basic circuit diagram for pc to microcontroller communication
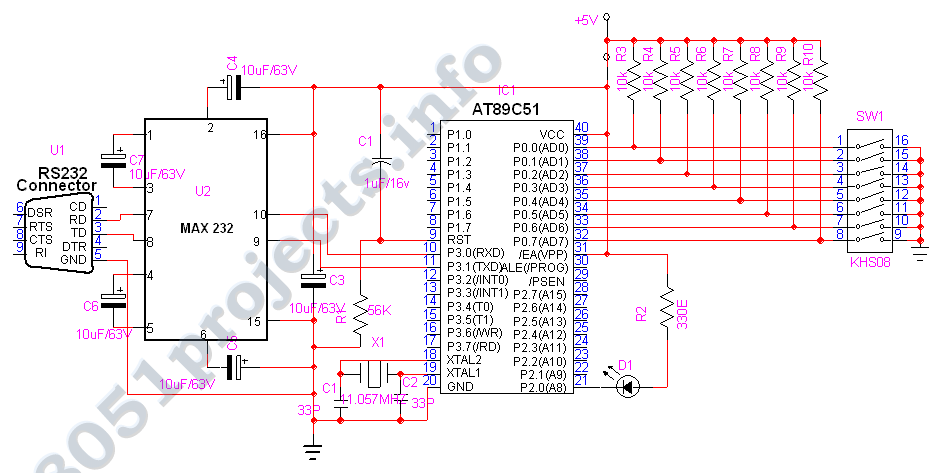
The 8051 microcontroller features a transmit channel and a receive channel for serial communication. The transmit data pin (TXD) is designated as P3.1, while the receive data pin (RXD) is located at P3.0. The serial signals on these pins operate at TTL signal levels and require amplification and inversion through a suitable converter, such as the MAX232, to meet RS232 standards. All operational modes are managed via the Serial Control register (SCON), which includes bits defined as SM0, SM1, SM2, REN, TB8, RB8, TI, and RI, arranged from most significant bit (MSB) to least significant bit (LSB). Timer operations are governed by the Timer Mode register (TMOD) and the Timer Control register (TCON).
The 8051 microcontroller's serial communication capabilities are essential for interfacing with various peripherals and devices. The TXD and RXD pins enable full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous data transmission and reception. The TTL signal levels on these pins are suitable for direct connection to other TTL-compatible devices. However, for communication with RS232 devices, which operate at higher voltage levels, the MAX232 level shifter is employed. This IC converts the TTL signals to RS232 levels and vice versa, ensuring compatibility with standard serial communication protocols.
The Serial Control register (SCON) plays a critical role in configuring the serial communication modes. The bits SM0 and SM1 determine the mode of operation, which can be set to either 8-bit variable baud rate, 8-bit fixed baud rate, or 9-bit communication. The REN bit enables the reception of data, while TB8 and RB8 are used for 9-bit data transmission and reception, respectively. The TI and RI flags indicate the status of transmission and reception, allowing the microcontroller to manage data flow effectively.
In addition to serial communication, the 8051 microcontroller utilizes timer registers (TMOD and TCON) to control timing operations. The TMOD register defines the mode of operation for the timers, while the TCON register manages the timer's start, stop, and overflow conditions. This combination of serial communication and timer functionality allows the 8051 to perform complex tasks in embedded systems, making it a versatile choice for various applications.8051 provides a transmit channel and a receive channel of serial communication. The transmit data pin (TXD) is specified at P3. 1, and the receive data pin (RXD) is at P3. 0. The serial signals provided on these pins are TTL signal levels and must be boosted and inverted through a suitable converter(MAX232) to comply with RS232 standard. All modes a re controlled through SCON, the Serial CONtrol register. The SCON bits are defined as SM0, SM1, SM2, REN, TB8, RB8, TI, RI from MSB to LSB. The timers are controlled using TMOD, the Timer MODe register, and TCON, the Timer CONtrol register. 🔗 External reference
The 8051 microcontroller's serial communication capabilities are essential for interfacing with various peripherals and devices. The TXD and RXD pins enable full-duplex communication, allowing simultaneous data transmission and reception. The TTL signal levels on these pins are suitable for direct connection to other TTL-compatible devices. However, for communication with RS232 devices, which operate at higher voltage levels, the MAX232 level shifter is employed. This IC converts the TTL signals to RS232 levels and vice versa, ensuring compatibility with standard serial communication protocols.
The Serial Control register (SCON) plays a critical role in configuring the serial communication modes. The bits SM0 and SM1 determine the mode of operation, which can be set to either 8-bit variable baud rate, 8-bit fixed baud rate, or 9-bit communication. The REN bit enables the reception of data, while TB8 and RB8 are used for 9-bit data transmission and reception, respectively. The TI and RI flags indicate the status of transmission and reception, allowing the microcontroller to manage data flow effectively.
In addition to serial communication, the 8051 microcontroller utilizes timer registers (TMOD and TCON) to control timing operations. The TMOD register defines the mode of operation for the timers, while the TCON register manages the timer's start, stop, and overflow conditions. This combination of serial communication and timer functionality allows the 8051 to perform complex tasks in embedded systems, making it a versatile choice for various applications.8051 provides a transmit channel and a receive channel of serial communication. The transmit data pin (TXD) is specified at P3. 1, and the receive data pin (RXD) is at P3. 0. The serial signals provided on these pins are TTL signal levels and must be boosted and inverted through a suitable converter(MAX232) to comply with RS232 standard. All modes a re controlled through SCON, the Serial CONtrol register. The SCON bits are defined as SM0, SM1, SM2, REN, TB8, RB8, TI, RI from MSB to LSB. The timers are controlled using TMOD, the Timer MODe register, and TCON, the Timer CONtrol register. 🔗 External reference