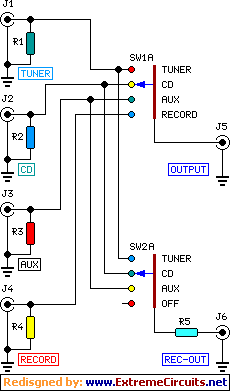
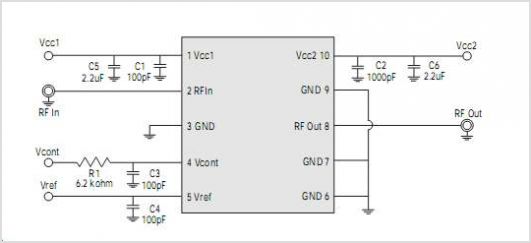
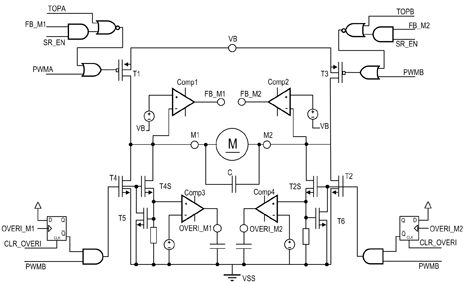
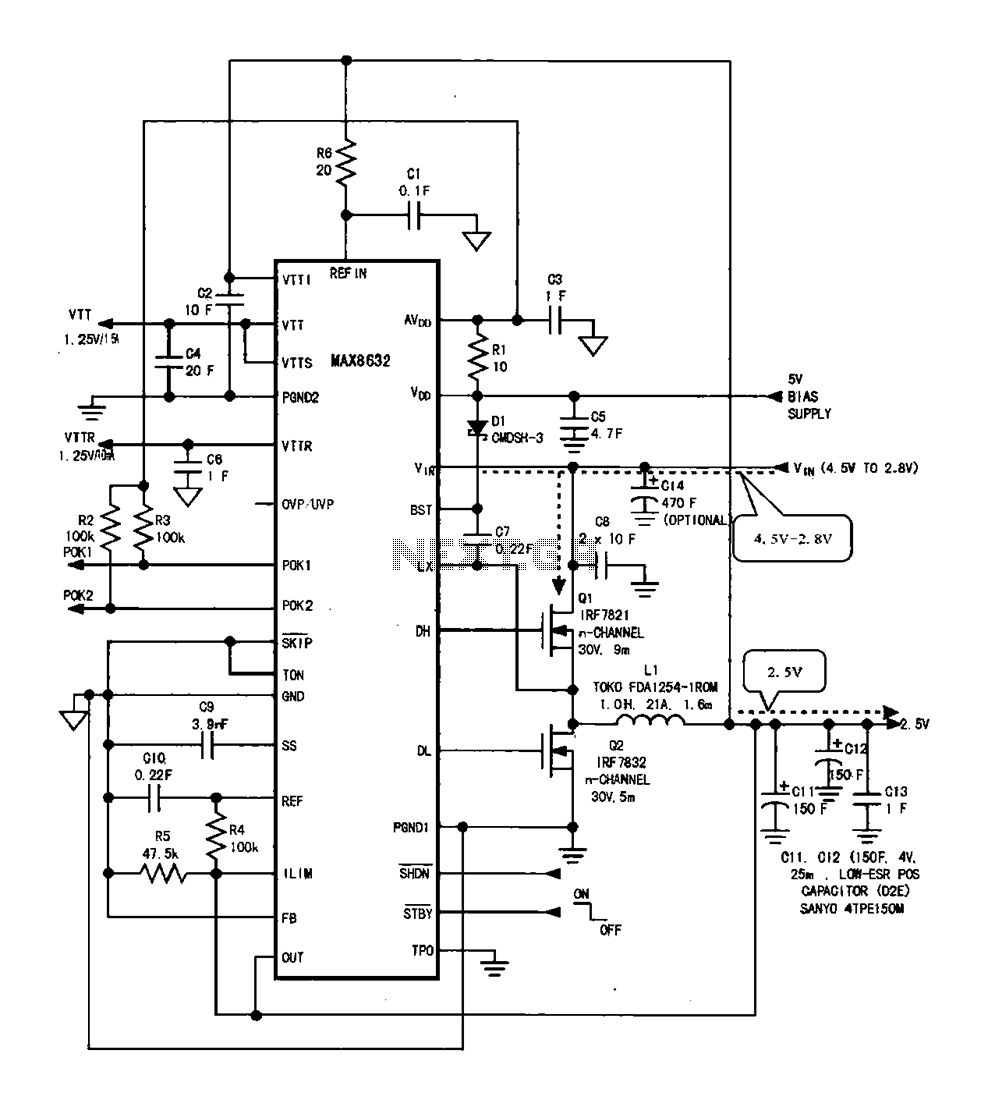
Switching Power Supply 14V

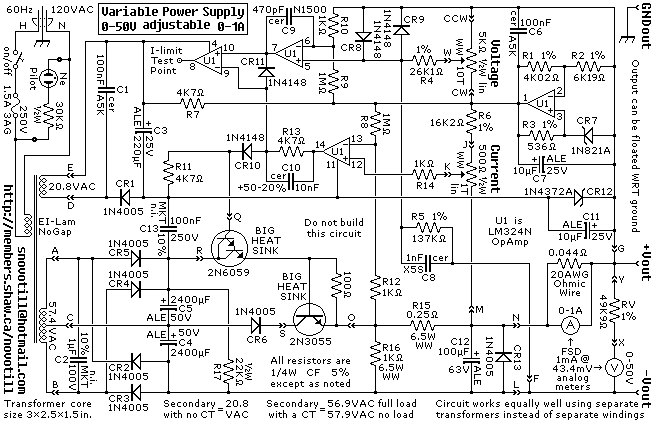
In this small switching power supply, a Schmitt trigger oscillator is used to drive a switching transistor that supplies current to a small inductor. Energy is stored in the inductor while the transistor is on, and released into the load circuit when the transistor switches off. The output voltage is dependent on the load resistance and is limited by a zener diode that stops the oscillator when the voltage reaches about 14 volts. Higher or lower voltages can be obtained by adjusting the voltage divider that feeds the zener diode. The efficiency is about 80% using a high Q inductor.
