Audio level meter circuit - VU Level Meter
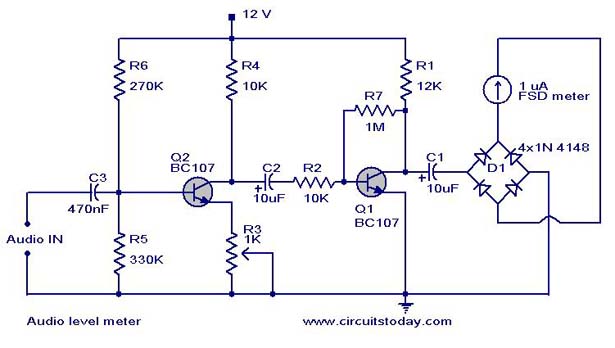
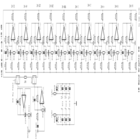
A simple audio level meter or Volume Unit (VU) level meter circuit with diagram and schematic. This sound level meter is designed using transistors with a flat frequency response in the range of 20Hz to 50kHz.
The audio level meter circuit, commonly referred to as a Volume Unit (VU) meter, serves the purpose of visually displaying the amplitude of audio signals. It typically employs a series of transistors configured to amplify the incoming audio signal, allowing for accurate representation of sound levels across a broad frequency spectrum.
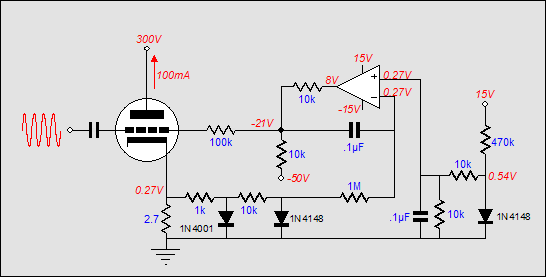
The circuit design includes a basic input stage where the audio signal is fed. This signal is then processed through a transistor-based amplifier, which boosts the signal to a level suitable for driving the meter. The transistors used in the circuit are selected for their linear characteristics, ensuring a flat frequency response from 20Hz to 50kHz. This range covers the majority of audible frequencies, making the VU meter effective for various audio applications.
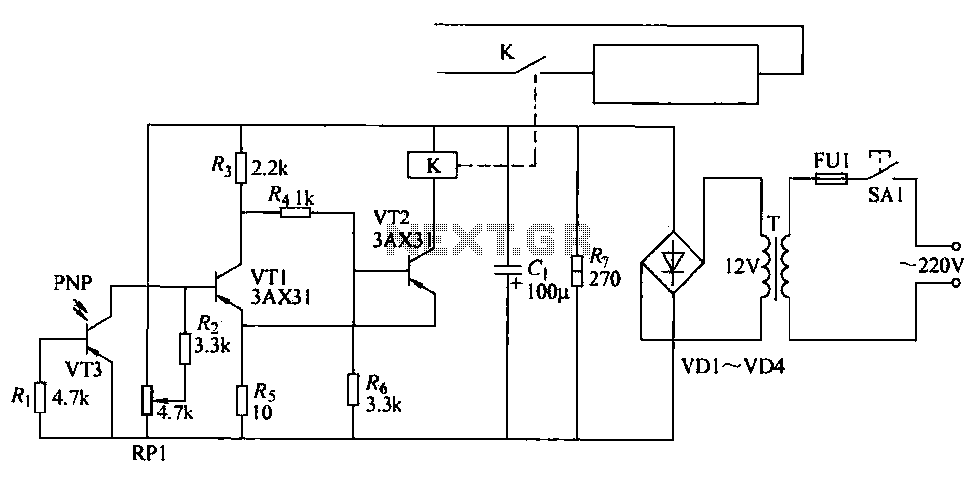
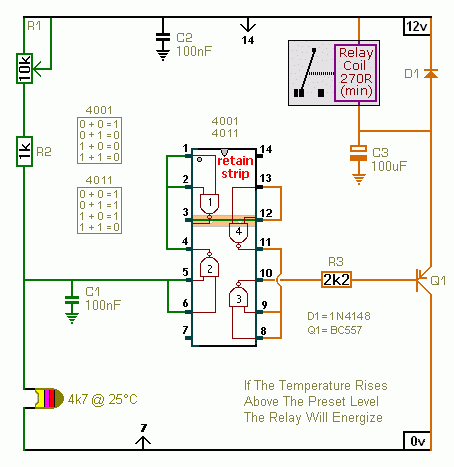
The output of the amplifier is connected to a needle or LED display that provides a visual indication of the audio level. The display is calibrated to reflect the intensity of the signal, allowing users to monitor audio levels in real-time. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors are included to filter noise and stabilize the circuit operation, ensuring reliable performance.
This audio level meter circuit is ideal for use in audio mixing environments, public address systems, and recording studios, where precise audio level monitoring is crucial for achieving optimal sound quality. The schematic diagram accompanying the circuit provides a clear representation of the connections and component values necessary for assembly.A simple audio level meter or a Volume unit VU level meter circuit with diagram and schematic. This sound level meter is designed using transistors with a flat frequency response in the range of 20Hz to 50Khz.. 🔗 External reference
The audio level meter circuit, commonly referred to as a Volume Unit (VU) meter, serves the purpose of visually displaying the amplitude of audio signals. It typically employs a series of transistors configured to amplify the incoming audio signal, allowing for accurate representation of sound levels across a broad frequency spectrum.
The circuit design includes a basic input stage where the audio signal is fed. This signal is then processed through a transistor-based amplifier, which boosts the signal to a level suitable for driving the meter. The transistors used in the circuit are selected for their linear characteristics, ensuring a flat frequency response from 20Hz to 50kHz. This range covers the majority of audible frequencies, making the VU meter effective for various audio applications.
The output of the amplifier is connected to a needle or LED display that provides a visual indication of the audio level. The display is calibrated to reflect the intensity of the signal, allowing users to monitor audio levels in real-time. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors are included to filter noise and stabilize the circuit operation, ensuring reliable performance.
This audio level meter circuit is ideal for use in audio mixing environments, public address systems, and recording studios, where precise audio level monitoring is crucial for achieving optimal sound quality. The schematic diagram accompanying the circuit provides a clear representation of the connections and component values necessary for assembly.A simple audio level meter or a Volume unit VU level meter circuit with diagram and schematic. This sound level meter is designed using transistors with a flat frequency response in the range of 20Hz to 50Khz.. 🔗 External reference