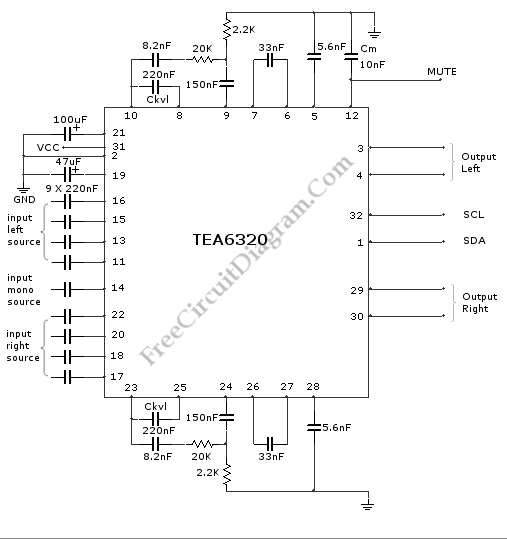
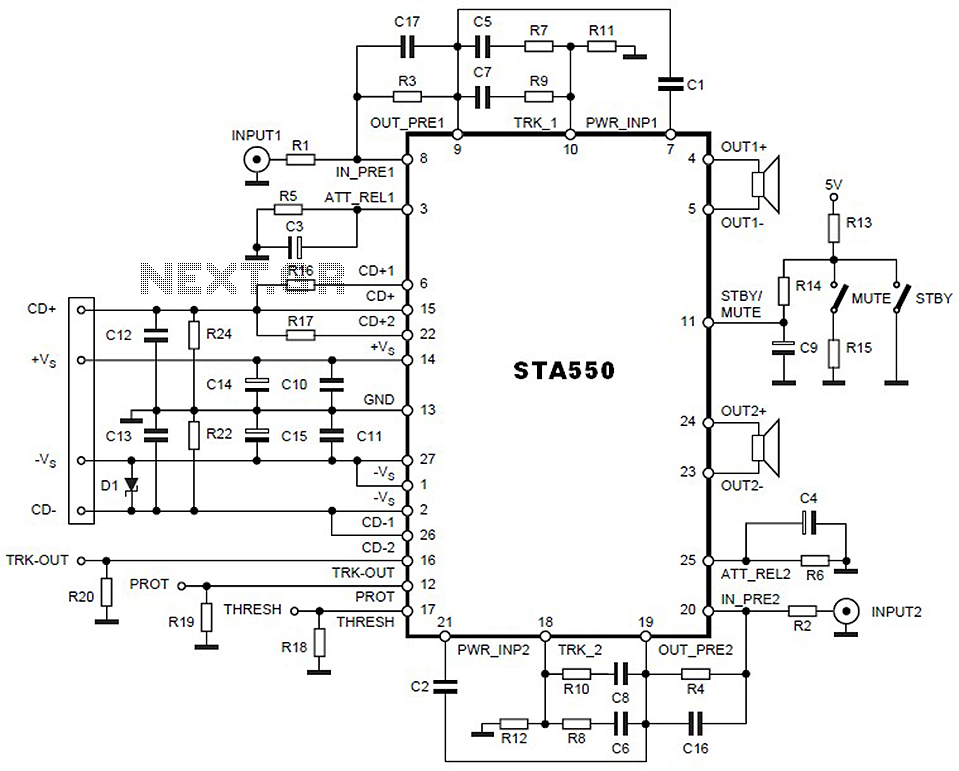
audio mixing
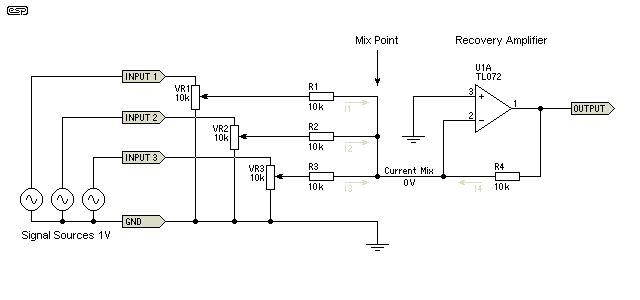
The fundamental principles of mixing audio signals are simple, yet they are often not clearly explained online. This article aims to address those gaps.
Mixing audio signals involves combining multiple sound sources to create a cohesive audio output. The process requires a fundamental understanding of various concepts such as levels, panning, equalization, and effects. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in achieving a balanced and professional-sounding mix.
Levels refer to the amplitude of each audio signal. Proper level management ensures that no single element overwhelms others, allowing for clarity and definition in the mix. It is essential to adjust levels appropriately to maintain a dynamic range that is neither too compressed nor too dynamic.
Panning involves positioning audio signals within the stereo field. By distributing sounds across the left and right channels, a mix can achieve depth and spatial awareness. Careful panning can create a more immersive listening experience, allowing listeners to perceive the arrangement of instruments and vocals.
Equalization (EQ) is a critical tool used to enhance or reduce specific frequency ranges within audio signals. By applying EQ, unwanted frequencies can be attenuated, and desirable characteristics can be emphasized. This process helps in reducing muddiness and harshness, ensuring that each element occupies its own frequency space.
Effects such as reverb, delay, and compression can further enhance the mix. Reverb adds a sense of space and depth, while delay can create rhythmic interest. Compression helps control dynamics by reducing the volume of louder signals and raising the volume of quieter ones, leading to a more consistent sound.
In summary, mixing audio signals requires a comprehensive understanding of levels, panning, equalization, and effects. Mastery of these principles can lead to clearer, more engaging audio productions that resonate with listeners.The essential principles of mixing audio signals are straightforward, but strangely are not explained very well at all on the Net. This article should fill the gaps.. 🔗 External reference
Mixing audio signals involves combining multiple sound sources to create a cohesive audio output. The process requires a fundamental understanding of various concepts such as levels, panning, equalization, and effects. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in achieving a balanced and professional-sounding mix.
Levels refer to the amplitude of each audio signal. Proper level management ensures that no single element overwhelms others, allowing for clarity and definition in the mix. It is essential to adjust levels appropriately to maintain a dynamic range that is neither too compressed nor too dynamic.
Panning involves positioning audio signals within the stereo field. By distributing sounds across the left and right channels, a mix can achieve depth and spatial awareness. Careful panning can create a more immersive listening experience, allowing listeners to perceive the arrangement of instruments and vocals.
Equalization (EQ) is a critical tool used to enhance or reduce specific frequency ranges within audio signals. By applying EQ, unwanted frequencies can be attenuated, and desirable characteristics can be emphasized. This process helps in reducing muddiness and harshness, ensuring that each element occupies its own frequency space.
Effects such as reverb, delay, and compression can further enhance the mix. Reverb adds a sense of space and depth, while delay can create rhythmic interest. Compression helps control dynamics by reducing the volume of louder signals and raising the volume of quieter ones, leading to a more consistent sound.
In summary, mixing audio signals requires a comprehensive understanding of levels, panning, equalization, and effects. Mastery of these principles can lead to clearer, more engaging audio productions that resonate with listeners.The essential principles of mixing audio signals are straightforward, but strangely are not explained very well at all on the Net. This article should fill the gaps.. 🔗 External reference