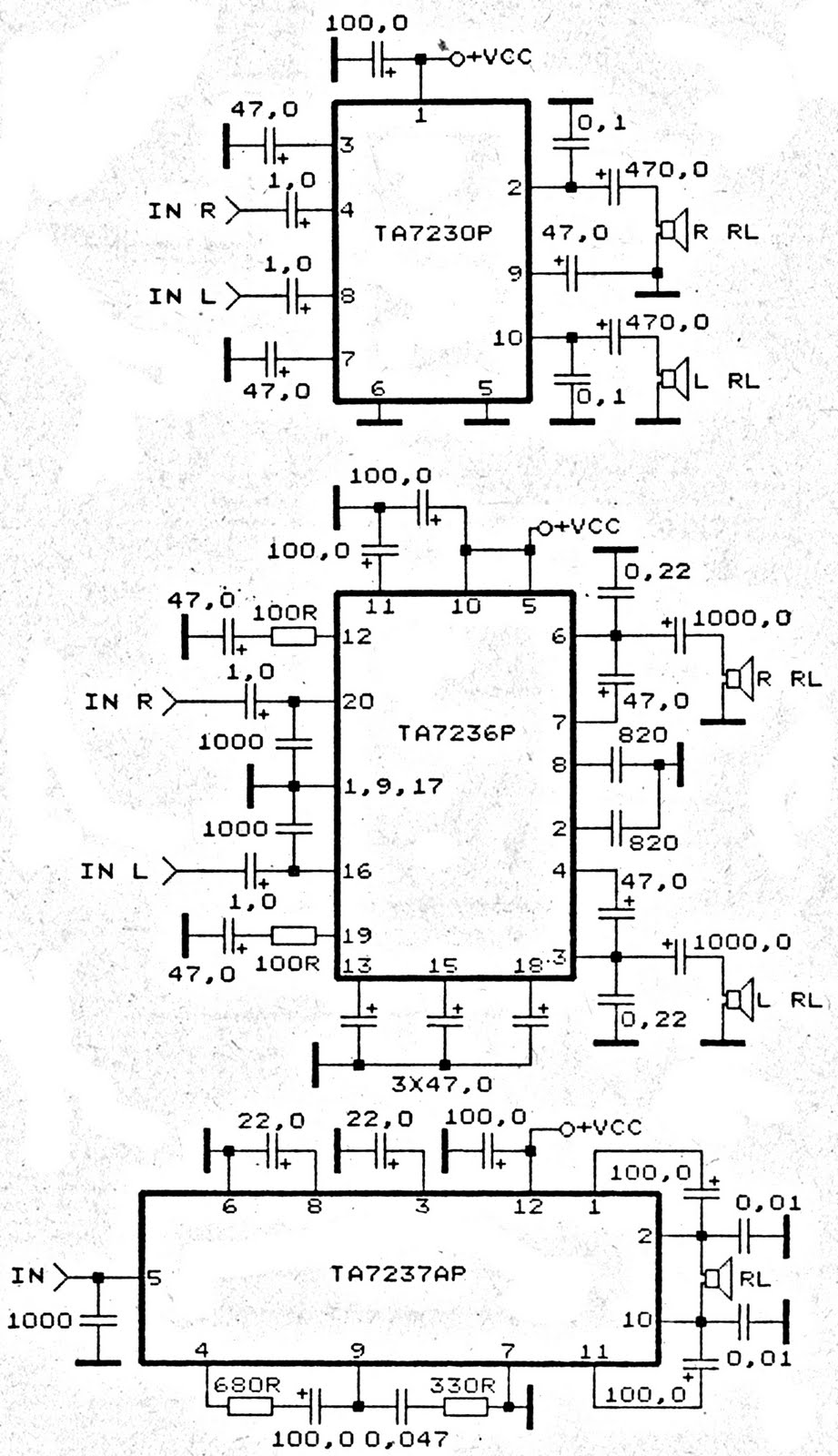
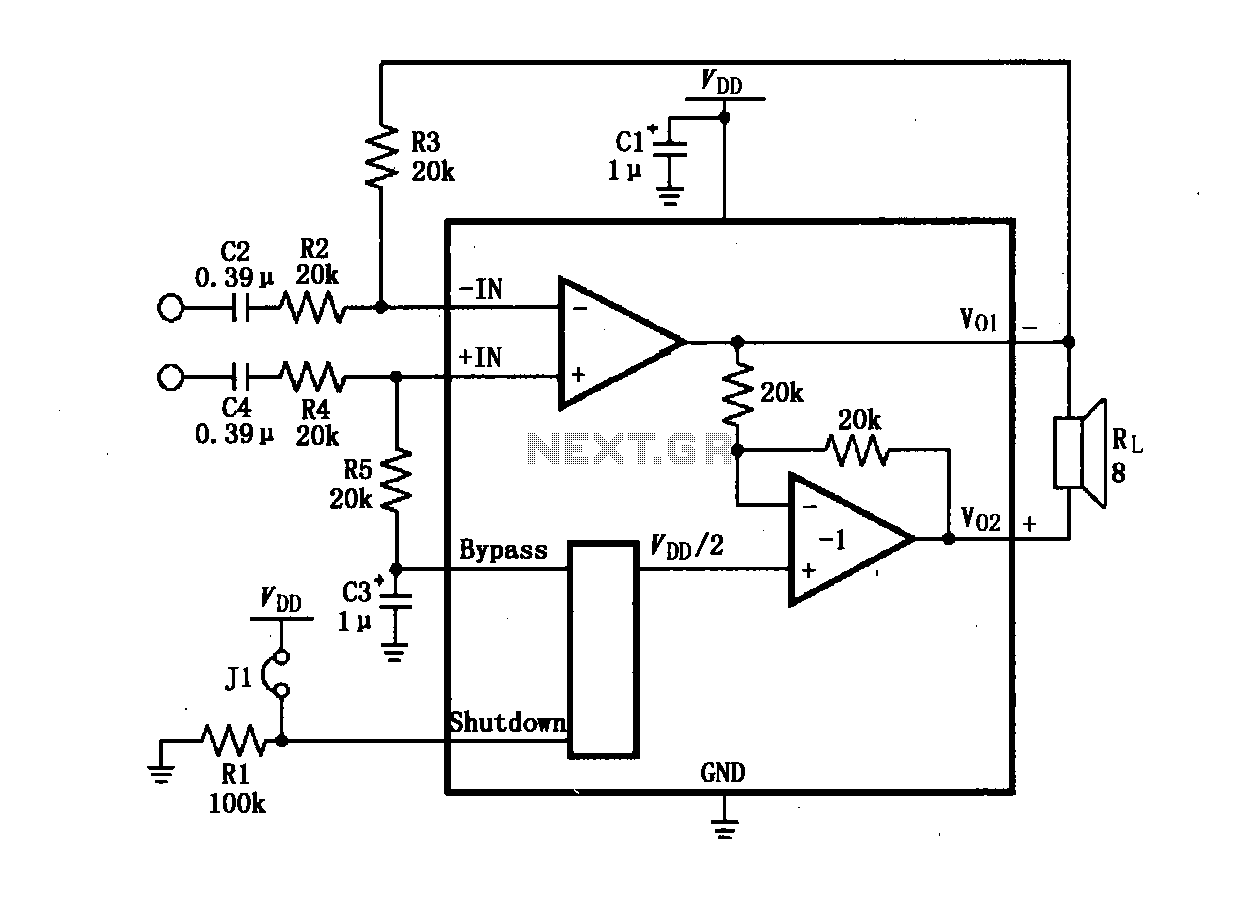
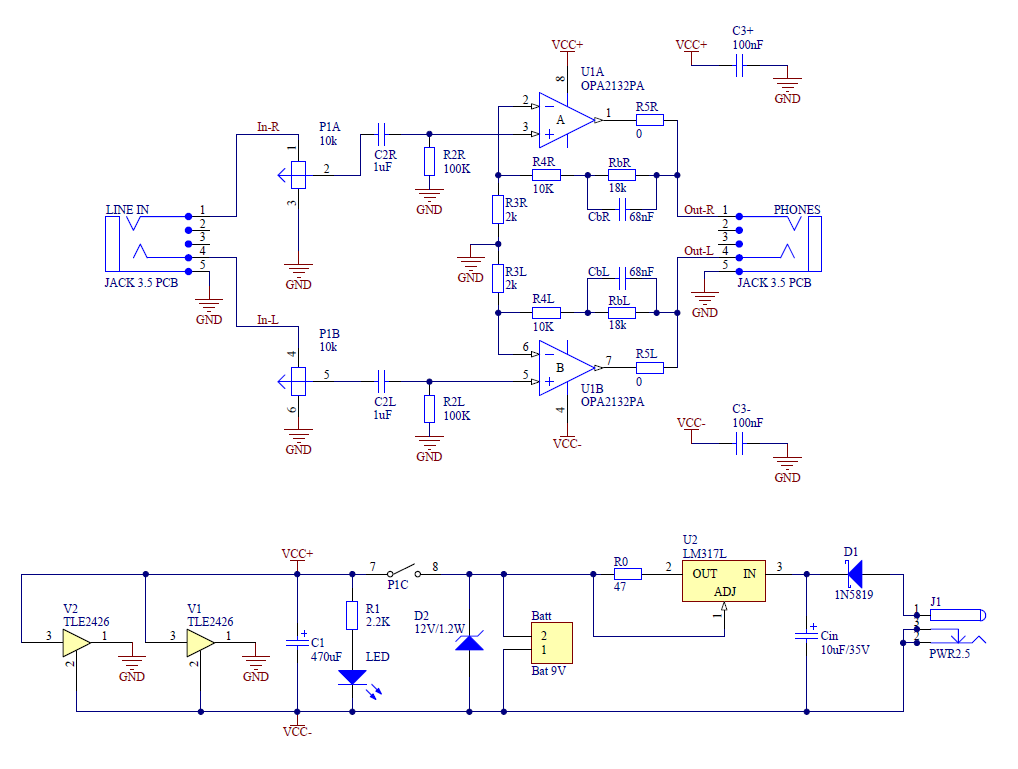
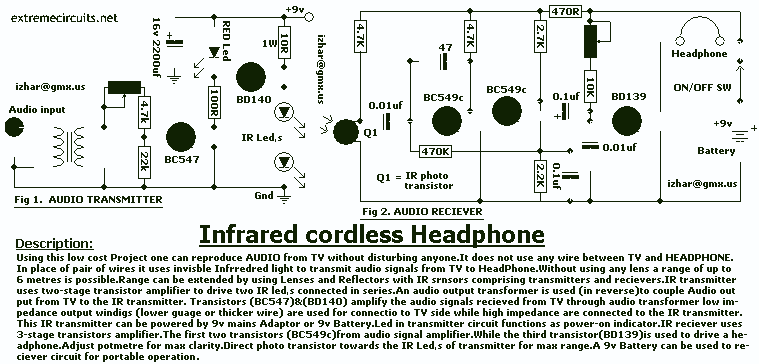
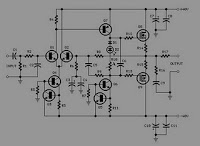
Balanced Microphone Amplifier
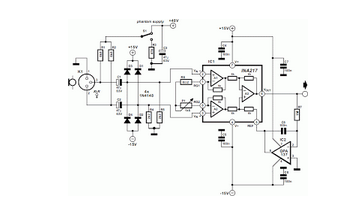
A design was published for a stereo microphone preamplifier featuring balanced inputs and a phantom power supply. The core of this circuit utilizes a specialized analog component.
The stereo microphone preamplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals captured by microphones while maintaining high fidelity and low noise levels. The balanced inputs are crucial for minimizing electromagnetic interference, which is particularly important in professional audio applications. This is achieved through the use of differential signaling, where two conductors carry the audio signal in opposite phases, allowing for effective noise cancellation.
The phantom power supply is an essential feature that provides the necessary voltage (typically +48V) to condenser microphones, enabling them to function correctly. This power is delivered through the same XLR cables used for the audio signal, simplifying the setup and reducing cable clutter.
The heart of the preamplifier circuit is a specialized analog component, such as an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured for low noise and high gain. This op-amp is selected for its excellent frequency response and low total harmonic distortion (THD), which is critical for maintaining audio quality. Additional components, including resistors and capacitors, are carefully chosen to set the gain levels and filter out unwanted frequencies, ensuring that only the desired audio signals are amplified.
