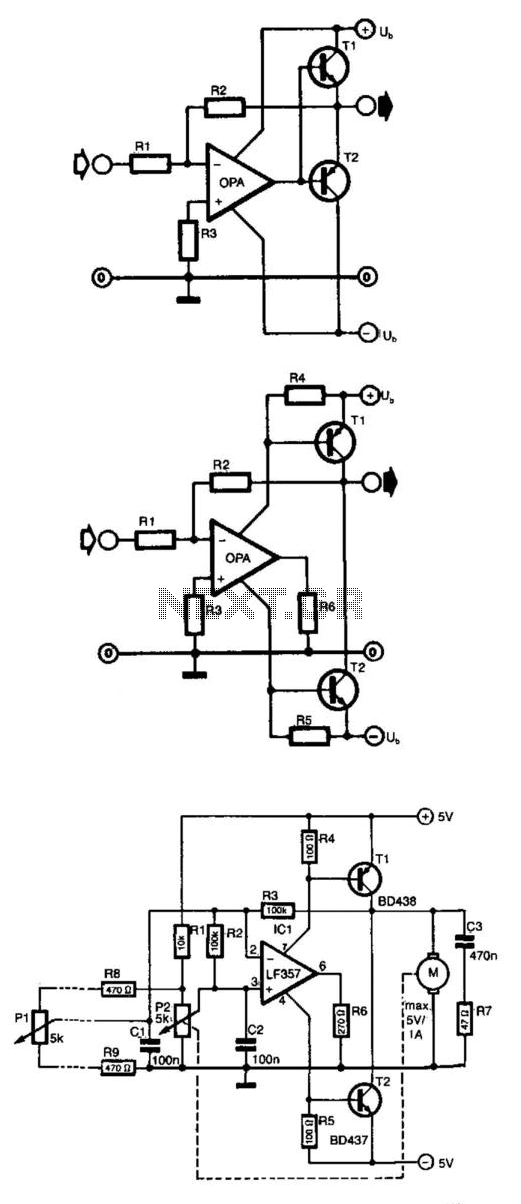
Basic Dual Polarity Power Supply
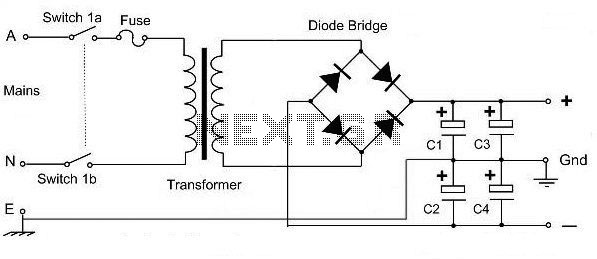
This is a basic dual polarity power supply circuit diagram. It requires the following components: a center-tapped transformer, four diode rectifiers (or one diode bridge), and four electrolytic capacitors. The value of each component is essential for the circuit's performance.
The dual polarity power supply circuit is designed to provide both positive and negative voltage outputs from a single transformer. The center-tapped transformer is the key component, featuring a primary winding connected to the AC mains and two equal secondary windings that produce two outputs, typically referred to as the positive and negative voltages.
The circuit utilizes four diodes arranged in a full-wave rectifier configuration. This setup can also be replaced by a single diode bridge rectifier, which simplifies the design by integrating the four diodes into one component. The rectification process converts the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC), producing both positive and negative voltages relative to the center tap.
Following the rectification, four electrolytic capacitors are employed to smooth the output voltage. These capacitors store charge and help reduce voltage ripple, ensuring a more stable DC output. The values of the capacitors should be selected based on the load requirements and the desired level of ripple voltage. Typically, larger capacitance values lead to lower ripple, but they also affect the response time of the power supply under load changes.
Overall, this dual polarity power supply circuit is fundamental in various electronic applications, including operational amplifiers, analog signal processing, and other devices that require dual voltage supplies. Proper selection of each component, including the transformer ratings, diode specifications, and capacitor values, is critical to the successful implementation of this circuit.This is a very basic dual polarity power supply circuit diagram. It just need the following components: - A Center Tapped Transformer - Diode rectifier 4 units (or diode bridge 1 unit) - Electrolityc capacitor 4 units The value of each comp.. 🔗 External reference
The dual polarity power supply circuit is designed to provide both positive and negative voltage outputs from a single transformer. The center-tapped transformer is the key component, featuring a primary winding connected to the AC mains and two equal secondary windings that produce two outputs, typically referred to as the positive and negative voltages.
The circuit utilizes four diodes arranged in a full-wave rectifier configuration. This setup can also be replaced by a single diode bridge rectifier, which simplifies the design by integrating the four diodes into one component. The rectification process converts the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC), producing both positive and negative voltages relative to the center tap.
Following the rectification, four electrolytic capacitors are employed to smooth the output voltage. These capacitors store charge and help reduce voltage ripple, ensuring a more stable DC output. The values of the capacitors should be selected based on the load requirements and the desired level of ripple voltage. Typically, larger capacitance values lead to lower ripple, but they also affect the response time of the power supply under load changes.
Overall, this dual polarity power supply circuit is fundamental in various electronic applications, including operational amplifiers, analog signal processing, and other devices that require dual voltage supplies. Proper selection of each component, including the transformer ratings, diode specifications, and capacitor values, is critical to the successful implementation of this circuit.This is a very basic dual polarity power supply circuit diagram. It just need the following components: - A Center Tapped Transformer - Diode rectifier 4 units (or diode bridge 1 unit) - Electrolityc capacitor 4 units The value of each comp.. 🔗 External reference