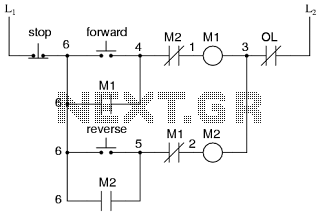
A on-shot circuit ideals

The digital circuit that is particularly useful is the One-Shot circuit, also known as a monostable multivibrator circuit. This circuit exhibits a specific behavior where it generates a single output pulse in response to an input trigger.
The One-Shot circuit, or monostable multivibrator, is a fundamental digital circuit that produces a single output pulse of a defined duration when triggered by an external event. This circuit typically consists of a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a logic gate or flip-flop configuration that defines its behavior.
When the input signal transitions from low to high, the circuit is triggered, causing the output to switch to a high state for a predetermined time period. The duration of the output pulse is primarily determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor used in the timing circuit, following the formula T = 1.1 * R * C, where T is the time period, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance.
Common applications of the One-Shot circuit include pulse width modulation, timer applications, and event debouncing in digital systems. It is widely utilized in various electronic devices for generating precise timing sequences and controlling the timing of events. The versatility and simplicity of the One-Shot circuit make it an essential component in digital electronics design.
In practical implementations, the circuit may be constructed using discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, or integrated into a single package using dedicated monostable multivibrator ICs. The choice of components and configuration will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including pulse duration, power consumption, and response time.The digital circuit additional a circuits taht is very useful is On-Shots circuit or Also known as Mono-stable multivibrator circuit. This behavior is the.. 🔗 External reference
The One-Shot circuit, or monostable multivibrator, is a fundamental digital circuit that produces a single output pulse of a defined duration when triggered by an external event. This circuit typically consists of a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a logic gate or flip-flop configuration that defines its behavior.
When the input signal transitions from low to high, the circuit is triggered, causing the output to switch to a high state for a predetermined time period. The duration of the output pulse is primarily determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor used in the timing circuit, following the formula T = 1.1 * R * C, where T is the time period, R is the resistance, and C is the capacitance.
Common applications of the One-Shot circuit include pulse width modulation, timer applications, and event debouncing in digital systems. It is widely utilized in various electronic devices for generating precise timing sequences and controlling the timing of events. The versatility and simplicity of the One-Shot circuit make it an essential component in digital electronics design.
In practical implementations, the circuit may be constructed using discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, or integrated into a single package using dedicated monostable multivibrator ICs. The choice of components and configuration will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including pulse duration, power consumption, and response time.The digital circuit additional a circuits taht is very useful is On-Shots circuit or Also known as Mono-stable multivibrator circuit. This behavior is the.. 🔗 External reference