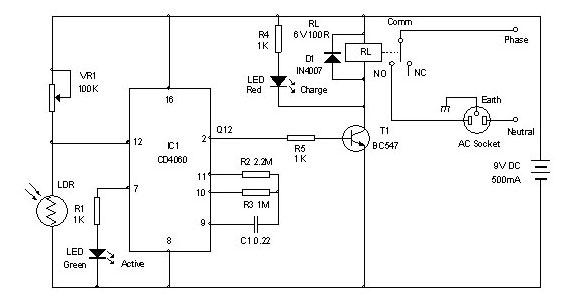
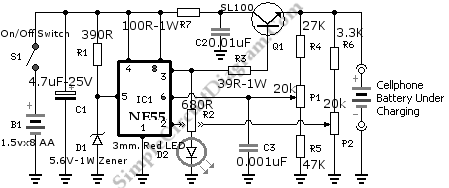
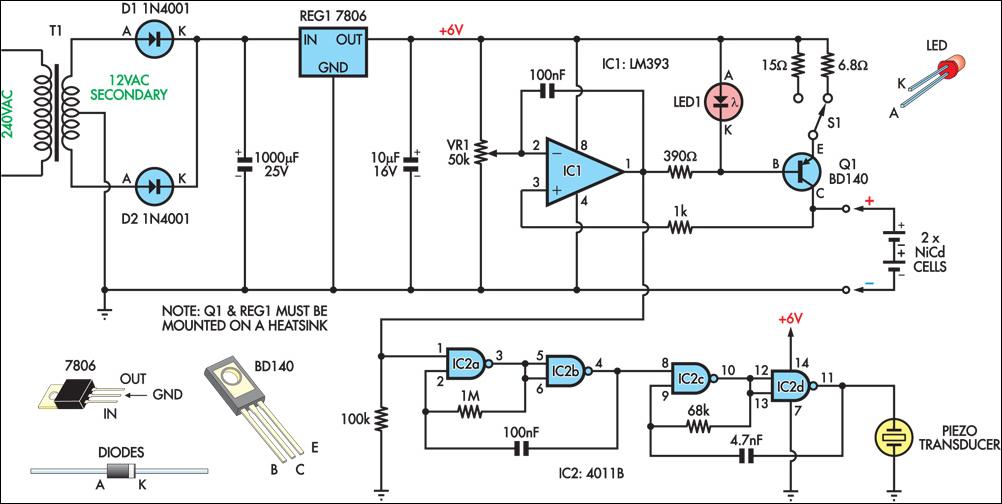
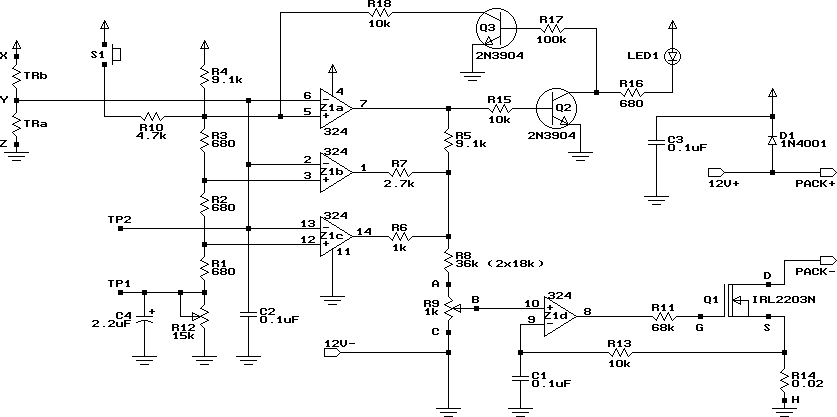
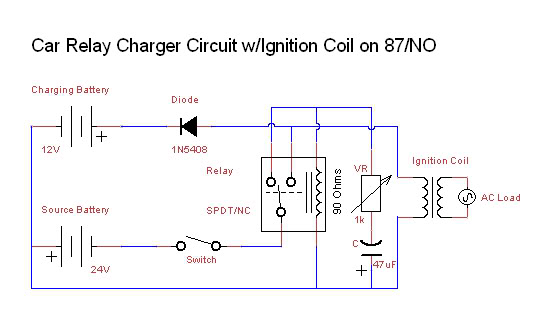
Battery charger
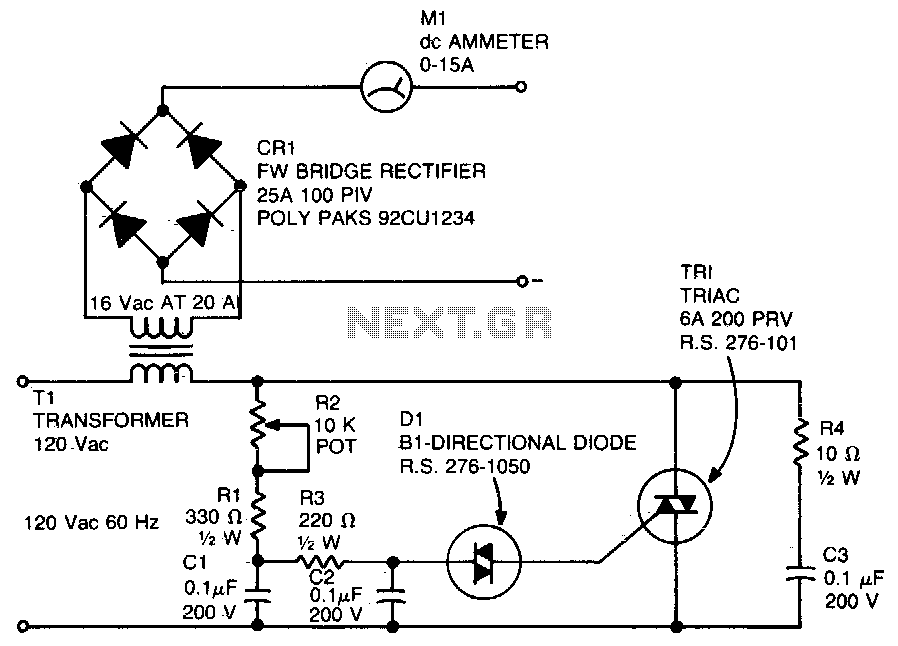
A diac is utilized in the gate circuit to enable operation for the signal applied to the gate. R1 sets a threshold level for triggering the triac. C3 and R4 are chosen to restrict the maximum charging current, forming a transient suppression network. Additionally, R1, in conjunction with R2, R3, C1, and C2, creates a phase-shift network.
The described circuit employs a diac in conjunction with a triac to control power delivery in AC applications. The diac functions as a switching device that allows current to flow only after a specific voltage threshold is reached, effectively controlling the gate of the triac. R1 is crucial as it determines the firing threshold of the triac; once the voltage across R1 exceeds this threshold, the diac conducts, triggering the triac and allowing current to flow through the load.
C3 and R4 are integral components of the transient suppression network, designed to protect the circuit from voltage spikes that may occur during operation. C3 acts as a filter capacitor, smoothing out any rapid changes in voltage and preventing unwanted triggering of the triac. R4 serves to limit the maximum charging current to C3, ensuring that the capacitor charges within safe limits and preventing damage to the circuit.
The phase-shift network composed of R1, R2, R3, C1, and C2 is essential for controlling the timing of the triac's firing. This network introduces a phase shift in the input signal, allowing for precise control over the power delivered to the load. The values of R2, R3, C1, and C2 can be adjusted to modify the phase angle, thus influencing the timing of when the triac is triggered during each AC cycle.
Overall, this circuit configuration is commonly found in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and other applications requiring phase control of AC loads. The combination of the diac and triac, along with the supporting components, enables efficient and reliable control of power in various electronic applications.A diac is used in the gate circuit to provide work for the signal being applied to the gate. R1 a threshold level for firing the triac. C3 and R4 is selected to limit the maximum charging cur-provide a transient suppression network Rl, rent at fullTotation of R2. R2, R3, Cl, and C2 provide a phase-shift net-. