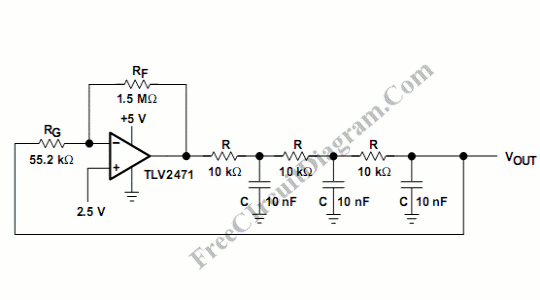
A simple and effective short-wave antenna amplifier circuit
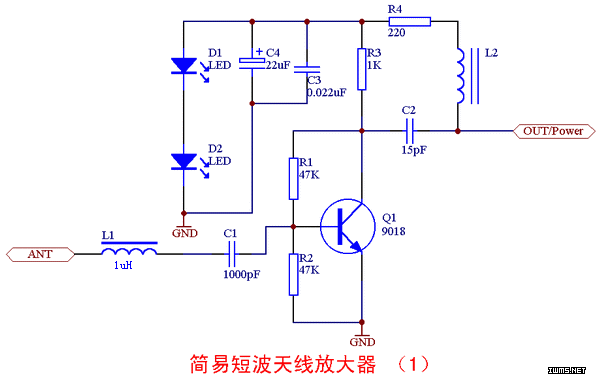
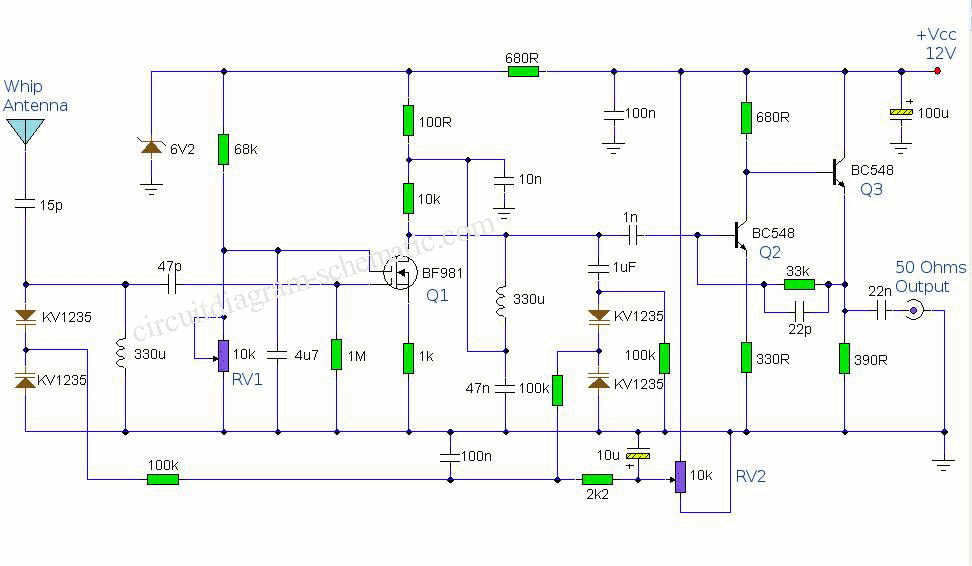
This amplifier is designed for outdoor installation and is connected to an indoor power line box. It utilizes either 50-ohm or 75-ohm coaxial cables for the connection between indoor and outdoor units. The amplifier circuit board is depicted in Figures 3 and 4, with Figure 3 showing the main circuit board, which has actual dimensions of 6.4 cm by 2.4 cm. Figure 4 illustrates the power supply box for the circuit board, measuring 5.1 cm. The circuit board is well-designed, and component selection follows the schematic. In Figure 1, L1 is indicated with a color code of 1 µH inductance, and resistance and capacitance values are chosen according to the diagram. The circuit employs a low-noise, high-quality transistor for ultra-high-frequency control; alternatives to the 9018 transistor include the 9016 and 1359 models. L2 is wound with the same wire diameter as L1, comprising 300 turns. Diodes D1 and D2 serve as indicators and regulators. The circuit in Figure 2 mirrors the design of Figure 1, utilizing L1 and L2, and incorporates a 100 mA fuse, with all other components identical to those in Figure 1.
This outdoor amplifier is engineered to enhance signal strength for applications requiring reliable performance in outdoor environments. The use of coaxial cables with 50-ohm or 75-ohm impedance ensures compatibility with various transmission lines, optimizing signal integrity. The main circuit board's compact size (6.4 cm x 2.4 cm) allows for efficient integration into a range of enclosures, while the power supply box, measuring 5.1 cm, is designed to accommodate the necessary voltage and current specifications for the amplifier's operation.
