modified battery charger circuit
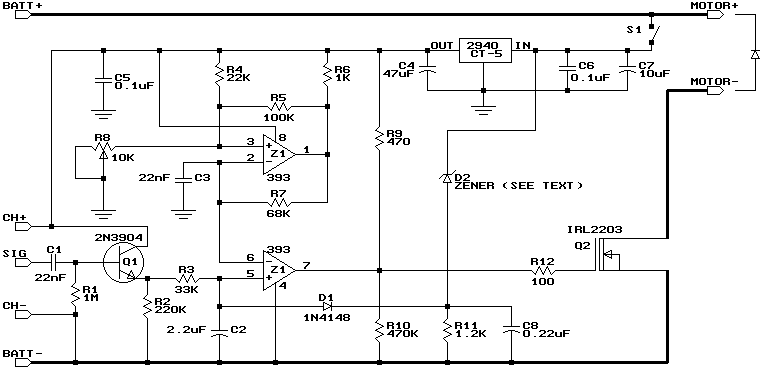
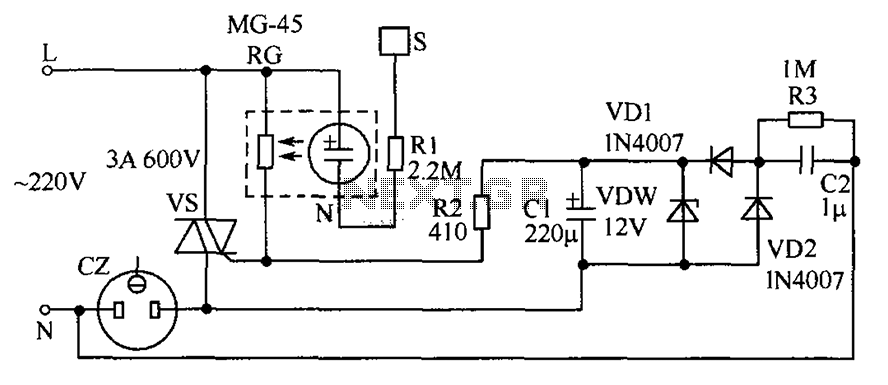
Using a transistor will not yield accurate results, and the adjustment process can become quite tedious. The circuit is technically correct; if the tripping point can be adjusted properly, it may function as intended. Vinod states that he created a charger with hysteresis but encountered an issue. He will attach an image to clarify the problem. When connecting a multimeter to specific points indicated by red dots, it shows a voltage of 16.8V (0.43A). However, when the battery is disconnected from the charger and measured again, the output reads 14.2V. Additionally, the other pin of the relay, through the current-limiting resistor, delivers a clean output voltage of 13.9V (0.033A). The reason for this discrepancy is unclear. The only modification made to the circuit was relocating the green LED and resistor R1 after diode D6. Swagatam finds it challenging to identify the fault, suggesting that if the meter probes are connected across the battery terminals, it should display the average battery voltage and supply voltage. The higher voltage reading is puzzling, and he recommends checking the multimeter's functionality. He suggests performing the measurement again by turning off the power supply and then turning it back on while the meter remains connected to points A and B. Vinod later confirms that he has successfully created a charger that meets his requirements and shares the schematic. The charger operates as a constant current charger (400-500mA) until the battery reaches 13V, after which the charging current drops to 25mA. LED indicators display the various charging stages.
The described circuit involves a hysteresis charger designed to manage the charging of a battery effectively. The primary components include a transistor, a relay, a diode (D6), a current-limiting resistor, and LED indicators. The transistor functions as a switching device to control the charging current based on the battery voltage level. The hysteresis feature allows for a stable transition between charging states, preventing rapid on-off cycling that could lead to inefficiencies or damage to the battery.
The initial observation of a voltage discrepancy suggests that there may be an issue with the circuit configuration or the measurement technique. When the multimeter indicates a voltage of 16.8V while connected to the circuit, it may imply that the charger is outputting a voltage influenced by the transient response of the circuit or an incorrect measurement setup. Disconnecting the battery and measuring again to observe an output of 14.2V indicates that the charger operates correctly under no-load conditions, but the presence of the battery alters the circuit dynamics.
The relocation of the green LED and resistor R1 after diode D6 could impact the feedback mechanism of the circuit, potentially affecting the voltage regulation. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of the feedback loop for accurate voltage regulation. The relay's output, delivering a clean voltage of 13.9V (0.033A), suggests that the circuit is capable of providing stable output under specific conditions.
To ensure proper functionality, it is advisable to verify the multimeter's calibration and confirm that the probes are correctly positioned during measurements. Further adjustments to the tripping point may be necessary to achieve the desired performance of the charger. The design allows for monitoring the charging process through LED indicators, which provide visual feedback on the charging stages, enhancing user experience and ensuring safe operation.Using a transistor won`t give accurate results, moreover the setting part would become very tedious. The circuit is technically correct, if you can adjust the tripping point correctly, then it might just work. Vinod: I made the charger (hysteresis) but there is a problem. i will attach the image to explain the problem. When i connect multimeter in that particular red dots, the voltage shows 16. 8. (0. 43 A) but when i disconnect battery from the charger and measured again. then there is no problem. the out put is 14. 2. And the other pin of the relay(through the current limiting resistor) will deliver a clean output voltage of 13. 9 (0. 033A). Why this is happening. The only change i have made from this circuit is to grab the green LED and R1 from there and connect it after the D6.
