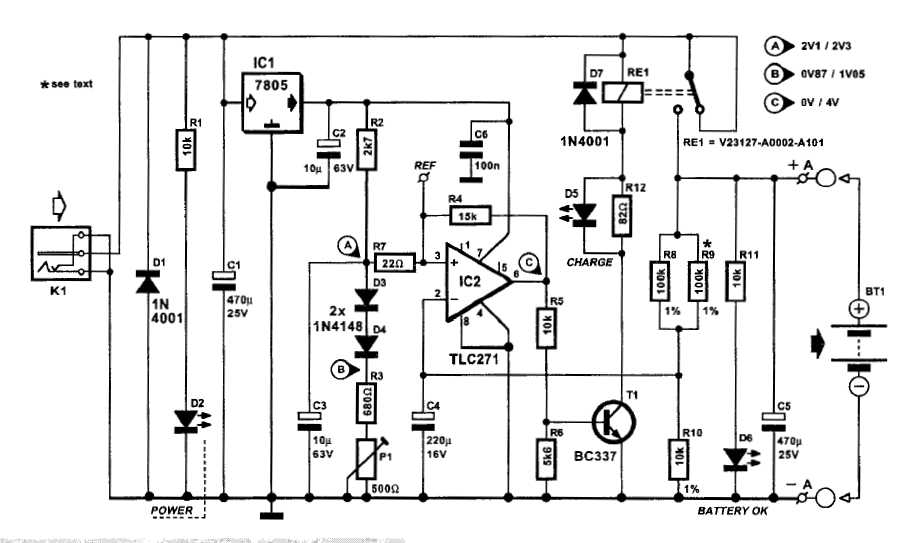
Automatic Ni-Cd Battery ChargerCircuit
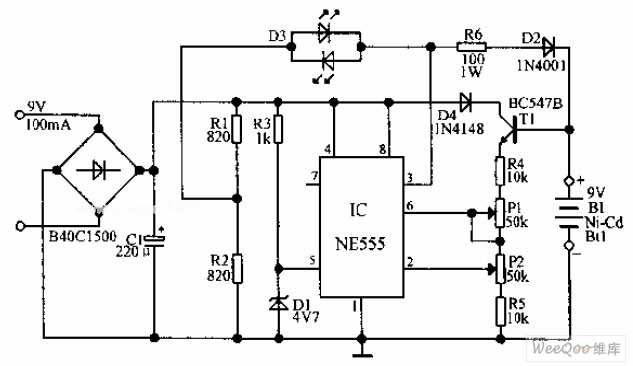
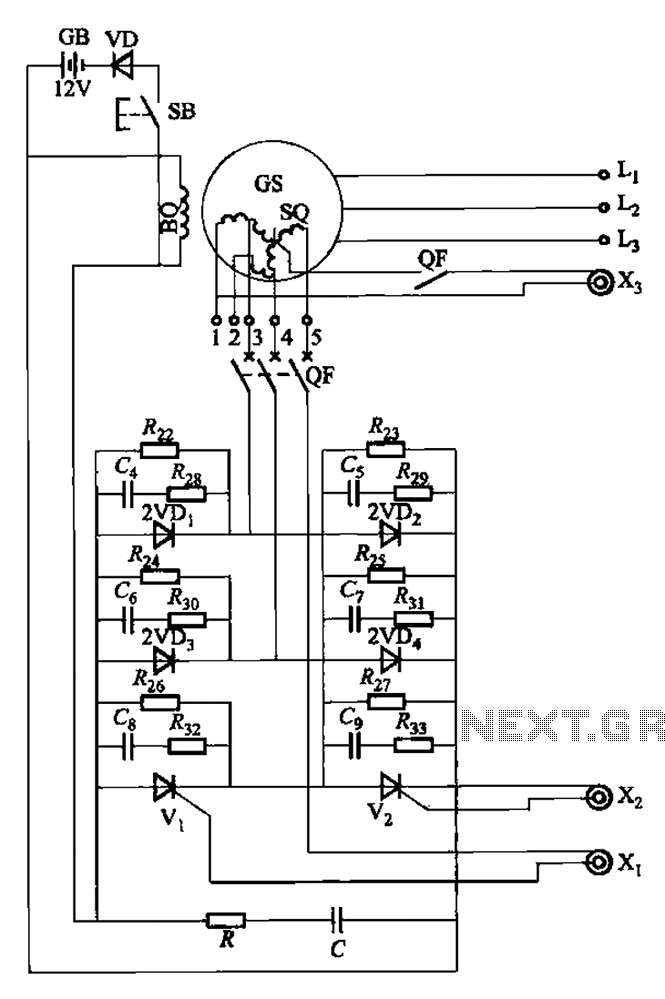
An automatic Ni-Cd battery charger circuit is depicted in the provided image. The internal comparator of the NE555 timer is configured to a reference voltage of 4.7V using a Zener diode. When the voltage at pin 6 exceeds this value, the output at pin 3 decreases. Conversely, if the voltage at pin 2 falls below half of the reference voltage, the output voltage increases. When the voltage of the...