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a diac in conjunction with a triac to control power delivery in AC applications. The diac functions as a switching device that allows current to flow only after a specific voltage threshold is reached, effectively controlling the gate of the triac. R1 is crucial as it determines the firing threshold of the triac; once the voltage across R1 exceeds this threshold, the diac conducts, triggering the triac and allowing current to flow through the load.
C3 and R4 are integral components of the transient suppression network, designed to protect the circuit from voltage spikes that may occur during operation. C3 acts as a filter capacitor, smoothing out any rapid changes in voltage and preventing unwanted triggering of the triac. R4 serves to limit the maximum charging current to C3, ensuring that the capacitor charges within safe limits and preventing damage to the circuit.
The phase-shift network composed of R1, R2, R3, C1, and C2 is essential for controlling the timing of the triac's firing. This network introduces a phase shift in the input signal, allowing for precise control over the power delivered to the load. The values of R2, R3, C1, and C2 can be adjusted to modify the phase angle, thus influencing the timing of when the triac is triggered during each AC cycle.
Overall, this circuit configuration is commonly found in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and other applications requiring phase control of AC loads. The combination of the diac and triac, along with the supporting components, enables efficient and reliable control of power in various electronic applications.A diac is used in the gate circuit to provide work for the signal being applied to the gate. R1 a threshold level for firing the triac. C3 and R4 is selected to limit the maximum charging cur-provide a transient suppression network Rl, rent at fullTotation of R2. R2, R3, Cl, and C2 provide a phase-shift net-. 🔗 External reference