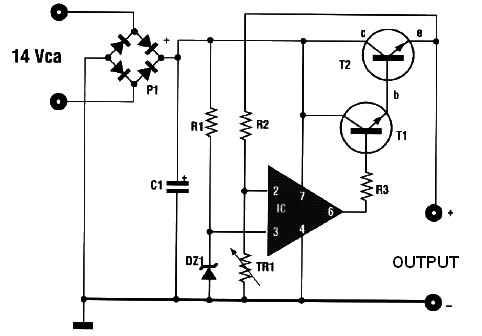
Switchless NiCd-NiMH Battery Charger
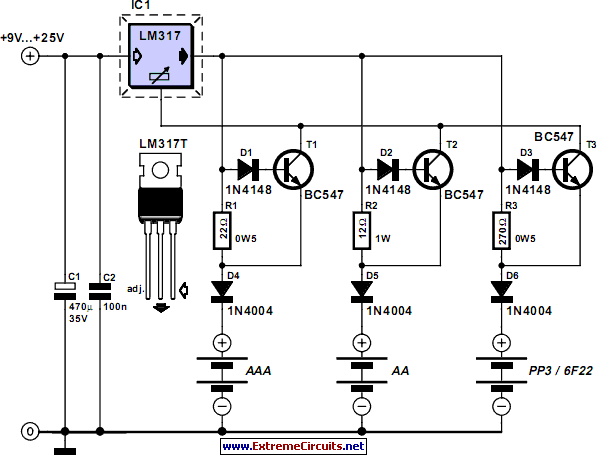
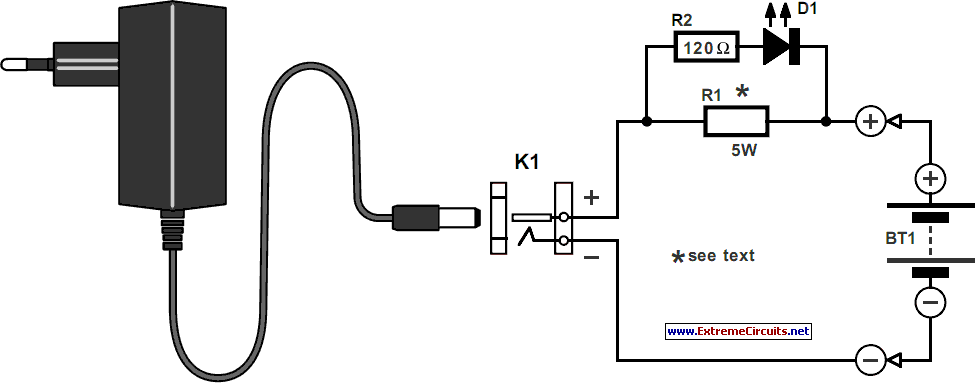
This circuit can be utilized as a replacement for the single current limiting resistor commonly found in inexpensive battery chargers. The alternative presented here will eventually...
This circuit serves as an improved solution for current limiting in battery chargers, particularly those designed for low-cost applications. Traditional battery chargers typically employ a single resistor for current limitation, which can lead to inefficiencies and heat generation. The proposed circuit enhances this design by incorporating additional components that optimize performance and reliability.
The schematic may include a combination of transistors, diodes, and operational amplifiers to create a more sophisticated current regulation mechanism. For instance, a transistor can be configured in a feedback loop to monitor the output current. When the current exceeds the preset limit, the feedback mechanism adjusts the base current of the transistor, thereby reducing the voltage drop across the load and maintaining the desired current level.
Additionally, the use of diodes can protect the circuit from reverse polarity and over-voltage conditions, further enhancing the safety and longevity of the charger. Operational amplifiers can be employed to provide precise voltage and current sensing, allowing for more accurate regulation and improved performance under varying load conditions.
Overall, this alternative circuit design not only replaces the traditional current limiting resistor but also provides a more efficient and reliable method for battery charging applications. By offering better thermal management and improved current regulation, it addresses the shortcomings of conventional designs, making it suitable for a wider range of battery types and charging scenarios.This circuit may be used to replace the single current limiting resistor often found in dirt cheap battery chargers. The alternative shown here will event.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as an improved solution for current limiting in battery chargers, particularly those designed for low-cost applications. Traditional battery chargers typically employ a single resistor for current limitation, which can lead to inefficiencies and heat generation. The proposed circuit enhances this design by incorporating additional components that optimize performance and reliability.
The schematic may include a combination of transistors, diodes, and operational amplifiers to create a more sophisticated current regulation mechanism. For instance, a transistor can be configured in a feedback loop to monitor the output current. When the current exceeds the preset limit, the feedback mechanism adjusts the base current of the transistor, thereby reducing the voltage drop across the load and maintaining the desired current level.
Additionally, the use of diodes can protect the circuit from reverse polarity and over-voltage conditions, further enhancing the safety and longevity of the charger. Operational amplifiers can be employed to provide precise voltage and current sensing, allowing for more accurate regulation and improved performance under varying load conditions.
Overall, this alternative circuit design not only replaces the traditional current limiting resistor but also provides a more efficient and reliable method for battery charging applications. By offering better thermal management and improved current regulation, it addresses the shortcomings of conventional designs, making it suitable for a wider range of battery types and charging scenarios.This circuit may be used to replace the single current limiting resistor often found in dirt cheap battery chargers. The alternative shown here will event.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713