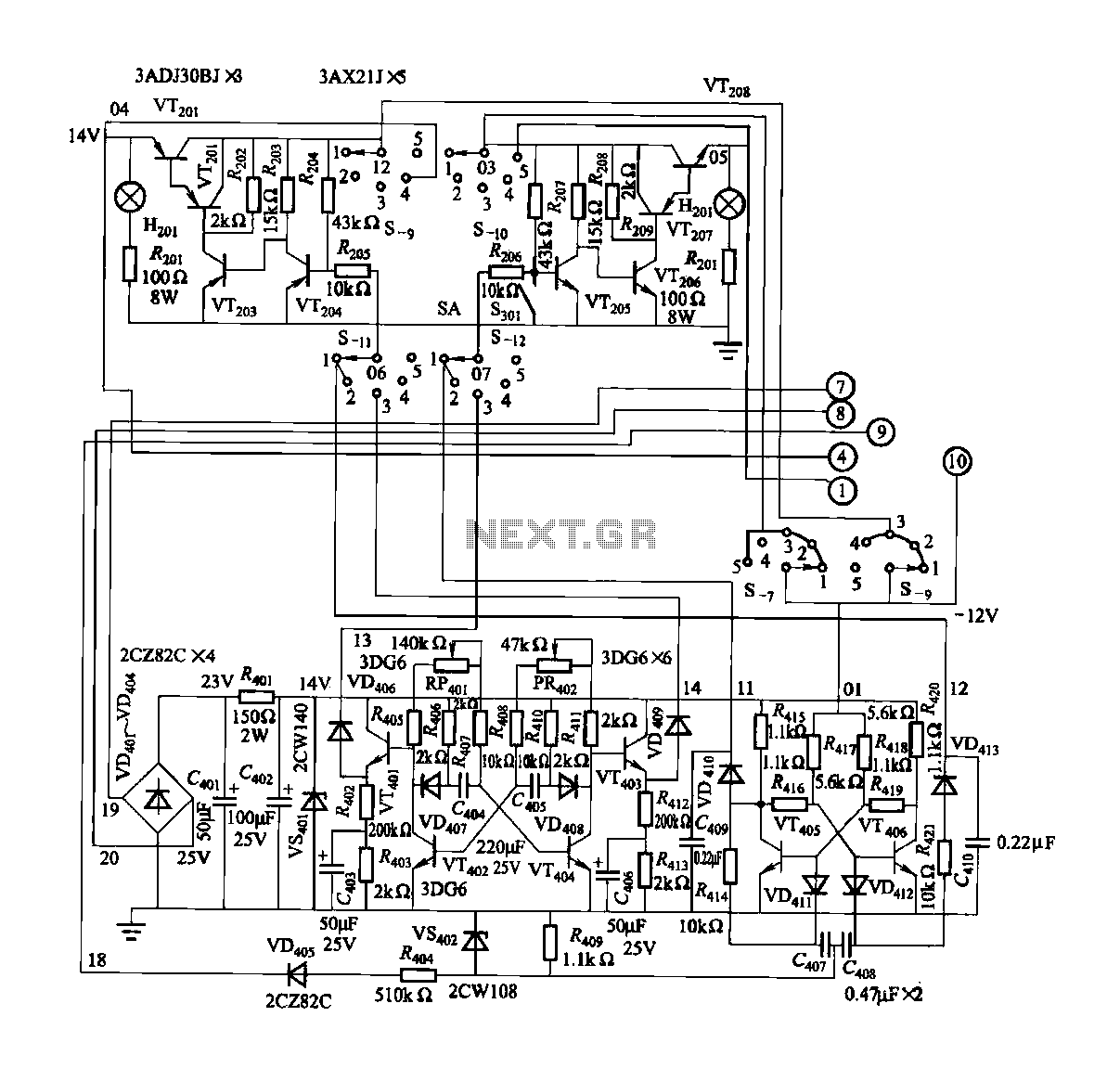
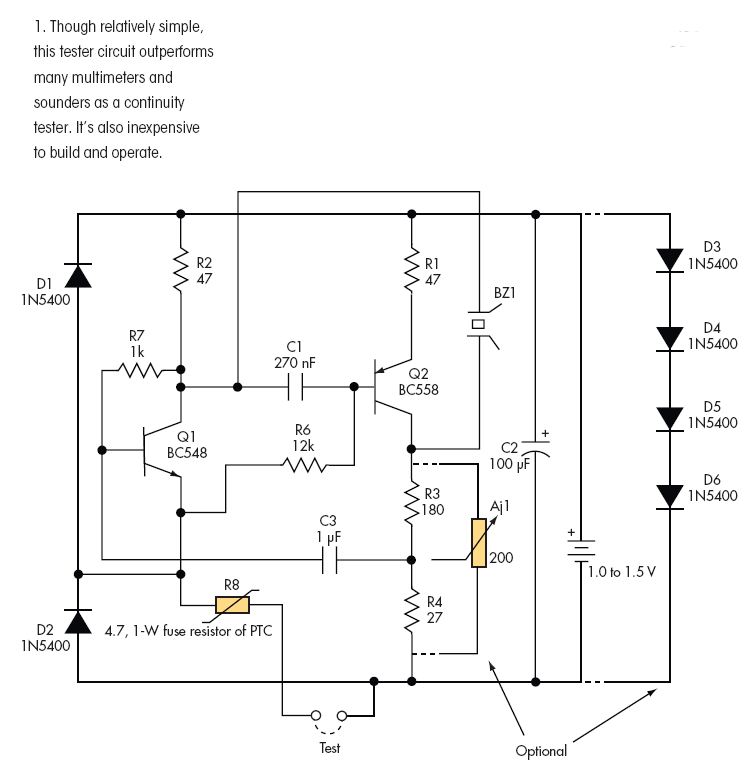
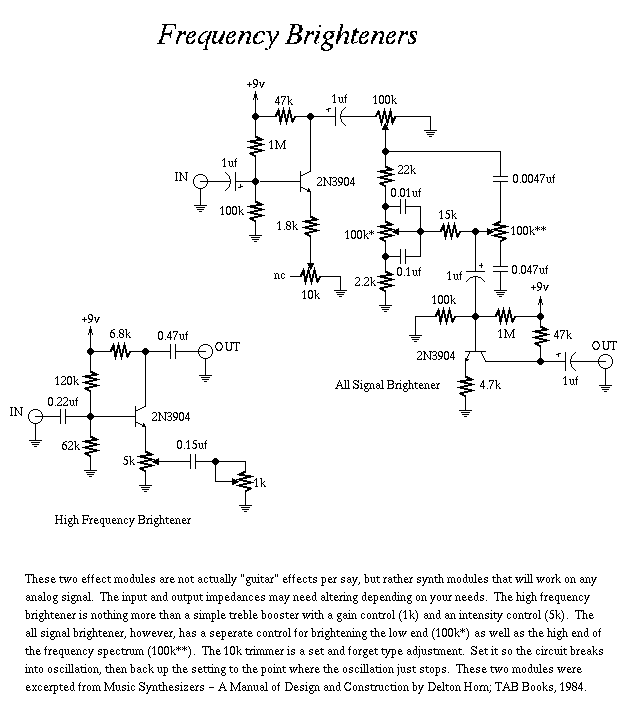
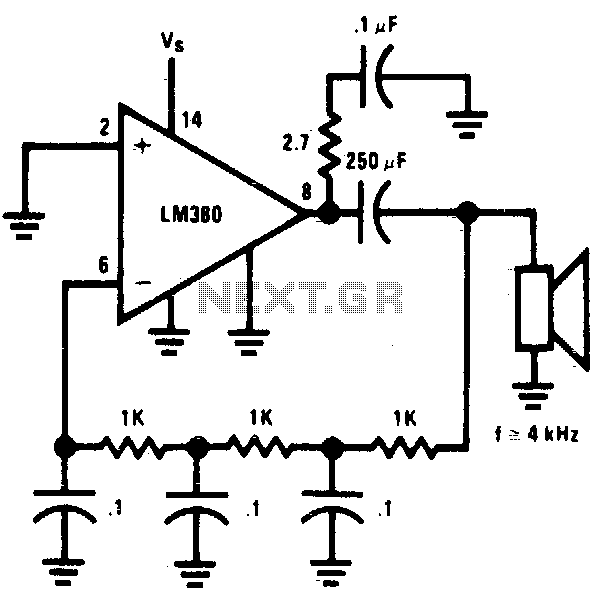
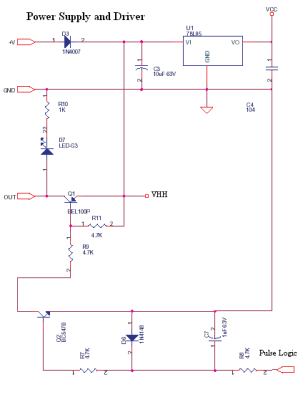
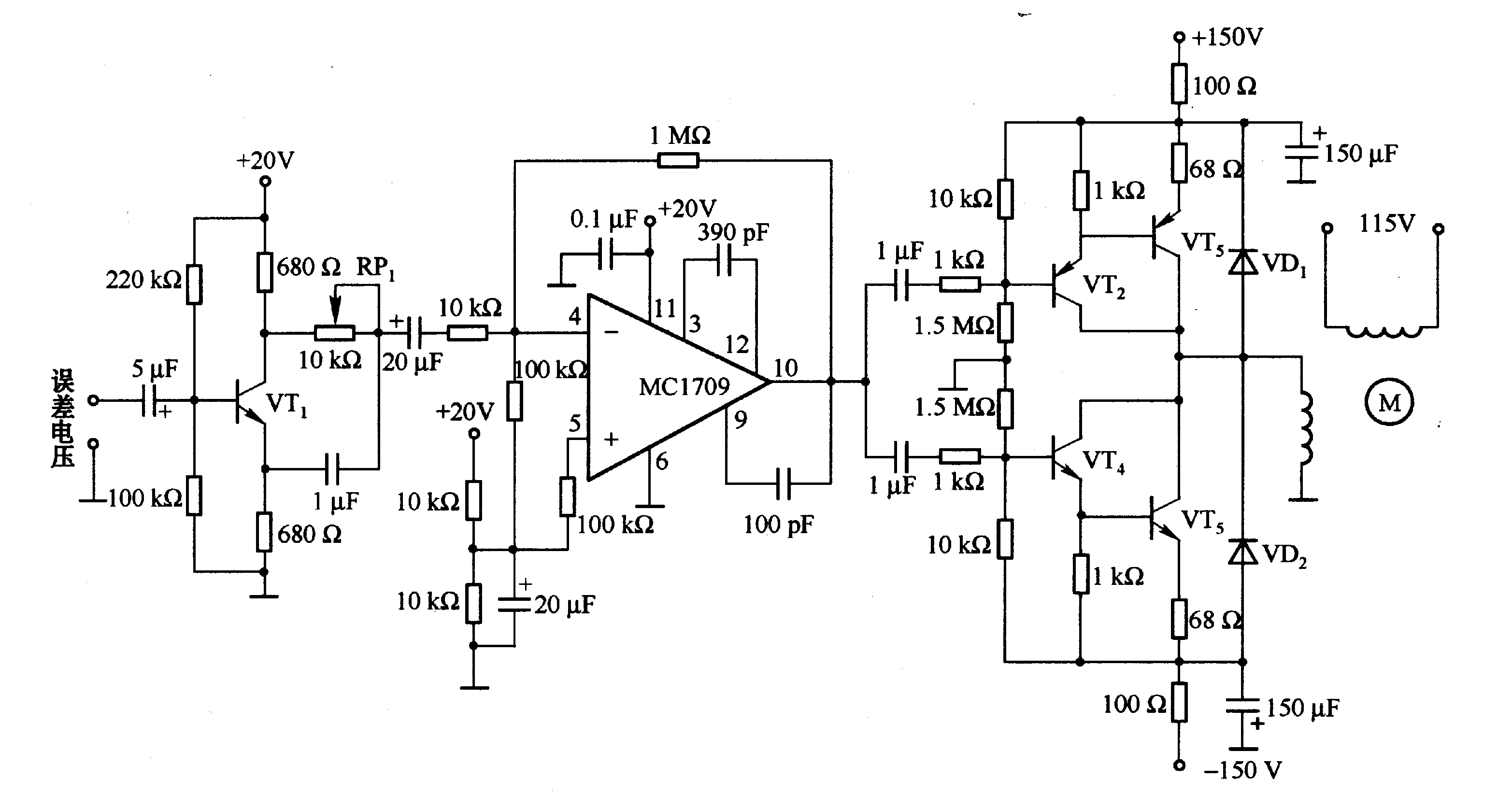
A three-alarm phase circuits
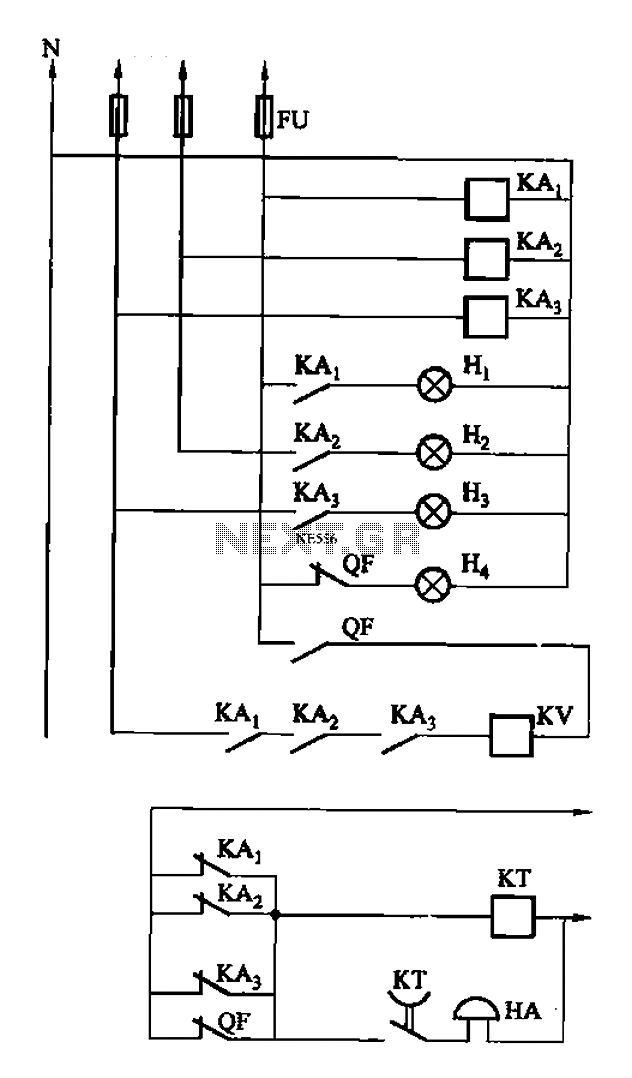
The circuit features intermediate relays KAi, KA2, and KA3, which are connected to the outlet end of the low-voltage circuit breakers. An alarm circuit is linked to a backup power supply or a battery power supply. This configuration serves to monitor the power phase and ensures that the low-voltage circuit breakers are tripped in the event of a fault. The KV circuit breaker QF is equipped with a loss of pressure coil.
The described circuit employs three intermediate relays (KAi, KA2, and KA3) that function as control elements in conjunction with low-voltage circuit breakers. These relays are strategically connected to the output terminals of the circuit breakers, facilitating the monitoring and control of electrical power distribution.
