
Automatic shutoff battery charger
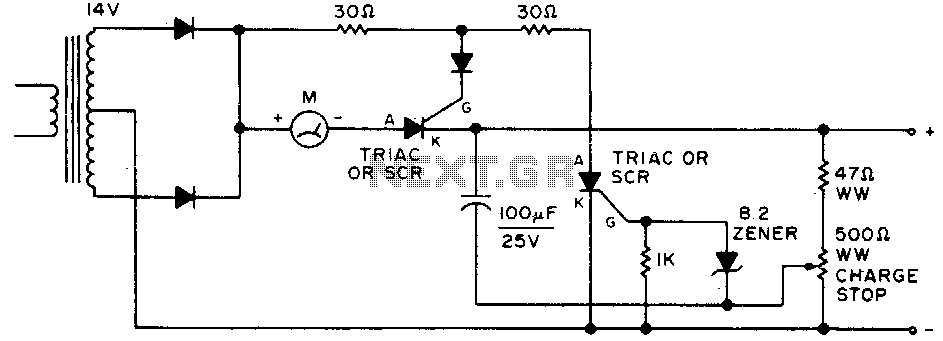
No description available.
Related Circuits
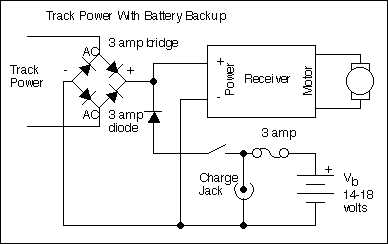
The primary motivation for utilizing battery power for trains is to eliminate the need for track cleaning and wiring. Track maintenance can pose significant challenges. Incorporating radio control into a battery-powered system enhances command control, an advantageous feature. In...
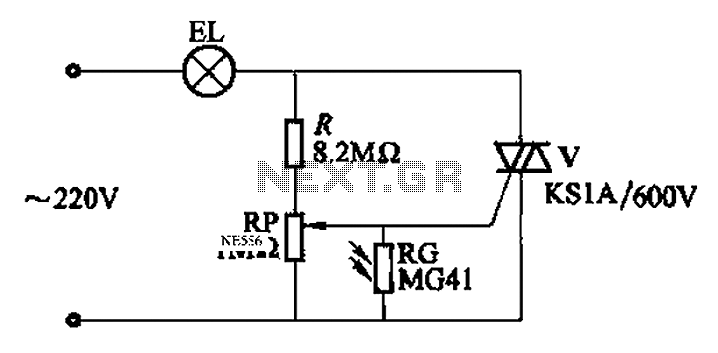
An automatic light control circuit is designed to illuminate a lamp when it is dark and to turn off the light at daybreak. The circuit, as shown in Figure 2-86, employs bidirectional thyristor tubes and features a straightforward design....
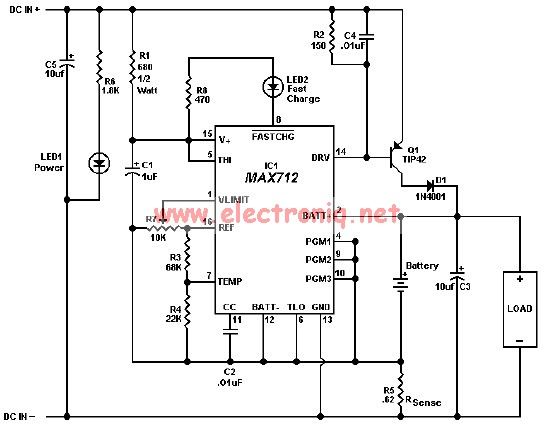
The MAX712 charger requires a power supply with an output voltage that is at least 1.5V higher than the maximum battery voltage. Charge completion is determined by a voltage-slope detecting analog-to-digital converter, a timer, and a temperature window comparator. The...
