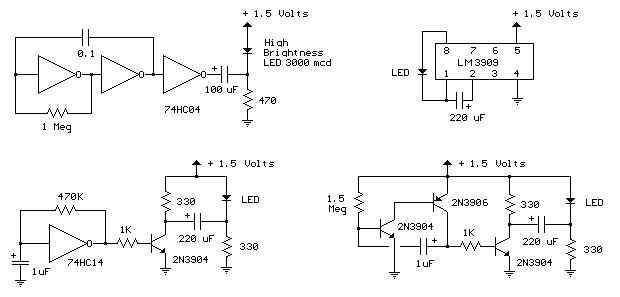
AD524J type thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit
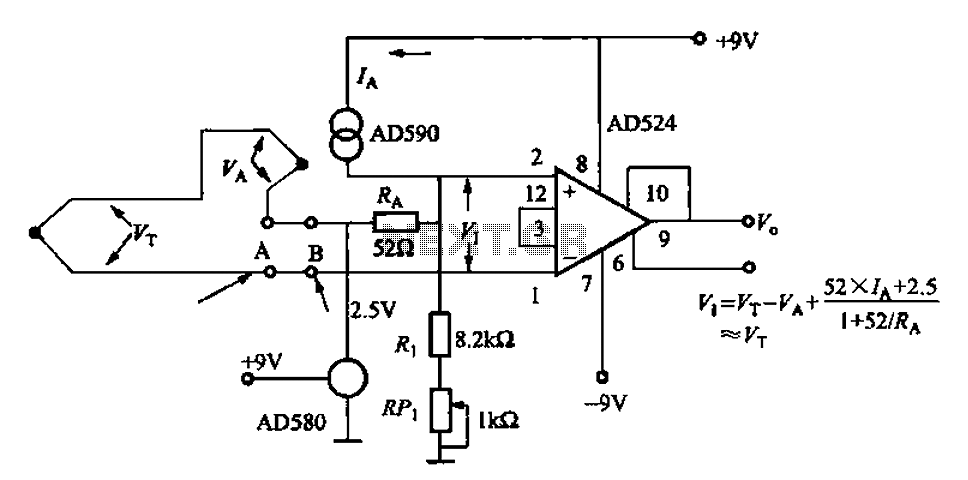
The AD524J type thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit is illustrated in Figure 1-20. This circuit utilizes J-type thermocouples, with the base reference voltage sourced from the AD580, an integrated temperature sensor, and the precision instrumentation amplifier AD524. The AD590 component compensates for changes in the cold junction temperature by outputting a current of 1 µA/K. This current flows through the AD524, forming a voltage amplifier, which results in a corresponding change in the output voltage. The AD580 provides a reference voltage of 2.5V. The AD524 is characterized by low drift (with a drift voltage of 0.5 mV and a maximum drift of 25 mV/°C), excellent linearity (gain of 1 with linearity of 0.003%), and high speed (output slew rate of 5 V/ms).
The AD524J thermocouple cold junction compensation circuit is designed to accurately measure temperature by compensating for the ambient temperature at the junction of the thermocouple. The J-type thermocouple, known for its reliability and wide temperature range, generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference between its measuring junction and the reference junction. The circuit's architecture integrates several critical components to ensure precise temperature readings.
The AD580 serves as a stable reference voltage source, providing a consistent 2.5V output that is crucial for the accurate operation of the circuit. The integration of the AD590 temperature sensor is essential for cold junction compensation, as it detects the temperature at the reference junction and outputs a corresponding current. This current is directly proportional to the temperature, simplifying the compensation process.
The AD524 acts as a precision instrumentation amplifier that amplifies the voltage signal generated by the thermocouple. Its low drift characteristics are vital in applications where temperature stability is crucial, as even minor variations can lead to significant measurement errors. With a drift voltage of only 0.5 mV and a maximum drift of 25 mV/°C, the AD524 ensures that the output remains stable across various environmental conditions.
Moreover, the high-speed performance of the AD524, with an output slew rate of 5 V/ms, allows for rapid response to temperature changes, making the circuit suitable for dynamic applications. The excellent linearity of 0.003% at a gain of 1 further enhances the accuracy of the temperature measurements, ensuring that the output closely follows the input signal without introducing significant distortion.
In summary, the AD524J thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit effectively combines precision components to deliver reliable and accurate temperature readings, making it an essential solution in various temperature sensing applications.AD524J type thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit shown in Figure 1-20. The circuit is detected by a J-type thermocouples, the base reference voltage sour ce AD580, AD590 integrated temperature sensor and precision instrumentation amplifier AD524 constitution, AD590 compensate for the cold junction, when the cold junction temperature changes, AD590 to lVA/K output current, the current in AD524 foot forming a voltage amplifier and the output is changed vI stack. AD580 provides 2.SV reference voltage. AD524 low-drift (drift voltage 0.5mV, maximum drift 25 mV/oC), good linearity (a gain of l, linearity 0,003%) of high-speed (output slew rate of 5V/ms) operational amplifier.
The AD524J thermocouple cold junction compensation circuit is designed to accurately measure temperature by compensating for the ambient temperature at the junction of the thermocouple. The J-type thermocouple, known for its reliability and wide temperature range, generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference between its measuring junction and the reference junction. The circuit's architecture integrates several critical components to ensure precise temperature readings.
The AD580 serves as a stable reference voltage source, providing a consistent 2.5V output that is crucial for the accurate operation of the circuit. The integration of the AD590 temperature sensor is essential for cold junction compensation, as it detects the temperature at the reference junction and outputs a corresponding current. This current is directly proportional to the temperature, simplifying the compensation process.
The AD524 acts as a precision instrumentation amplifier that amplifies the voltage signal generated by the thermocouple. Its low drift characteristics are vital in applications where temperature stability is crucial, as even minor variations can lead to significant measurement errors. With a drift voltage of only 0.5 mV and a maximum drift of 25 mV/°C, the AD524 ensures that the output remains stable across various environmental conditions.
Moreover, the high-speed performance of the AD524, with an output slew rate of 5 V/ms, allows for rapid response to temperature changes, making the circuit suitable for dynamic applications. The excellent linearity of 0.003% at a gain of 1 further enhances the accuracy of the temperature measurements, ensuring that the output closely follows the input signal without introducing significant distortion.
In summary, the AD524J thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit effectively combines precision components to deliver reliable and accurate temperature readings, making it an essential solution in various temperature sensing applications.AD524J type thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation circuit shown in Figure 1-20. The circuit is detected by a J-type thermocouples, the base reference voltage sour ce AD580, AD590 integrated temperature sensor and precision instrumentation amplifier AD524 constitution, AD590 compensate for the cold junction, when the cold junction temperature changes, AD590 to lVA/K output current, the current in AD524 foot forming a voltage amplifier and the output is changed vI stack. AD580 provides 2.SV reference voltage. AD524 low-drift (drift voltage 0.5mV, maximum drift 25 mV/oC), good linearity (a gain of l, linearity 0,003%) of high-speed (output slew rate of 5V/ms) operational amplifier.