audible logic pulses
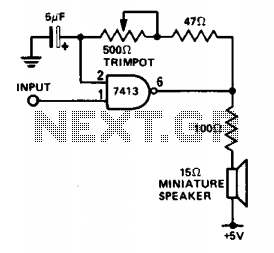
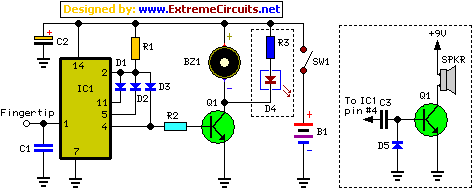
This circuit is useful for monitoring slow logic pulses as a keying monitor or digital clock alarm. The Schmitt trigger is connected as an oscillator. The trimpot controls the pitch of the output. When the input goes high, the circuit will oscillate.
The described circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger configured as an oscillator to monitor slow logic pulses effectively. It serves dual purposes: functioning as a keying monitor and acting as a digital clock alarm. The Schmitt trigger's inherent hysteresis provides stable switching characteristics, which are essential for distinguishing between high and low logic levels, particularly in slow pulse applications.
The circuit incorporates a trimpot (trimming potentiometer) that allows for precise adjustment of the output frequency or pitch. This feature is particularly useful in applications where specific timing or frequency characteristics are required. As the input signal transitions to a high state, the oscillator becomes activated, producing an oscillating output.
In terms of implementation, the Schmitt trigger is typically connected in a feedback configuration, which establishes the oscillation. The output frequency can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the trimpot, thus changing the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor in the circuit. This adjustment enables fine-tuning of the oscillation period, allowing the circuit to adapt to different monitoring needs or alarm conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a versatile approach to pulse monitoring, leveraging the reliable properties of the Schmitt trigger and the adjustable nature of the trimpot to meet various application requirements.This circuit is useful for monitoring slow logic pulses as a keying monitor or digital clock alarm. The Schmitt trigger is connected as an oscillator. The trimpot controls the pitch of the output. When the input goes high, the circuit will oscillate. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger configured as an oscillator to monitor slow logic pulses effectively. It serves dual purposes: functioning as a keying monitor and acting as a digital clock alarm. The Schmitt trigger's inherent hysteresis provides stable switching characteristics, which are essential for distinguishing between high and low logic levels, particularly in slow pulse applications.
The circuit incorporates a trimpot (trimming potentiometer) that allows for precise adjustment of the output frequency or pitch. This feature is particularly useful in applications where specific timing or frequency characteristics are required. As the input signal transitions to a high state, the oscillator becomes activated, producing an oscillating output.
In terms of implementation, the Schmitt trigger is typically connected in a feedback configuration, which establishes the oscillation. The output frequency can be adjusted by varying the resistance of the trimpot, thus changing the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor in the circuit. This adjustment enables fine-tuning of the oscillation period, allowing the circuit to adapt to different monitoring needs or alarm conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a versatile approach to pulse monitoring, leveraging the reliable properties of the Schmitt trigger and the adjustable nature of the trimpot to meet various application requirements.This circuit is useful for monitoring slow logic pulses as a keying monitor or digital clock alarm. The Schmitt trigger is connected as an oscillator. The trimpot controls the pitch of the output. When the input goes high, the circuit will oscillate. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713