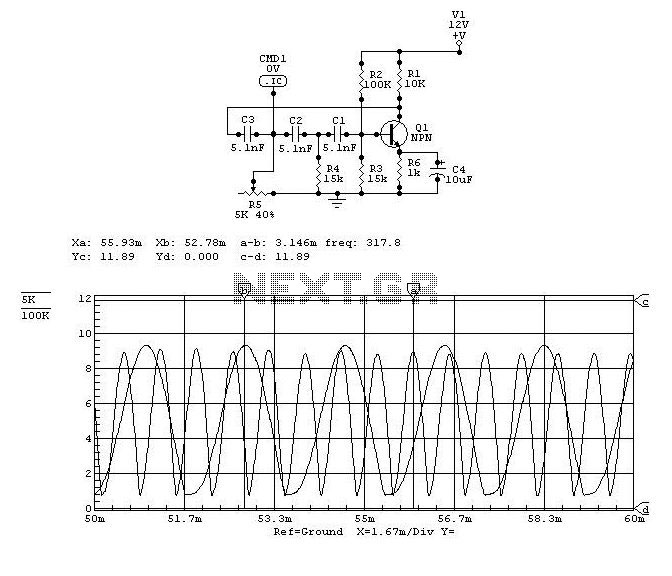
The circuit utilizes the Trigger and Threshold pins (2 and 6) to monitor maximum and minimum voltage levels. Two voltage comparator operational amplifiers within the 555 timer manage the output state, switching it on or off. The Trigger pin...
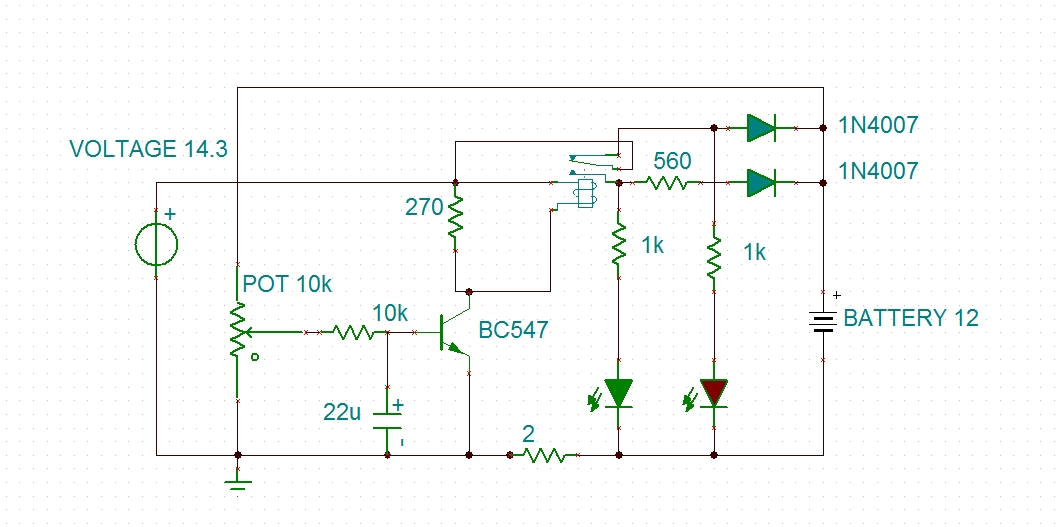
Using a transistor will not yield accurate results, and the adjustment process can become quite tedious. The circuit is technically correct; if the tripping point can be adjusted properly, it may function as intended. Vinod states that he created...
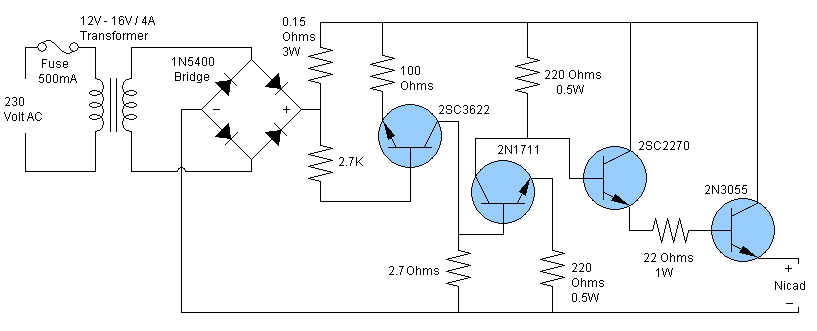
NiCd battery charger schematic and description. This NiCd battery charger circuit can charge 12V, 6V, and 9V battery packs. The NiCd battery charger circuit is designed to efficiently charge nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, specifically those with voltage ratings of 12V, 6V,...
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze traffic, and serve personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more