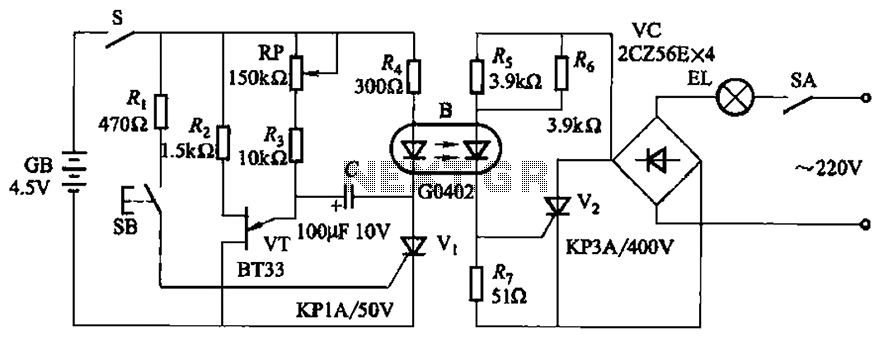
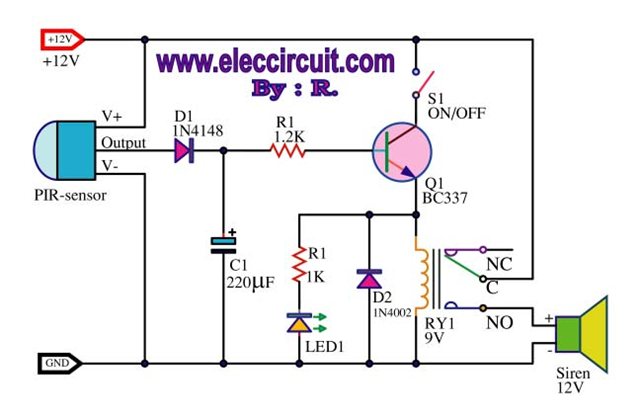
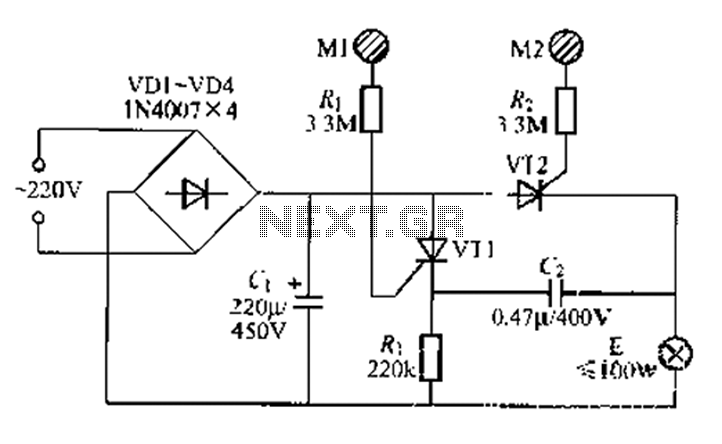
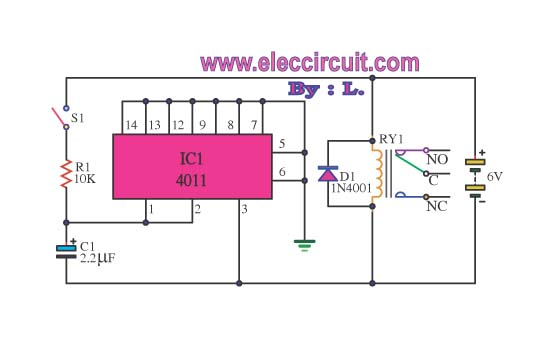
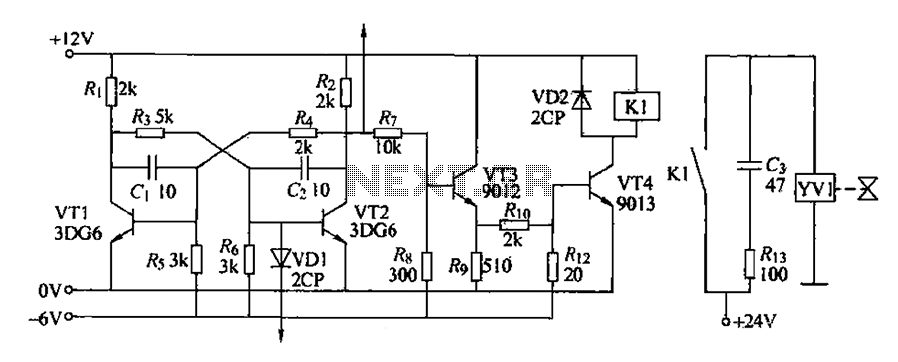
AC LED drive circuit
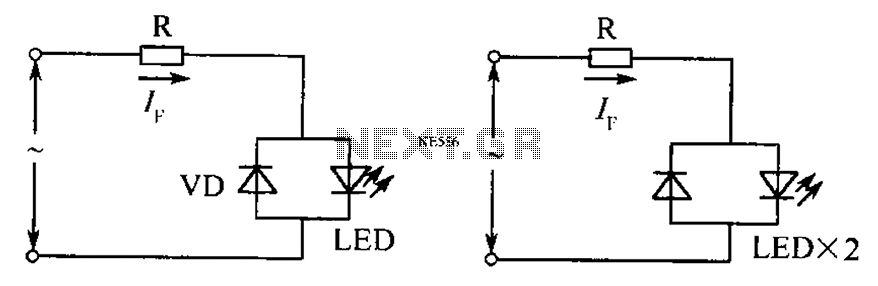
The circuit operates effectively even when the polarity of the voltage or the power supply is reversed. It functions with DC drives similar to AC drives, utilizing a current limiting resistor R. The value of this resistor is determined based on the AC RMS voltage.
The described circuit is designed to accommodate both AC and DC power sources, ensuring reliable operation regardless of polarity. It incorporates a current limiting resistor, denoted as R, which plays a critical role in protecting the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage components. The resistor's value is calculated in relation to the root mean square (RMS) voltage of the AC supply, which is essential for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe current limits.
In practical applications, the circuit can be employed in various devices where power supply polarity may be uncertain. This feature is particularly advantageous in environments where power connections may be made incorrectly, as it mitigates the risk of damage to sensitive electronic components. The design may also include additional protective elements such as diodes to prevent reverse polarity damage and to ensure that the circuit remains functional under varying conditions.
When designing the current limiting resistor, it is important to consider the maximum expected RMS voltage and the desired current limit for the application. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, where the resistance R is equal to the voltage (V) divided by the current (I). This relationship ensures that the circuit operates efficiently and safely, maintaining the integrity of both the power supply and the connected loads.
