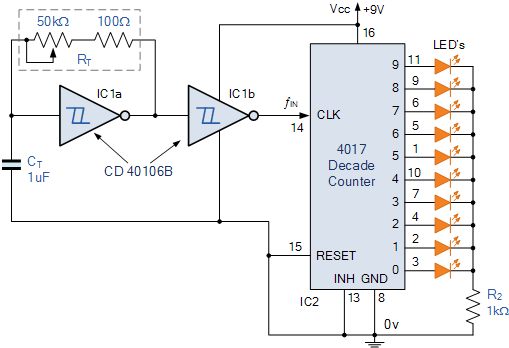
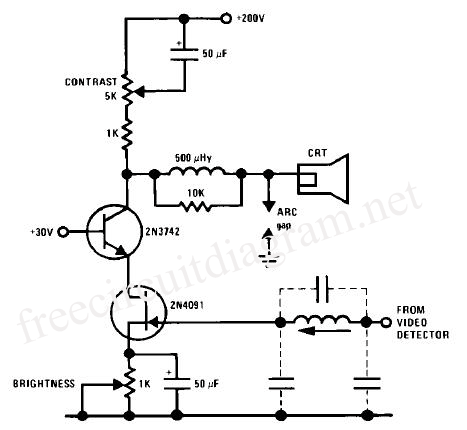
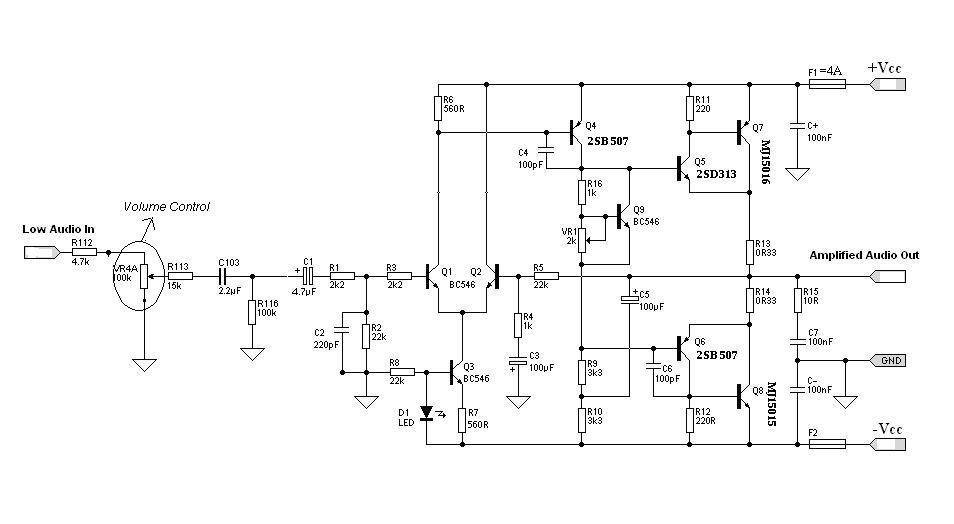
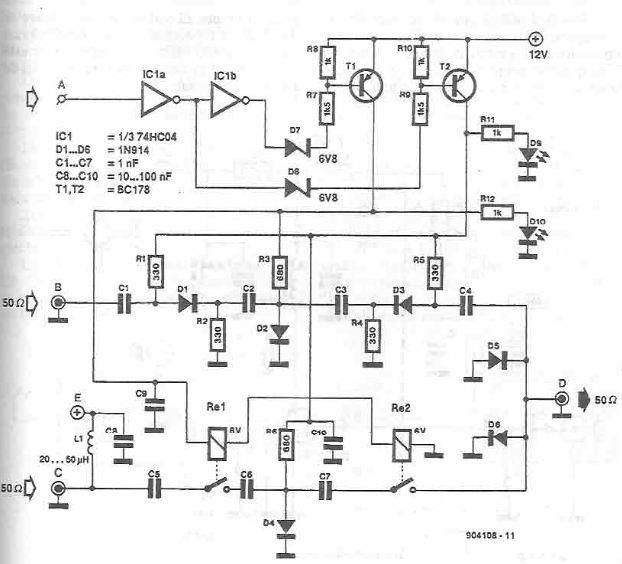
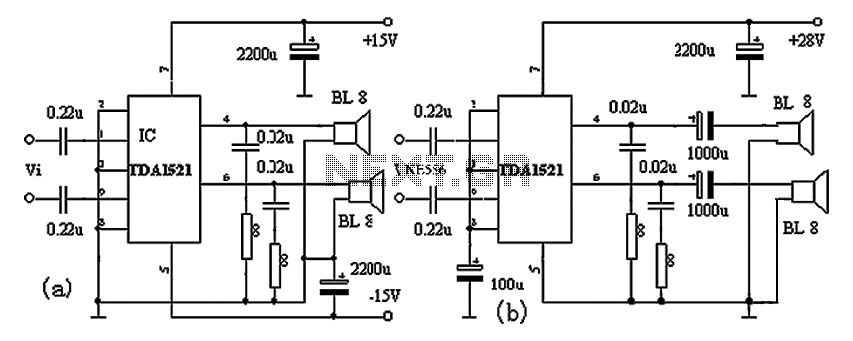
Acid-Rain Monitor Circuit
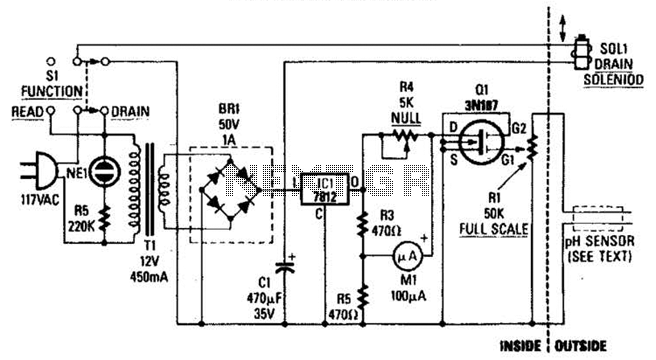
The drain-to-source resistance of Q1 varies depending on the acidity of the sample presented to Q1's gate circuit. This variable resistance influences the current flowing through the bridge, which is proportional to pH.
The circuit involves a field-effect transistor (FET), specifically Q1, whose drain-to-source resistance (R_DS) is affected by the pH level of the sample solution. When the acidity of the sample changes, it alters the gate voltage of Q1, which in turn modifies the resistance. This change in resistance directly affects the current (I) flowing through the bridge circuit, where the bridge is typically configured to measure small changes in voltage that correspond to variations in current.
The bridge circuit may consist of resistors arranged in a Wheatstone bridge configuration, allowing for precise measurements of the current changes. The output voltage from the bridge is then related to the pH level, enabling the circuit to function as a pH sensor.
For optimal performance, it is essential to consider the characteristics of Q1, including its threshold voltage, transconductance, and output conductance, as these parameters will determine the sensitivity and accuracy of the pH measurement. Additionally, the selection of appropriate reference electrodes and calibration techniques will enhance the reliability of the readings obtained from the circuit. The overall design should ensure minimal noise and interference, which can affect the precision of the pH measurement. The drain-to-source resistance of Ql varies depending on the acidity of the sample presented to Ql`s gate circuit. That variable resistance varies the current flowing through the bridge; that current is proportional to pH. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involves a field-effect transistor (FET), specifically Q1, whose drain-to-source resistance (R_DS) is affected by the pH level of the sample solution. When the acidity of the sample changes, it alters the gate voltage of Q1, which in turn modifies the resistance. This change in resistance directly affects the current (I) flowing through the bridge circuit, where the bridge is typically configured to measure small changes in voltage that correspond to variations in current.
The bridge circuit may consist of resistors arranged in a Wheatstone bridge configuration, allowing for precise measurements of the current changes. The output voltage from the bridge is then related to the pH level, enabling the circuit to function as a pH sensor.
For optimal performance, it is essential to consider the characteristics of Q1, including its threshold voltage, transconductance, and output conductance, as these parameters will determine the sensitivity and accuracy of the pH measurement. Additionally, the selection of appropriate reference electrodes and calibration techniques will enhance the reliability of the readings obtained from the circuit. The overall design should ensure minimal noise and interference, which can affect the precision of the pH measurement. The drain-to-source resistance of Ql varies depending on the acidity of the sample presented to Ql`s gate circuit. That variable resistance varies the current flowing through the bridge; that current is proportional to pH. 🔗 External reference