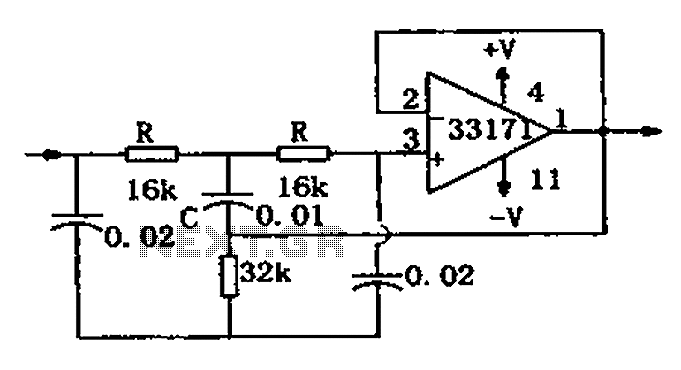
Diagram description GPS support kit
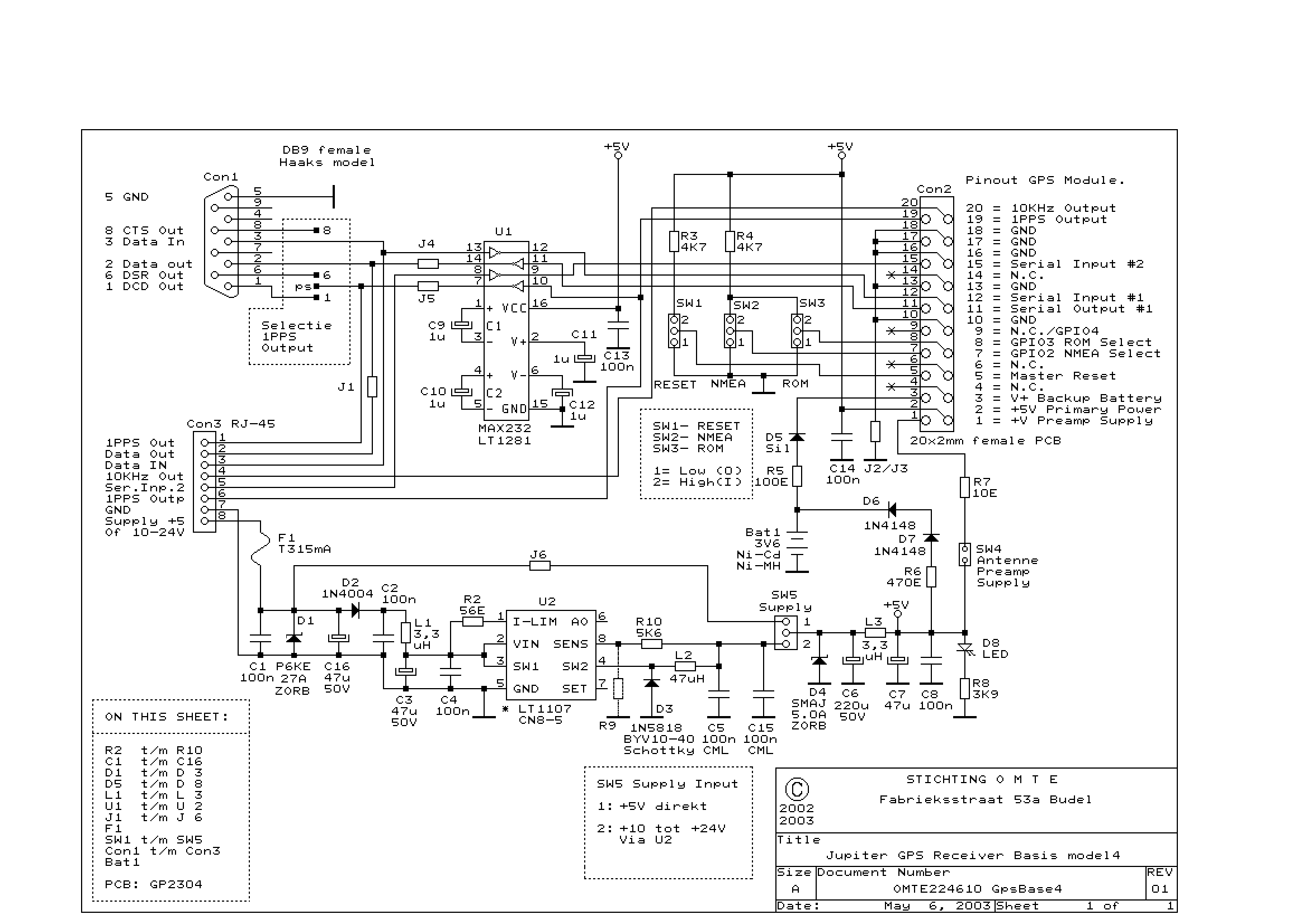
The GPS interface can be fed in 2 ways: with a stabilized 5V supply or with a 10 to 25V unregulated DC supply. In both cases, the power is fed into the RJ45 connector on point 8. Pin 7 is DC ground. The power supply current is first secured with a slow 315mA fuse (in socket). Then there is a Transzorb device to ground. This device is a short-circuit for reverse polarity voltages and for voltages above 27V. It causes the fuse to blow and in doing so, protecting the other electronics and GPS module.
