A Simple but Good Battery Charger
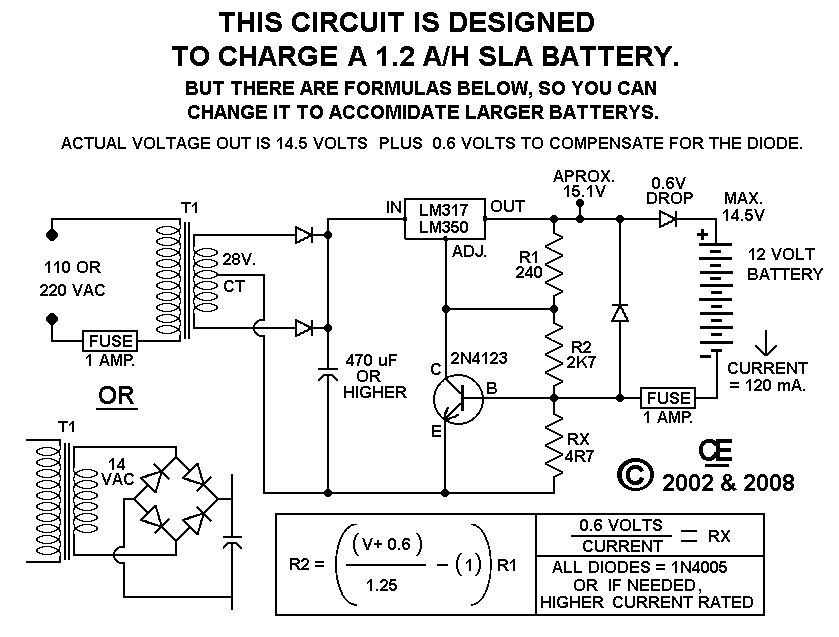
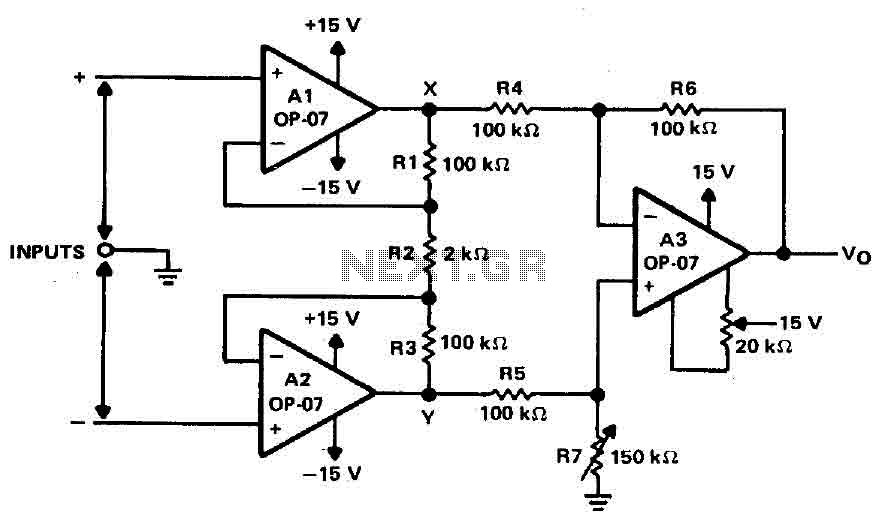
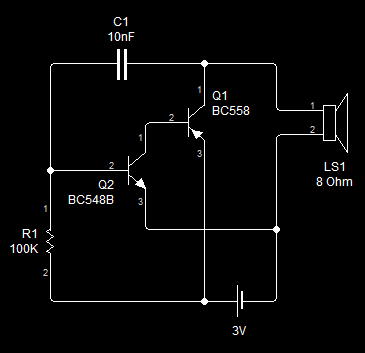
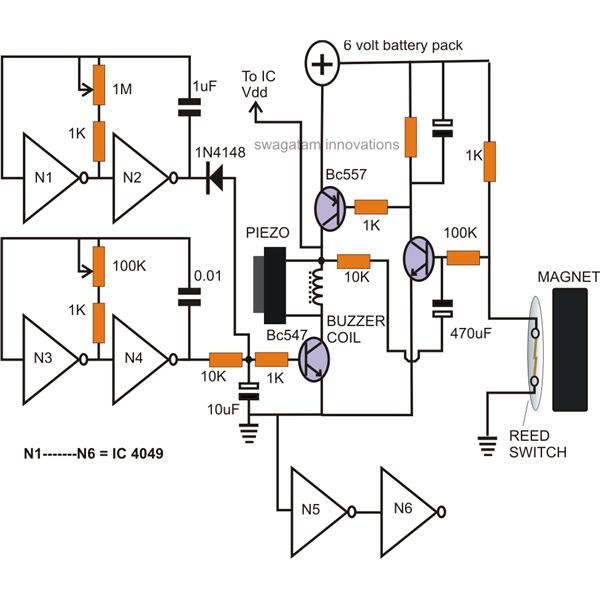
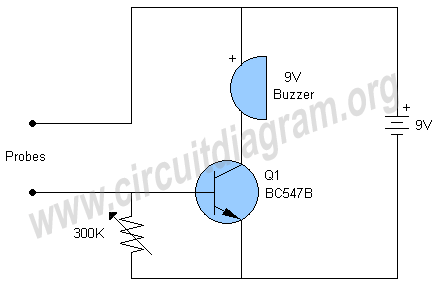
This circuit provides effective charging results for Gel Cell or Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) type batteries, which are utilized in metal detector projects. It can be modified to accommodate higher current batteries and is likely suitable for batteries with a rating of up to 10 Amp-Hours (A/H).
The described circuit is designed for efficient charging of Gel Cell and SLA batteries, which are commonly used in various portable electronic devices, including metal detectors. The circuit can be configured to handle different battery capacities, specifically accommodating those rated up to 10 A/H, making it versatile for various applications.
The charging circuit typically employs a voltage regulator or a dedicated battery management IC to ensure that the charging voltage and current remain within safe limits for the battery type. The circuit may include features such as over-voltage protection, over-current protection, and temperature monitoring to enhance safety and efficiency during the charging process.
To modify the circuit for higher current batteries, adjustments can be made to the current limiting resistors and the specifications of the components used, such as the transformer or switching regulator, to ensure they can handle the increased current without overheating or failing.
Additionally, the circuit may include indicators such as LEDs to display the charging status, providing visual feedback to the user. Proper layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize resistance and inductance in the circuit, which can affect charging efficiency.