This switching power supply circuit operates by utilizing a Schmitt trigger oscillator to generate a square wave signal that drives a switching transistor, typically a MOSFET or bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The transistor alternately connects and disconnects the inductor to the supply voltage, allowing energy to be stored in the magnetic field of the inductor when the transistor is in the 'on' state.
When the transistor turns 'off', the magnetic energy stored in the inductor is released, causing a voltage spike. This spike is crucial as it allows the inductor to transfer energy to the load. The output voltage can be regulated based on the load resistance, which influences the amount of current flowing through the inductor and subsequently the voltage across the load.
A zener diode is incorporated into the circuit to provide voltage regulation. When the output voltage reaches approximately 14 volts, the zener diode becomes reverse-biased and effectively stops the Schmitt trigger oscillator from oscillating, thereby preventing further increases in output voltage. This feedback mechanism ensures that the power supply maintains a stable output voltage, protecting connected components from overvoltage conditions.
To adjust the output voltage levels, a voltage divider can be implemented, allowing for fine-tuning of the input to the zener diode. By changing the resistor values in the divider, various output voltages can be achieved, making the power supply versatile for different applications.
The efficiency of the power supply is approximately 80%, which is a significant factor in its design. Utilizing a high Q inductor minimizes energy losses due to core losses and skin effect, contributing to the overall performance of the circuit. This efficiency rating is essential for applications where power conservation is critical, such as in battery-operated devices or compact electronic systems.
Overall, this small switching power supply design showcases a practical application of basic electronic principles, combining oscillation, energy storage, and voltage regulation to achieve a reliable power source.In this small switching power supply, a Schmitt trigger oscillator is used to drive a switching transistor that supplies current to a small inductor. Energy is stored in the inductor while the transistor is on, and released into the load circuit when the transistor switches off.
The output voltage is dependent on the load resistance and is limited by a zener diode that stops the oscillator when the voltage reaches about 14 volts. Higher or lower voltages can be obtained by adjusting the voltage divider that feeds the zener diode. The efficiency is about 80% using a high Q inductor. 🔗 External reference
This switching power supply circuit operates by utilizing a Schmitt trigger oscillator to generate a square wave signal that drives a switching transistor, typically a MOSFET or bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The transistor alternately connects and disconnects the inductor to the supply voltage, allowing energy to be stored in the magnetic field of the inductor when the transistor is in the 'on' state.
When the transistor turns 'off', the magnetic energy stored in the inductor is released, causing a voltage spike. This spike is crucial as it allows the inductor to transfer energy to the load. The output voltage can be regulated based on the load resistance, which influences the amount of current flowing through the inductor and subsequently the voltage across the load.
A zener diode is incorporated into the circuit to provide voltage regulation. When the output voltage reaches approximately 14 volts, the zener diode becomes reverse-biased and effectively stops the Schmitt trigger oscillator from oscillating, thereby preventing further increases in output voltage. This feedback mechanism ensures that the power supply maintains a stable output voltage, protecting connected components from overvoltage conditions.
To adjust the output voltage levels, a voltage divider can be implemented, allowing for fine-tuning of the input to the zener diode. By changing the resistor values in the divider, various output voltages can be achieved, making the power supply versatile for different applications.
The efficiency of the power supply is approximately 80%, which is a significant factor in its design. Utilizing a high Q inductor minimizes energy losses due to core losses and skin effect, contributing to the overall performance of the circuit. This efficiency rating is essential for applications where power conservation is critical, such as in battery-operated devices or compact electronic systems.
Overall, this small switching power supply design showcases a practical application of basic electronic principles, combining oscillation, energy storage, and voltage regulation to achieve a reliable power source.In this small switching power supply, a Schmitt trigger oscillator is used to drive a switching transistor that supplies current to a small inductor. Energy is stored in the inductor while the transistor is on, and released into the load circuit when the transistor switches off.
The output voltage is dependent on the load resistance and is limited by a zener diode that stops the oscillator when the voltage reaches about 14 volts. Higher or lower voltages can be obtained by adjusting the voltage divider that feeds the zener diode. The efficiency is about 80% using a high Q inductor. 🔗 External reference