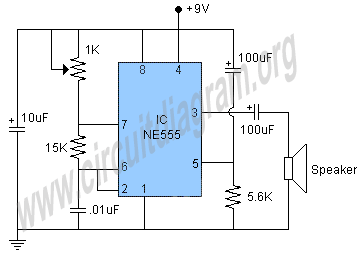
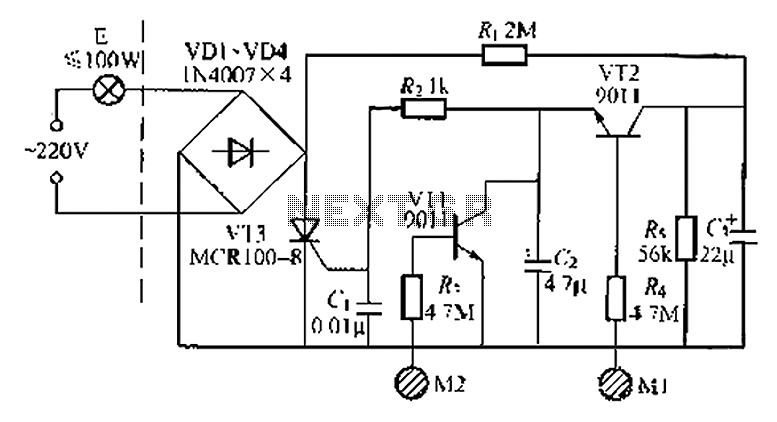
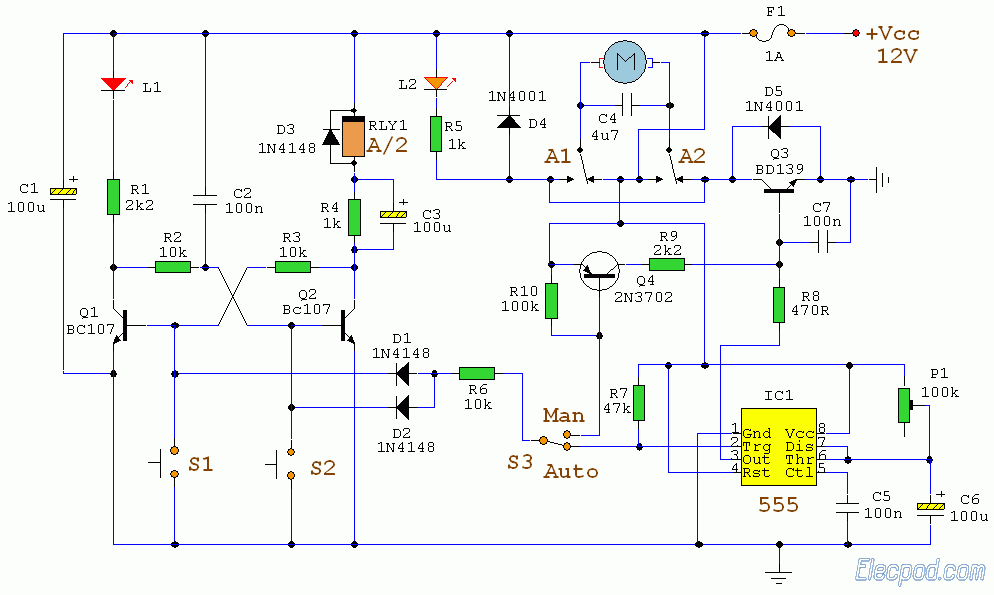
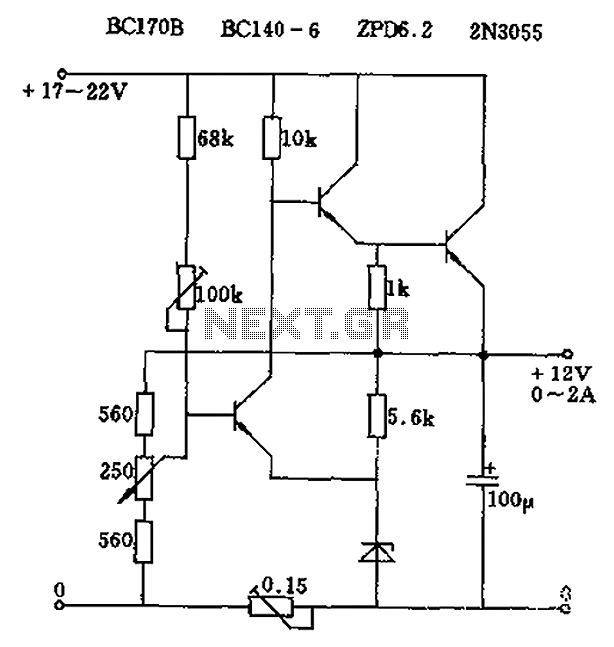
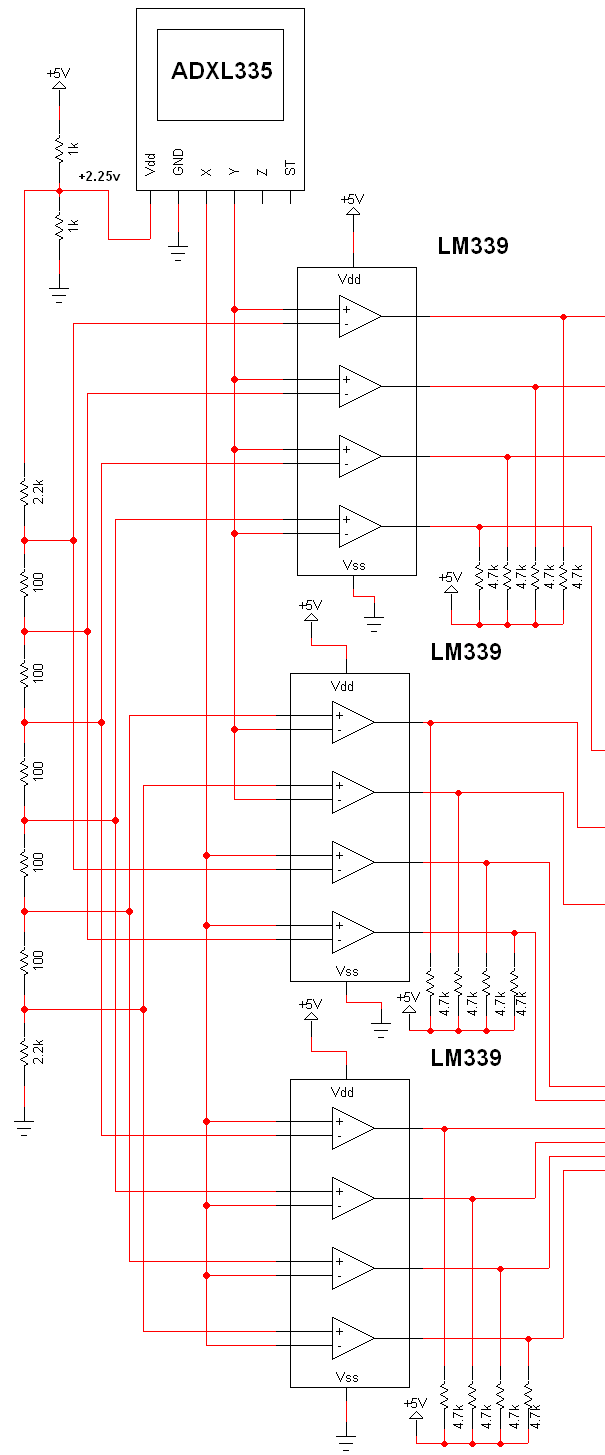
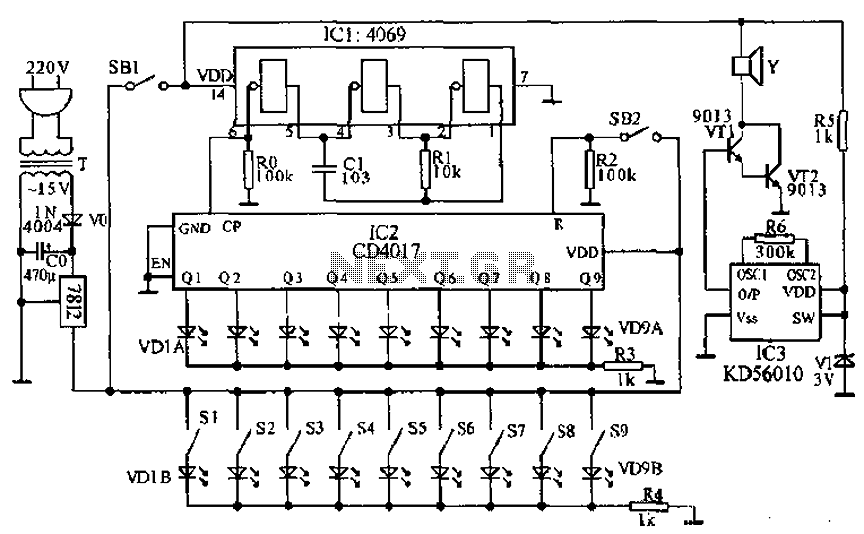
Automatic Gain Control - AGC Circuit
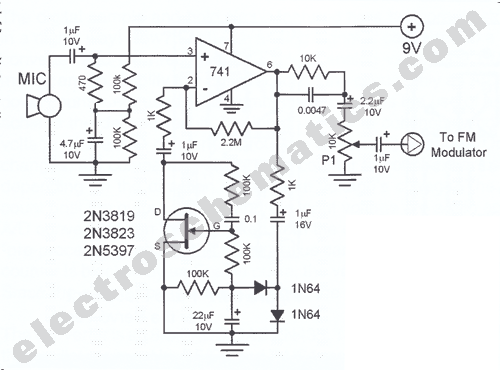
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) is a circuit design that maintains a consistent level of amplification for sound or radio frequency signals. If the signal is too low, the AGC increases the gain to ensure the output remains at a desired level.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuits are integral to various electronic applications, including audio processing, telecommunications, and broadcasting. The primary function of AGC is to automatically adjust the gain of an amplifier to maintain a steady output level despite varying input signal strengths. This is particularly useful in environments where signal levels fluctuate significantly, such as in radio receivers or during live audio performances.
An AGC circuit typically comprises several key components: a detector, an amplifier, and a feedback loop. The detector monitors the output signal level and compares it to a reference level. When the output deviates from this reference, the detector generates a control voltage that is fed back to the amplifier to adjust its gain. This feedback mechanism allows the AGC to respond dynamically to changes in the input signal.