Swagatam: It`s difficult to understand the fault, if you are the connecting meter prods across the battery terminals, it should show the average voltage of the battery and the supply voltage. not sure why it`s showing a higher voltage. Is your meter OK You can repeat the checking by switching OFF the power supply and then again switching ON the power supply keeping the meter connected to the points A and B.
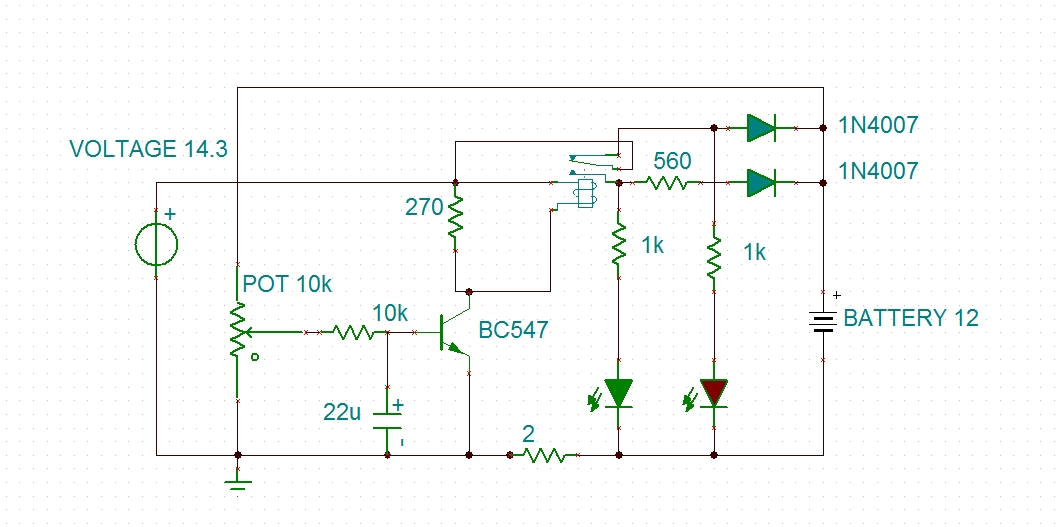
Hi Swagat, Atlast i made a charger that suits my needs. this is the schematic. (plz look attachment). Until battery gets 13v this is a constant current charger(400-500mA). After 13v, charging current is 25mA. And the LED`s indicate the charging stages. Regards Vinod chandran 🔗 External reference
The described circuit involves a hysteresis charger designed to manage the charging of a battery effectively. The primary components include a transistor, a relay, a diode (D6), a current-limiting resistor, and LED indicators. The transistor functions as a switching device to control the charging current based on the battery voltage level. The hysteresis feature allows for a stable transition between charging states, preventing rapid on-off cycling that could lead to inefficiencies or damage to the battery.
The initial observation of a voltage discrepancy suggests that there may be an issue with the circuit configuration or the measurement technique. When the multimeter indicates a voltage of 16.8V while connected to the circuit, it may imply that the charger is outputting a voltage influenced by the transient response of the circuit or an incorrect measurement setup. Disconnecting the battery and measuring again to observe an output of 14.2V indicates that the charger operates correctly under no-load conditions, but the presence of the battery alters the circuit dynamics.
The relocation of the green LED and resistor R1 after diode D6 could impact the feedback mechanism of the circuit, potentially affecting the voltage regulation. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of the feedback loop for accurate voltage regulation. The relay's output, delivering a clean voltage of 13.9V (0.033A), suggests that the circuit is capable of providing stable output under specific conditions.
To ensure proper functionality, it is advisable to verify the multimeter's calibration and confirm that the probes are correctly positioned during measurements. Further adjustments to the tripping point may be necessary to achieve the desired performance of the charger. The design allows for monitoring the charging process through LED indicators, which provide visual feedback on the charging stages, enhancing user experience and ensuring safe operation.Using a transistor won`t give accurate results, moreover the setting part would become very tedious. The circuit is technically correct, if you can adjust the tripping point correctly, then it might just work. Vinod: I made the charger (hysteresis) but there is a problem. i will attach the image to explain the problem. When i connect multimeter in that particular red dots, the voltage shows 16. 8. (0. 43 A) but when i disconnect battery from the charger and measured again. then there is no problem. the out put is 14. 2. And the other pin of the relay(through the current limiting resistor) will deliver a clean output voltage of 13. 9 (0. 033A). Why this is happening. The only change i have made from this circuit is to grab the green LED and R1 from there and connect it after the D6.
Swagatam: It`s difficult to understand the fault, if you are the connecting meter prods across the battery terminals, it should show the average voltage of the battery and the supply voltage. not sure why it`s showing a higher voltage. Is your meter OK You can repeat the checking by switching OFF the power supply and then again switching ON the power supply keeping the meter connected to the points A and B.
Hi Swagat, Atlast i made a charger that suits my needs. this is the schematic. (plz look attachment). Until battery gets 13v this is a constant current charger(400-500mA). After 13v, charging current is 25mA. And the LED`s indicate the charging stages. Regards Vinod chandran 🔗 External reference