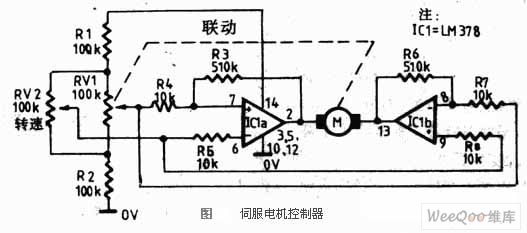
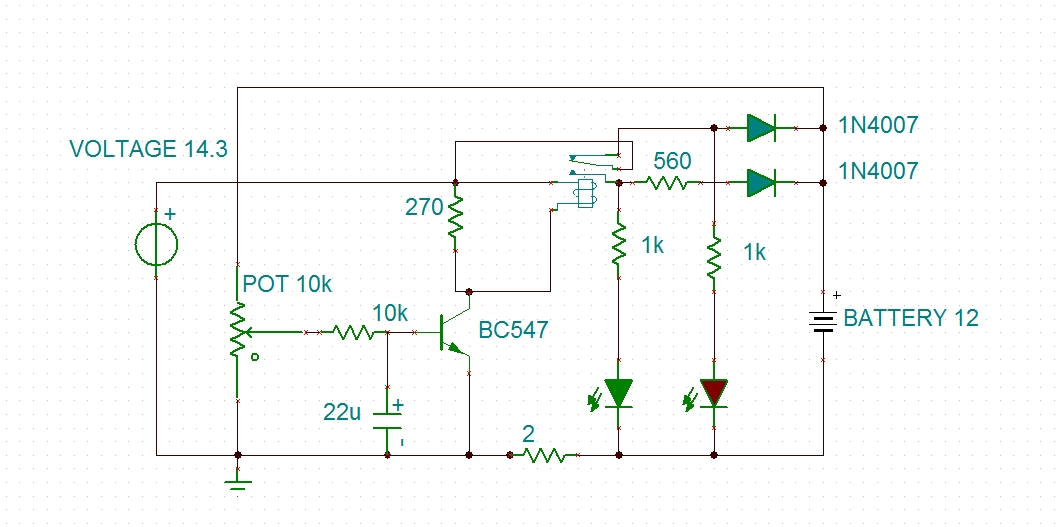
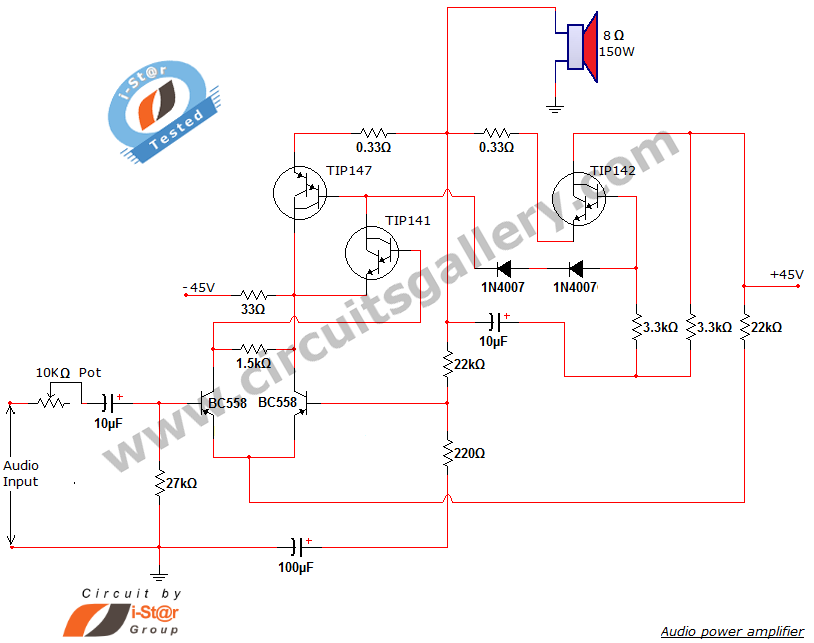
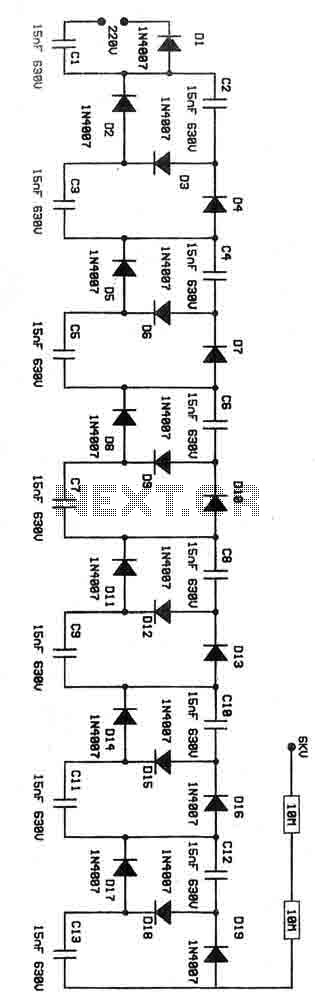
Adjustable output voltage power supply circuit MAX610
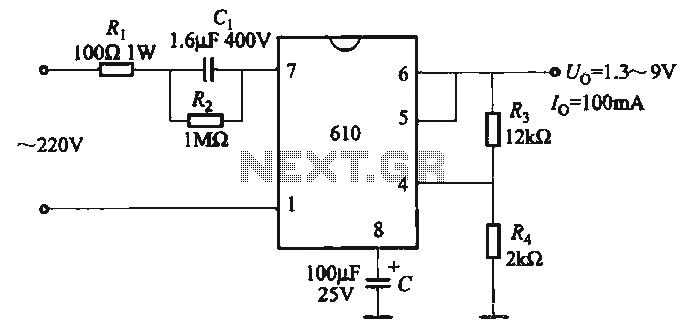
The output voltage can be calculated as follows: U = 1.3 (1 + R3 / R4) (V), where R3 and R4 are part of an adjustment potentiometer, allowing for a continuously adjustable output voltage.
The described circuit involves a voltage output that is dependent on the resistors R3 and R4, which form a voltage divider configuration in conjunction with a potentiometer. The formula indicates that the output voltage (U) is 1.3 times the sum of 1 and the ratio of R3 to R4. This implies that by varying the resistance values of R3 and R4, the output voltage can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements.
In practical applications, the potentiometer serves as a means to adjust the resistance values dynamically. When R3 is increased relative to R4, the output voltage increases, whereas decreasing R3 or increasing R4 will lower the output voltage. This circuit can be utilized in various applications where precise voltage control is necessary, such as in power supplies, signal conditioning, or sensor interfaces.
The stability of the output voltage can be influenced by the tolerance of the resistors used, as well as the quality of the potentiometer. It is essential to select components that can withstand the operational conditions to ensure reliable performance. Additionally, the circuit may include filtering capacitors to stabilize the output and minimize voltage ripple, particularly in applications that require smooth and consistent voltage levels. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be employed to reduce noise and interference in the circuit.The output voltage can be calculated as follows: U. . = 1. 3 (1 + R3 / R4) (V) adjustment potentiometer , continuously adjustable output voltage.
The described circuit involves a voltage output that is dependent on the resistors R3 and R4, which form a voltage divider configuration in conjunction with a potentiometer. The formula indicates that the output voltage (U) is 1.3 times the sum of 1 and the ratio of R3 to R4. This implies that by varying the resistance values of R3 and R4, the output voltage can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements.
In practical applications, the potentiometer serves as a means to adjust the resistance values dynamically. When R3 is increased relative to R4, the output voltage increases, whereas decreasing R3 or increasing R4 will lower the output voltage. This circuit can be utilized in various applications where precise voltage control is necessary, such as in power supplies, signal conditioning, or sensor interfaces.
The stability of the output voltage can be influenced by the tolerance of the resistors used, as well as the quality of the potentiometer. It is essential to select components that can withstand the operational conditions to ensure reliable performance. Additionally, the circuit may include filtering capacitors to stabilize the output and minimize voltage ripple, particularly in applications that require smooth and consistent voltage levels. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be employed to reduce noise and interference in the circuit.The output voltage can be calculated as follows: U. . = 1. 3 (1 + R3 / R4) (V) adjustment potentiometer , continuously adjustable output voltage.