The design of an AGC circuit can vary depending on the application. For instance, in audio systems, it is crucial to ensure that the gain adjustment is smooth to avoid distortion or abrupt changes in volume. In radio frequency applications, the AGC must respond quickly to changes in signal strength to maintain signal integrity.
The performance of an AGC circuit is characterized by parameters such as attack time, release time, and gain range. The attack time refers to how quickly the AGC responds to an increase in signal level, while the release time is the duration it takes to return to the original gain level after the signal decreases. The gain range indicates the minimum and maximum gain levels that the AGC can provide.
In summary, Automatic Gain Control circuits are essential for maintaining consistent output levels in various electronic systems, ensuring optimal performance across a range of signal conditions.Automatic Gain Control or AGC is a circuit design which maintain the same level of amplification for sound or radio frequency. If the signal is too low the.. 🔗 External reference
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuits are integral to various electronic applications, including audio processing, telecommunications, and broadcasting. The primary function of AGC is to automatically adjust the gain of an amplifier to maintain a steady output level despite varying input signal strengths. This is particularly useful in environments where signal levels fluctuate significantly, such as in radio receivers or during live audio performances.
An AGC circuit typically comprises several key components: a detector, an amplifier, and a feedback loop. The detector monitors the output signal level and compares it to a reference level. When the output deviates from this reference, the detector generates a control voltage that is fed back to the amplifier to adjust its gain. This feedback mechanism allows the AGC to respond dynamically to changes in the input signal.
The design of an AGC circuit can vary depending on the application. For instance, in audio systems, it is crucial to ensure that the gain adjustment is smooth to avoid distortion or abrupt changes in volume. In radio frequency applications, the AGC must respond quickly to changes in signal strength to maintain signal integrity.
The performance of an AGC circuit is characterized by parameters such as attack time, release time, and gain range. The attack time refers to how quickly the AGC responds to an increase in signal level, while the release time is the duration it takes to return to the original gain level after the signal decreases. The gain range indicates the minimum and maximum gain levels that the AGC can provide.
In summary, Automatic Gain Control circuits are essential for maintaining consistent output levels in various electronic systems, ensuring optimal performance across a range of signal conditions.Automatic Gain Control or AGC is a circuit design which maintain the same level of amplification for sound or radio frequency. If the signal is too low the.. 🔗 External reference