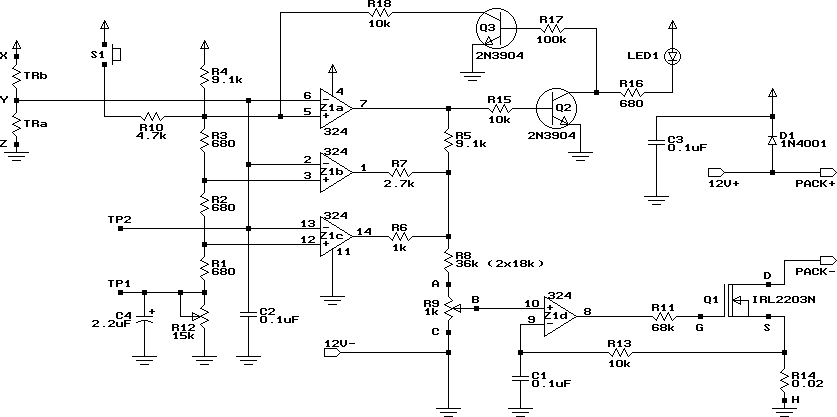
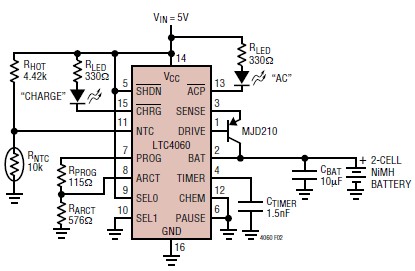
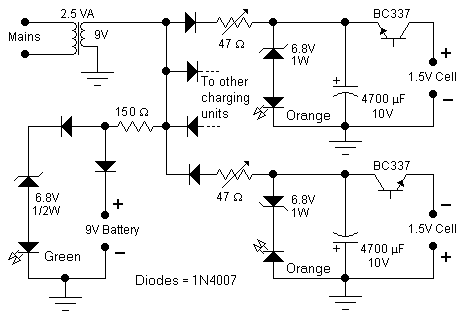
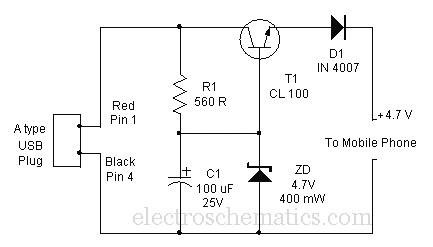
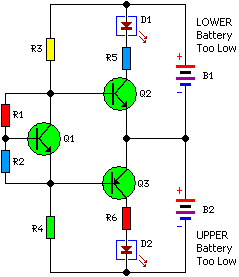
Battery Charger For Sla Nicd Nimh And Li-ion Batteries
FM Radio has a long history, starting from its development in 1933. Today, FM Radio is an integral part of almost all mobile phones. In a typical mobile phone, the earphone cable acts as the antenna for FM reception, where the antenna size is somewhat flexible. To enable FM Radio usage without the earphone, the antenna must be integrated within the phone. However, this integration presents challenges due to space constraints affecting antenna design. Reducing the antenna size leads to increased loss in the system, which negatively impacts receiver performance, particularly receiver sensitivity. A Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) can address this issue by improving receiver sensitivity. Nonetheless, designing an LNA for this purpose involves several challenges. The very small size of the antenna results in a high impedance, necessitating that the LNA be matched to this high impedance while also providing a low noise figure. Additionally, the use of the LNA in handheld devices requires low current consumption, a power-off function, and high linearity to accommodate the presence of cellular bands. Other specifications for the LNA include support for the worldwide FM band (76-108 MHz) and ESD robustness of 4 kV (HBM) at the RF-in port. Infineon offers its LNA solution, BGB707L7ESD, which meets all the aforementioned performance criteria in a compact, leadless package (TSLP-7-1) measuring 2.0 x 1.3 x 0.4 mm. It features integrated active biasing that ensures consistent operation across varying temperatures and process variations. This LNA is suitable for a wide range of mobile devices, including mobile phones, PDAs, and portable FM Radio MP3 players.
The FM Radio circuit design incorporates various components to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The core of the circuit is the integrated Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), which significantly enhances signal sensitivity, allowing the receiver to capture weak FM signals effectively. The LNA must be carefully matched to the high impedance of the integrated antenna to minimize signal loss and maintain a low noise figure, which is crucial for clear audio output.
In addition to the LNA, the circuit may include a band-pass filter to eliminate unwanted signals outside the FM band, ensuring that only the desired frequencies (76-108 MHz) are processed. This filter helps to improve the overall selectivity of the receiver, allowing it to distinguish between closely spaced stations.