Furthermore, the circuit design may incorporate features such as a high-pass filter to eliminate low-frequency noise and a gain control mechanism to adjust the output level according to the specific requirements of the audio source. The overall layout is optimized for performance, with attention given to the placement of components to minimize signal degradation and interference.
In summary, this stereo microphone preamplifier design is a sophisticated solution for professional audio applications, combining balanced inputs, phantom power supply, and high-quality analog circuitry to deliver superior audio performance.We published a design for a stereo microphone preamplifier with balanced inputs and a phantom power supply. The heart of this circuit was a special Analog.. 🔗 External reference
The stereo microphone preamplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals captured by microphones while maintaining high fidelity and low noise levels. The balanced inputs are crucial for minimizing electromagnetic interference, which is particularly important in professional audio applications. This is achieved through the use of differential signaling, where two conductors carry the audio signal in opposite phases, allowing for effective noise cancellation.
The phantom power supply is an essential feature that provides the necessary voltage (typically +48V) to condenser microphones, enabling them to function correctly. This power is delivered through the same XLR cables used for the audio signal, simplifying the setup and reducing cable clutter.
The heart of the preamplifier circuit is a specialized analog component, such as an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured for low noise and high gain. This op-amp is selected for its excellent frequency response and low total harmonic distortion (THD), which is critical for maintaining audio quality. Additional components, including resistors and capacitors, are carefully chosen to set the gain levels and filter out unwanted frequencies, ensuring that only the desired audio signals are amplified.
Furthermore, the circuit design may incorporate features such as a high-pass filter to eliminate low-frequency noise and a gain control mechanism to adjust the output level according to the specific requirements of the audio source. The overall layout is optimized for performance, with attention given to the placement of components to minimize signal degradation and interference.
In summary, this stereo microphone preamplifier design is a sophisticated solution for professional audio applications, combining balanced inputs, phantom power supply, and high-quality analog circuitry to deliver superior audio performance.We published a design for a stereo microphone preamplifier with balanced inputs and a phantom power supply. The heart of this circuit was a special Analog.. 🔗 External reference