The automatic Ni-Cd battery charger circuit utilizes the NE555 timer IC in a comparator configuration to regulate the charging process. The Zener diode is employed to establish a stable reference voltage of 4.7V, which is crucial for determining the charging state of the battery. This reference voltage is connected to pin 6 of the NE555, while the voltage at pin 2 is monitored to assess the battery's charge level.
During operation, if the voltage at pin 6 surpasses 4.7V, the output at pin 3 transitions to a low state, signaling a reduction in the charging current to prevent overcharging. This feature is essential for maintaining the longevity and safety of the Ni-Cd batteries. On the other hand, if the voltage at pin 2 drops below half of the reference voltage (approximately 2.35V), the NE555 output at pin 3 will increase, allowing more current to flow into the battery for charging.
The circuit typically includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation and to filter out any noise that might affect the performance of the NE555 timer. A diode may also be included to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit and the battery from damage.
In summary, this automatic Ni-Cd battery charger circuit effectively monitors and controls the charging process through the use of the NE555 timer IC, ensuring safe and efficient charging of the batteries while extending their operational life.Automatic Ni-Cd Battery Charger circuit is shown in the above picture. The internal comparator of NE555 is set as 4.7V by Zener diode. If the potential of pin 6 becomes higher than this value, the output of pin 3 become lower; if the potential of pin 2 is lower than half of the reference voltage, the output voltage becomes higher,. When the voltage of the.. 🔗 External reference
The automatic Ni-Cd battery charger circuit utilizes the NE555 timer IC in a comparator configuration to regulate the charging process. The Zener diode is employed to establish a stable reference voltage of 4.7V, which is crucial for determining the charging state of the battery. This reference voltage is connected to pin 6 of the NE555, while the voltage at pin 2 is monitored to assess the battery's charge level.
During operation, if the voltage at pin 6 surpasses 4.7V, the output at pin 3 transitions to a low state, signaling a reduction in the charging current to prevent overcharging. This feature is essential for maintaining the longevity and safety of the Ni-Cd batteries. On the other hand, if the voltage at pin 2 drops below half of the reference voltage (approximately 2.35V), the NE555 output at pin 3 will increase, allowing more current to flow into the battery for charging.
The circuit typically includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation and to filter out any noise that might affect the performance of the NE555 timer. A diode may also be included to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the circuit and the battery from damage.
In summary, this automatic Ni-Cd battery charger circuit effectively monitors and controls the charging process through the use of the NE555 timer IC, ensuring safe and efficient charging of the batteries while extending their operational life.Automatic Ni-Cd Battery Charger circuit is shown in the above picture. The internal comparator of NE555 is set as 4.7V by Zener diode. If the potential of pin 6 becomes higher than this value, the output of pin 3 become lower; if the potential of pin 2 is lower than half of the reference voltage, the output voltage becomes higher,. When the voltage of the.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713