Power management is another critical aspect of the design, particularly in handheld devices where battery life is a concern. The LNA's low current consumption feature is essential for extending operational time. Furthermore, the integrated active biasing within the BGB707L7ESD LNA stabilizes performance over a range of temperatures and manufacturing variations, which is vital for maintaining consistent audio quality.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is also a key consideration, as mobile devices are often exposed to various environmental factors. The BGB707L7ESD's robustness of 4 kV (HBM) at the RF-in port ensures that the device can withstand accidental discharges, thereby protecting the sensitive components from damage.
Overall, the integration of the LNA and additional components into a compact form factor allows for the effective implementation of FM Radio functionality in modern mobile devices, ensuring high-quality audio reception while addressing the constraints of size and power efficiency. This design approach not only enhances user experience but also aligns with the ongoing trend of miniaturization in electronic devices.FM Radio has a long history to its credit starting from its development in 1933. Today, FM Radio is an integral part of almost all mobile phones. In a common mobile phone, the cable to the earphone serves as the Antenna for FM reception, wherein the Antenna size is a bit relaxed. To be able to use FM Radio also without the earphone, the Antenna ha s to be integrated inside the phone. But in this case, the space constraint poses a challenge on the Antenna design. Shrinking the size of the Antenna introduces a high loss in the system which deteriorates the receiver performance, namely the receiver sensitivity. Using a Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), CAN solve this problem by enhancing the receiver sensitivity. However, there are a few difficulties in the design of the LNA for this purpose. Due to the very small size, the Antenna impedance is very high and thus the LNA has to be matched to this high impedance and in addition offer a low noise figure.
Using it in a hand held device also demands low current consumption, power-off function and high linearity due to the co-existence of cellular bands. Other requirements on the LNA include worldwide FM band support (76- 108 MHz) and ESD robustness of 4 kV (HBM) at the RF-in port.
Infineon offers its LNA solution BGB707L7ESD which fulfills all the aforementioned performance criteria in a very small and leadless package TSLP-7-1 (2. 0 x 1. 3 x 0. 4 mm). It comes with an integrated active biasing which enables consistent operation with varying temperatures and process variations.
It finds its application in all kinds of mobile devices like mobile phones, PDAs, portable FM Radio MP3 players etc. 🔗 External reference
The FM Radio circuit design incorporates various components to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The core of the circuit is the integrated Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), which significantly enhances signal sensitivity, allowing the receiver to capture weak FM signals effectively. The LNA must be carefully matched to the high impedance of the integrated antenna to minimize signal loss and maintain a low noise figure, which is crucial for clear audio output.
In addition to the LNA, the circuit may include a band-pass filter to eliminate unwanted signals outside the FM band, ensuring that only the desired frequencies (76-108 MHz) are processed. This filter helps to improve the overall selectivity of the receiver, allowing it to distinguish between closely spaced stations.
Power management is another critical aspect of the design, particularly in handheld devices where battery life is a concern. The LNA's low current consumption feature is essential for extending operational time. Furthermore, the integrated active biasing within the BGB707L7ESD LNA stabilizes performance over a range of temperatures and manufacturing variations, which is vital for maintaining consistent audio quality.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is also a key consideration, as mobile devices are often exposed to various environmental factors. The BGB707L7ESD's robustness of 4 kV (HBM) at the RF-in port ensures that the device can withstand accidental discharges, thereby protecting the sensitive components from damage.
Overall, the integration of the LNA and additional components into a compact form factor allows for the effective implementation of FM Radio functionality in modern mobile devices, ensuring high-quality audio reception while addressing the constraints of size and power efficiency. This design approach not only enhances user experience but also aligns with the ongoing trend of miniaturization in electronic devices.FM Radio has a long history to its credit starting from its development in 1933. Today, FM Radio is an integral part of almost all mobile phones. In a common mobile phone, the cable to the earphone serves as the Antenna for FM reception, wherein the Antenna size is a bit relaxed. To be able to use FM Radio also without the earphone, the Antenna ha s to be integrated inside the phone. But in this case, the space constraint poses a challenge on the Antenna design. Shrinking the size of the Antenna introduces a high loss in the system which deteriorates the receiver performance, namely the receiver sensitivity. Using a Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), CAN solve this problem by enhancing the receiver sensitivity. However, there are a few difficulties in the design of the LNA for this purpose. Due to the very small size, the Antenna impedance is very high and thus the LNA has to be matched to this high impedance and in addition offer a low noise figure.
Using it in a hand held device also demands low current consumption, power-off function and high linearity due to the co-existence of cellular bands. Other requirements on the LNA include worldwide FM band support (76- 108 MHz) and ESD robustness of 4 kV (HBM) at the RF-in port.
Infineon offers its LNA solution BGB707L7ESD which fulfills all the aforementioned performance criteria in a very small and leadless package TSLP-7-1 (2. 0 x 1. 3 x 0. 4 mm). It comes with an integrated active biasing which enables consistent operation with varying temperatures and process variations.
It finds its application in all kinds of mobile devices like mobile phones, PDAs, portable FM Radio MP3 players etc. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713