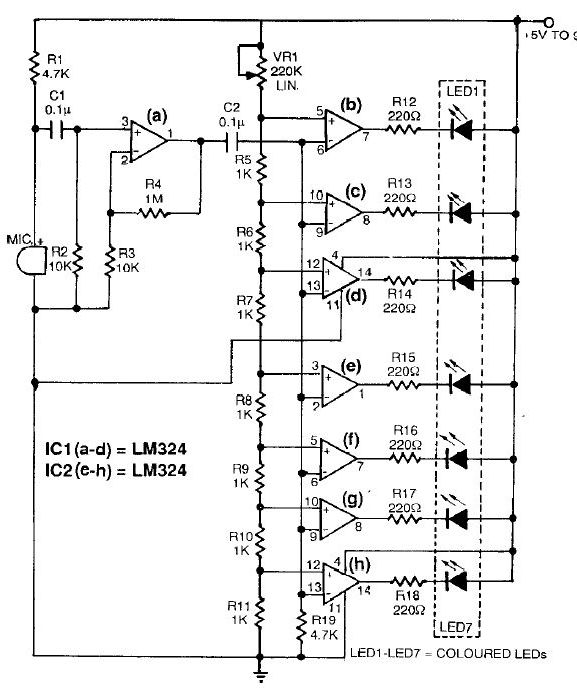
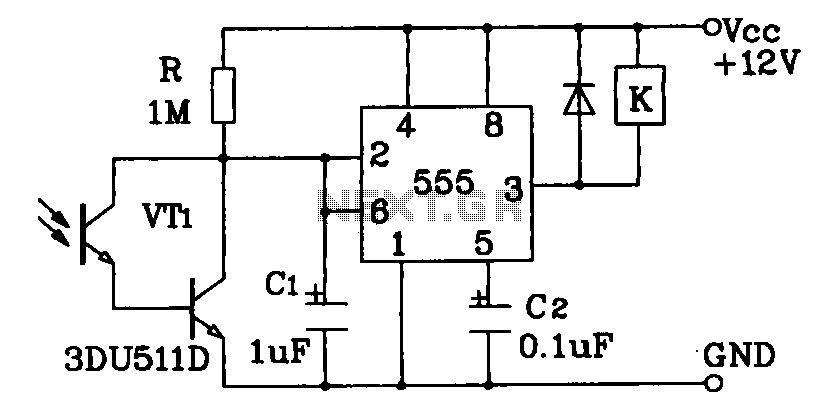
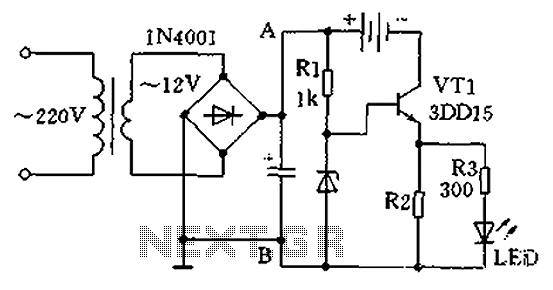
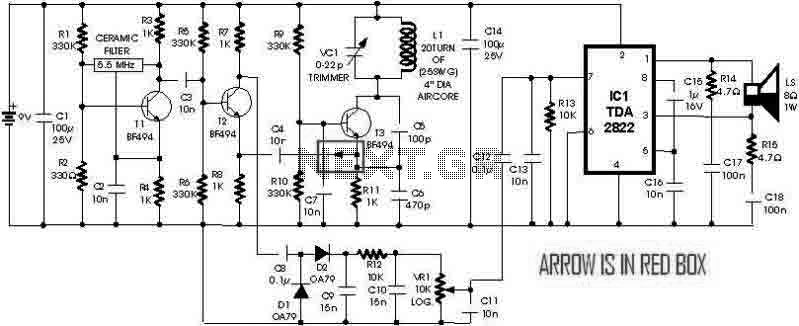
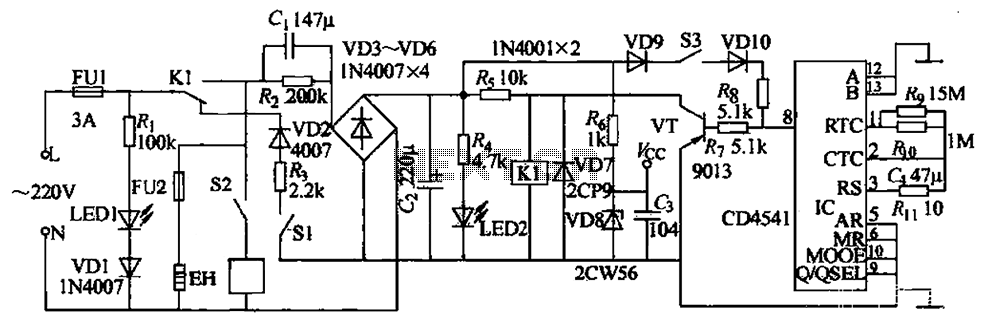
Optionally extended charging pulse count switch circuit diagram

The count switching circuit consists of an electronic switch and a pulse delay circuit for control.
The count switching circuit is designed to manage the switching of signals in a controlled manner. The electronic switch serves as the primary component for toggling the circuit states, allowing for the connection or disconnection of various circuit paths based on the control signals received. This switch can be implemented using a variety of technologies, including transistors, MOSFETs, or relays, depending on the required specifications such as load current, voltage, and switching speed.
The pulse delay circuit is crucial for ensuring that the switching occurs at the appropriate time. It introduces a predefined delay in the control signal, allowing for synchronization between different components in the system. This delay can be achieved using capacitors and resistors in an RC timing configuration or through more complex digital delay circuits, depending on the precision and flexibility needed in the application.
In operation, when a control signal is generated, it first passes through the pulse delay circuit, which modifies the timing of the signal before it reaches the electronic switch. This ensures that the switch only activates after the specified delay, preventing premature switching that could lead to circuit malfunction or damage. The overall design of the count switching circuit allows for efficient control of multiple outputs or stages in electronic systems, making it suitable for applications such as digital counters, timers, and automated control systems. As shown, the count switching circuit comprises an electronic switch and a pulse delay circuit control.
The count switching circuit is designed to manage the switching of signals in a controlled manner. The electronic switch serves as the primary component for toggling the circuit states, allowing for the connection or disconnection of various circuit paths based on the control signals received. This switch can be implemented using a variety of technologies, including transistors, MOSFETs, or relays, depending on the required specifications such as load current, voltage, and switching speed.
The pulse delay circuit is crucial for ensuring that the switching occurs at the appropriate time. It introduces a predefined delay in the control signal, allowing for synchronization between different components in the system. This delay can be achieved using capacitors and resistors in an RC timing configuration or through more complex digital delay circuits, depending on the precision and flexibility needed in the application.
In operation, when a control signal is generated, it first passes through the pulse delay circuit, which modifies the timing of the signal before it reaches the electronic switch. This ensures that the switch only activates after the specified delay, preventing premature switching that could lead to circuit malfunction or damage. The overall design of the count switching circuit allows for efficient control of multiple outputs or stages in electronic systems, making it suitable for applications such as digital counters, timers, and automated control systems. As shown, the count switching circuit comprises an electronic switch and a pulse delay circuit control.