The GPS interface is designed to accommodate two distinct power supply configurations, enhancing its versatility in various applications. The first configuration utilizes a stabilized 5V supply, which is ideal for direct connection to devices that require a consistent voltage level. The second option allows for a broader input range of 10 to 25V from an unregulated DC supply, making it suitable for environments where voltage levels may fluctuate.
Power is introduced to the circuit through an RJ45 connector, specifically at pin 8, ensuring a standardized connection method that is commonly used in networking equipment. The ground reference for the power supply is established at pin 7, providing a common return path for current and ensuring proper operation of the circuit.
To protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions, a slow-blow 315mA fuse is incorporated into the design. This fuse is strategically placed within a socket, allowing for easy replacement in the event of a fault. The slow-blow characteristic is crucial for applications where inrush currents may temporarily exceed the fuse rating without causing it to blow, thus maintaining circuit functionality during normal operation.
In addition to the fuse, a Transzorb device is connected to ground, serving as a protective measure against voltage transients. This device is specifically designed to clamp reverse polarity voltages and voltages that exceed 27V, effectively preventing damage to the GPS module and associated circuitry. In the event of a fault, the Transzorb facilitates a short circuit condition that triggers the fuse to blow, thereby isolating the affected section of the circuit and safeguarding the remaining components.
Overall, this design emphasizes reliability and protection, ensuring that the GPS interface can operate safely under varying power supply conditions while minimizing the risk of damage from overvoltage or reverse polarity scenarios.The GPS interface can be fed in 2 ways: with a stabilized 5V supply or with a 10 to 25V unregulated DC supply. In both cases the power is fed into the RJ45 connector on point 8. Pin 7 is DC ground. The power supply current is first secured with a slow 315mA fuse (in socket). Then there is a Transzorb device to ground. This device is a short-circuit for reverse polarity voltages and for voltages above 27V. It causes the fuse to blow and in doing so, protecting the other electronics and GPS module. 🔗 External reference
The GPS interface is designed to accommodate two distinct power supply configurations, enhancing its versatility in various applications. The first configuration utilizes a stabilized 5V supply, which is ideal for direct connection to devices that require a consistent voltage level. The second option allows for a broader input range of 10 to 25V from an unregulated DC supply, making it suitable for environments where voltage levels may fluctuate.
Power is introduced to the circuit through an RJ45 connector, specifically at pin 8, ensuring a standardized connection method that is commonly used in networking equipment. The ground reference for the power supply is established at pin 7, providing a common return path for current and ensuring proper operation of the circuit.
To protect the circuit from overcurrent conditions, a slow-blow 315mA fuse is incorporated into the design. This fuse is strategically placed within a socket, allowing for easy replacement in the event of a fault. The slow-blow characteristic is crucial for applications where inrush currents may temporarily exceed the fuse rating without causing it to blow, thus maintaining circuit functionality during normal operation.
In addition to the fuse, a Transzorb device is connected to ground, serving as a protective measure against voltage transients. This device is specifically designed to clamp reverse polarity voltages and voltages that exceed 27V, effectively preventing damage to the GPS module and associated circuitry. In the event of a fault, the Transzorb facilitates a short circuit condition that triggers the fuse to blow, thereby isolating the affected section of the circuit and safeguarding the remaining components.
Overall, this design emphasizes reliability and protection, ensuring that the GPS interface can operate safely under varying power supply conditions while minimizing the risk of damage from overvoltage or reverse polarity scenarios.The GPS interface can be fed in 2 ways: with a stabilized 5V supply or with a 10 to 25V unregulated DC supply. In both cases the power is fed into the RJ45 connector on point 8. Pin 7 is DC ground. The power supply current is first secured with a slow 315mA fuse (in socket). Then there is a Transzorb device to ground. This device is a short-circuit for reverse polarity voltages and for voltages above 27V. It causes the fuse to blow and in doing so, protecting the other electronics and GPS module. 🔗 External reference

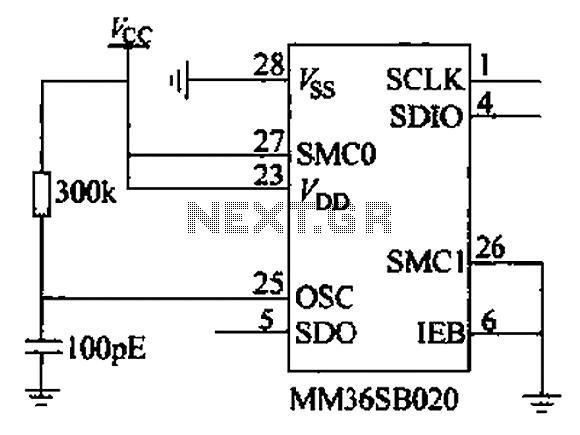
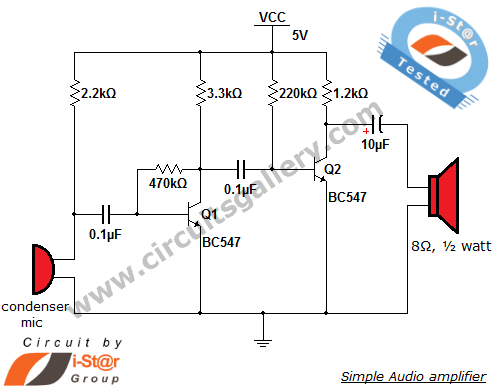
%2BCircuit%2Bdiagram%2Busing%2BCD4047%2Band%2BIRFZ44%2Bpower%2BMOSFET.png)