The alarm circuit is crucial for providing alerts when the system is operating under abnormal conditions. It is designed to connect to either a backup power supply or a dedicated battery power supply, ensuring continuous operation even in the event of a primary power failure. This redundancy is essential for maintaining system reliability and safety.
The primary function of this circuit is to act as a protective measure by monitoring the power phase. In cases where a fault condition is detected, such as an overload or short circuit, the intermediate relays will initiate a trip command to the low-voltage circuit breakers. This action disconnects the affected circuit, thereby preventing potential damage to equipment or hazards to personnel.
Additionally, the KV circuit breaker QF includes a loss of pressure coil, which is a safety feature designed to detect drops in pressure within the system. If the pressure falls below a predetermined threshold, the coil will activate, signaling the circuit breaker to trip and isolate the circuit from the power source. This mechanism is vital for protecting the integrity of the electrical system and ensuring safe operation under varying conditions.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety, reliability, and continuous monitoring, making it suitable for various applications in electrical distribution systems. As shown in (a), KAi, KA2, KA3 intermediate relay, connected to the outlet end of the low-voltage circuit breakers total. Alarm circuit connected to the backup power supply or battery power supply. The circuit can not only play the role of the police power phase, and can always breaker tripping low-voltage gate. KV circuit breaker QF loss of pressure coil.
The described circuit employs three intermediate relays (KAi, KA2, and KA3) that function as control elements in conjunction with low-voltage circuit breakers. These relays are strategically connected to the output terminals of the circuit breakers, facilitating the monitoring and control of electrical power distribution.
The alarm circuit is crucial for providing alerts when the system is operating under abnormal conditions. It is designed to connect to either a backup power supply or a dedicated battery power supply, ensuring continuous operation even in the event of a primary power failure. This redundancy is essential for maintaining system reliability and safety.
The primary function of this circuit is to act as a protective measure by monitoring the power phase. In cases where a fault condition is detected, such as an overload or short circuit, the intermediate relays will initiate a trip command to the low-voltage circuit breakers. This action disconnects the affected circuit, thereby preventing potential damage to equipment or hazards to personnel.
Additionally, the KV circuit breaker QF includes a loss of pressure coil, which is a safety feature designed to detect drops in pressure within the system. If the pressure falls below a predetermined threshold, the coil will activate, signaling the circuit breaker to trip and isolate the circuit from the power source. This mechanism is vital for protecting the integrity of the electrical system and ensuring safe operation under varying conditions.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety, reliability, and continuous monitoring, making it suitable for various applications in electrical distribution systems. As shown in (a), KAi, KA2, KA3 intermediate relay, connected to the outlet end of the low-voltage circuit breakers total. Alarm circuit connected to the backup power supply or battery power supply. The circuit can not only play the role of the police power phase, and can always breaker tripping low-voltage gate. KV circuit breaker QF loss of pressure coil.