In terms of component selection, the use of a 1 µH inductor (L1) is critical for the circuit's functionality, as it helps to filter and stabilize the signal. The precise resistance and capacitance values are essential for tuning the circuit to the desired frequency range, ensuring that the amplifier operates effectively within its intended parameters. The choice of a low-noise transistor enhances the amplifier’s performance by minimizing signal degradation, which is particularly important in high-frequency applications.
The winding of L2 with 300 turns of wire of the same diameter as L1 ensures consistent inductance characteristics, which are vital for maintaining signal quality. The inclusion of diodes D1 and D2 not only serves as indicators but also stabilizes the voltage levels within the circuit, preventing fluctuations that could lead to performance issues.
The integration of a 100 mA fuse adds a layer of protection to the circuit, safeguarding against overcurrent conditions that could potentially damage the components. This design consideration is crucial for outdoor applications where environmental factors could lead to unexpected electrical challenges.
Overall, this amplifier circuit is a robust solution for outdoor installations, combining thoughtful design with high-quality components to deliver reliable performance in demanding conditions.This amplifier is the outdoor type, line installed outdoors, the amp`s main line; Figure 2 is the indoor power line box. Indoor and outdoor use between 50 ohm or 75 ohm coaxial cable to connect. e› 3 Figure 3, Figure 4 is the amplifier circuit board, and Figure 3 is the main circuit board, the actual size is 6.
4 cm G— 2. 4 cm Figure 4 is a circuit board power supply box, the actual size of 5. 1 cm. Good circuit board in Figure After processing, followed by selecting components, circuit in Figure 1, L1 with the color code 1uH inductance, resistance and capacitance values selected according to the diagram, transistor low noise high quality ultra-high-frequency control, in addition to the figure of 9018, you can also use 9016, 1359 and so on, L2 winding with waste in the week, the week of the original wire diameter with the same number of laps for the 300 laps, D1, D2 is light, but also for regulators to use. Figure 2 circuit in Figure 1 in the L1 with the L2 as the production, use 100mA fuse on it, with the other components are the same as in Figure 1, click the image selection.
🔗 External reference
This outdoor amplifier is engineered to enhance signal strength for applications requiring reliable performance in outdoor environments. The use of coaxial cables with 50-ohm or 75-ohm impedance ensures compatibility with various transmission lines, optimizing signal integrity. The main circuit board's compact size (6.4 cm x 2.4 cm) allows for efficient integration into a range of enclosures, while the power supply box, measuring 5.1 cm, is designed to accommodate the necessary voltage and current specifications for the amplifier's operation.
In terms of component selection, the use of a 1 µH inductor (L1) is critical for the circuit's functionality, as it helps to filter and stabilize the signal. The precise resistance and capacitance values are essential for tuning the circuit to the desired frequency range, ensuring that the amplifier operates effectively within its intended parameters. The choice of a low-noise transistor enhances the amplifier’s performance by minimizing signal degradation, which is particularly important in high-frequency applications.
The winding of L2 with 300 turns of wire of the same diameter as L1 ensures consistent inductance characteristics, which are vital for maintaining signal quality. The inclusion of diodes D1 and D2 not only serves as indicators but also stabilizes the voltage levels within the circuit, preventing fluctuations that could lead to performance issues.
The integration of a 100 mA fuse adds a layer of protection to the circuit, safeguarding against overcurrent conditions that could potentially damage the components. This design consideration is crucial for outdoor applications where environmental factors could lead to unexpected electrical challenges.
Overall, this amplifier circuit is a robust solution for outdoor installations, combining thoughtful design with high-quality components to deliver reliable performance in demanding conditions.This amplifier is the outdoor type, line installed outdoors, the amp`s main line; Figure 2 is the indoor power line box. Indoor and outdoor use between 50 ohm or 75 ohm coaxial cable to connect. e› 3 Figure 3, Figure 4 is the amplifier circuit board, and Figure 3 is the main circuit board, the actual size is 6.
4 cm G— 2. 4 cm Figure 4 is a circuit board power supply box, the actual size of 5. 1 cm. Good circuit board in Figure After processing, followed by selecting components, circuit in Figure 1, L1 with the color code 1uH inductance, resistance and capacitance values selected according to the diagram, transistor low noise high quality ultra-high-frequency control, in addition to the figure of 9018, you can also use 9016, 1359 and so on, L2 winding with waste in the week, the week of the original wire diameter with the same number of laps for the 300 laps, D1, D2 is light, but also for regulators to use. Figure 2 circuit in Figure 1 in the L1 with the L2 as the production, use 100mA fuse on it, with the other components are the same as in Figure 1, click the image selection.
🔗 External reference