Overall, this charging circuit is a robust solution for powering Gel Cell and SLA batteries, ensuring reliable performance in applications such as metal detectors and other electronic devices requiring portable power sources.Using this circuit will give Good Charging results to a Gell Cell or SLA type Batterys as used in my Metal Detector project. And it can be modified to accomidate higher current batterys. It is Probably quite Suitable for up to a 10 A/H Rating 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed for efficient charging of Gel Cell and SLA batteries, which are commonly used in various portable electronic devices, including metal detectors. The circuit can be configured to handle different battery capacities, specifically accommodating those rated up to 10 A/H, making it versatile for various applications.
The charging circuit typically employs a voltage regulator or a dedicated battery management IC to ensure that the charging voltage and current remain within safe limits for the battery type. The circuit may include features such as over-voltage protection, over-current protection, and temperature monitoring to enhance safety and efficiency during the charging process.
To modify the circuit for higher current batteries, adjustments can be made to the current limiting resistors and the specifications of the components used, such as the transformer or switching regulator, to ensure they can handle the increased current without overheating or failing.
Additionally, the circuit may include indicators such as LEDs to display the charging status, providing visual feedback to the user. Proper layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize resistance and inductance in the circuit, which can affect charging efficiency.
Overall, this charging circuit is a robust solution for powering Gel Cell and SLA batteries, ensuring reliable performance in applications such as metal detectors and other electronic devices requiring portable power sources.Using this circuit will give Good Charging results to a Gell Cell or SLA type Batterys as used in my Metal Detector project. And it can be modified to accomidate higher current batterys. It is Probably quite Suitable for up to a 10 A/H Rating 🔗 External reference