Overall, the circuit's ability to handle reversed polarity and its adaptability to both AC and DC drives make it a versatile solution in electronic design, suitable for a wide range of applications. As shown, still work in the case of unknown polarity of the voltage or the power supply polarity is reversed. And DC Drives as AC drives, the current limiting resistor R whose value is: where, AC RMS voltage.
The described circuit is designed to accommodate both AC and DC power sources, ensuring reliable operation regardless of polarity. It incorporates a current limiting resistor, denoted as R, which plays a critical role in protecting the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage components. The resistor's value is calculated in relation to the root mean square (RMS) voltage of the AC supply, which is essential for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe current limits.
In practical applications, the circuit can be employed in various devices where power supply polarity may be uncertain. This feature is particularly advantageous in environments where power connections may be made incorrectly, as it mitigates the risk of damage to sensitive electronic components. The design may also include additional protective elements such as diodes to prevent reverse polarity damage and to ensure that the circuit remains functional under varying conditions.
When designing the current limiting resistor, it is important to consider the maximum expected RMS voltage and the desired current limit for the application. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, where the resistance R is equal to the voltage (V) divided by the current (I). This relationship ensures that the circuit operates efficiently and safely, maintaining the integrity of both the power supply and the connected loads.
Overall, the circuit's ability to handle reversed polarity and its adaptability to both AC and DC drives make it a versatile solution in electronic design, suitable for a wide range of applications. As shown, still work in the case of unknown polarity of the voltage or the power supply polarity is reversed. And DC Drives as AC drives, the current limiting resistor R whose value is: where, AC RMS voltage.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713