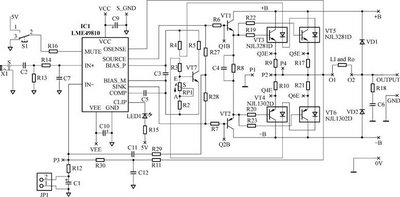
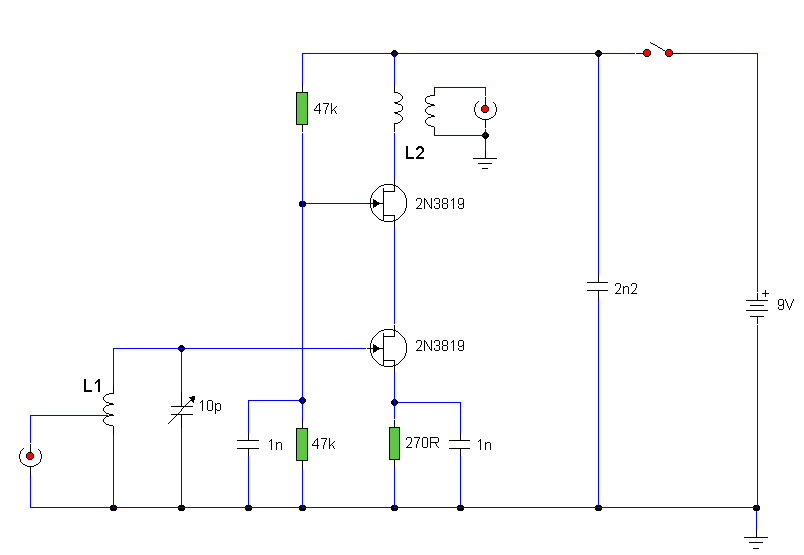
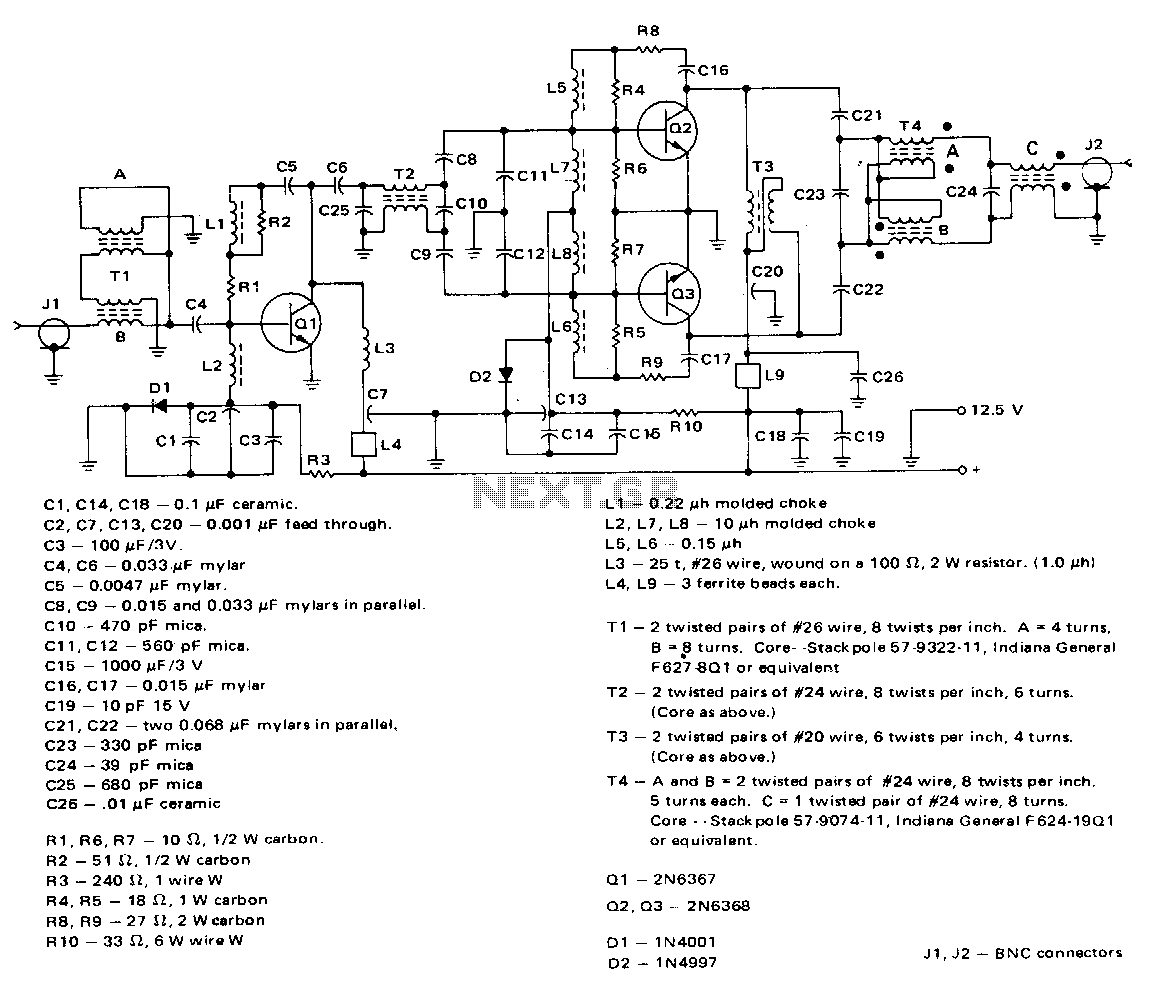
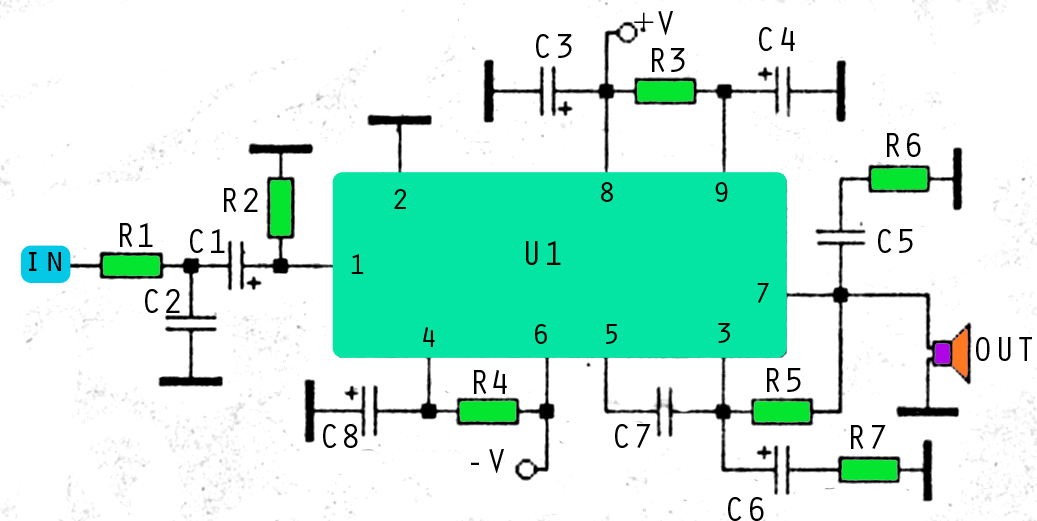
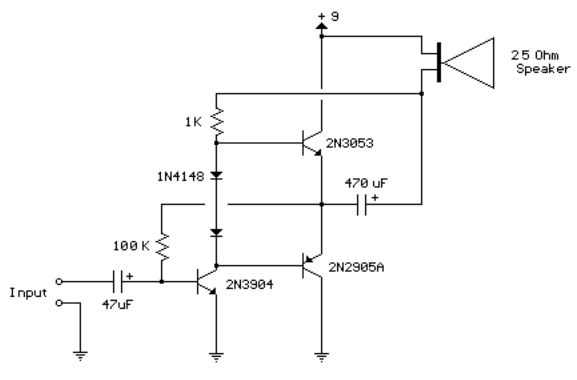
Audio Amplifier 25 Watt
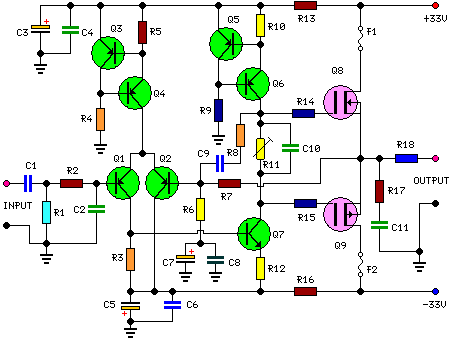
The following circuit illustrates an audio amplifier circuit diagram with a power output of 25 watts. Features include its widespread use in nearly all mass-market stereo receivers produced, providing enhanced sound quality.
This audio amplifier circuit is designed to deliver a power output of 25 watts, making it suitable for various applications, including home audio systems, portable speakers, and other audio devices. The circuit typically employs a combination of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and possibly an operational amplifier to achieve the desired amplification.
The input stage of the amplifier often consists of a differential amplifier configuration, which helps in improving the signal-to-noise ratio and reduces distortion. The transistors used in the output stage are usually configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for efficient amplification of both the positive and negative halves of the audio signal. This configuration enhances the overall performance by minimizing crossover distortion.
Power supply considerations are crucial for achieving optimal performance in audio amplifiers. A regulated power supply is recommended to ensure stable voltage levels, thus preventing fluctuations that could affect sound quality. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included to filter out high-frequency noise, further improving the amplifier's performance.
Heat dissipation is another important aspect to consider, as amplifiers can generate significant heat during operation. Adequate heat sinks or cooling mechanisms should be implemented to maintain the transistors within safe operating temperatures, ensuring reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Overall, this 25-watt audio amplifier circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various audio applications, providing robust performance and high-quality sound reproduction in consumer audio products.The following circuit shows about Audio Amplifier 25 Watt Circuit Diagram. Features: used in practically every mass market stereo receiver manufactured, better .. 🔗 External reference
This audio amplifier circuit is designed to deliver a power output of 25 watts, making it suitable for various applications, including home audio systems, portable speakers, and other audio devices. The circuit typically employs a combination of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and possibly an operational amplifier to achieve the desired amplification.
The input stage of the amplifier often consists of a differential amplifier configuration, which helps in improving the signal-to-noise ratio and reduces distortion. The transistors used in the output stage are usually configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for efficient amplification of both the positive and negative halves of the audio signal. This configuration enhances the overall performance by minimizing crossover distortion.
Power supply considerations are crucial for achieving optimal performance in audio amplifiers. A regulated power supply is recommended to ensure stable voltage levels, thus preventing fluctuations that could affect sound quality. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be included to filter out high-frequency noise, further improving the amplifier's performance.
Heat dissipation is another important aspect to consider, as amplifiers can generate significant heat during operation. Adequate heat sinks or cooling mechanisms should be implemented to maintain the transistors within safe operating temperatures, ensuring reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Overall, this 25-watt audio amplifier circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various audio applications, providing robust performance and high-quality sound reproduction in consumer audio products.The following circuit shows about Audio Amplifier 25 Watt Circuit Diagram. Features: used in practically every mass market stereo receiver manufactured, better .. 🔗 External reference