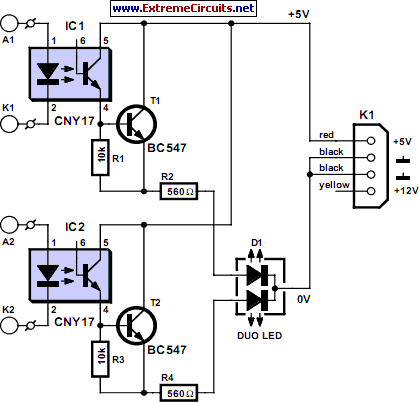
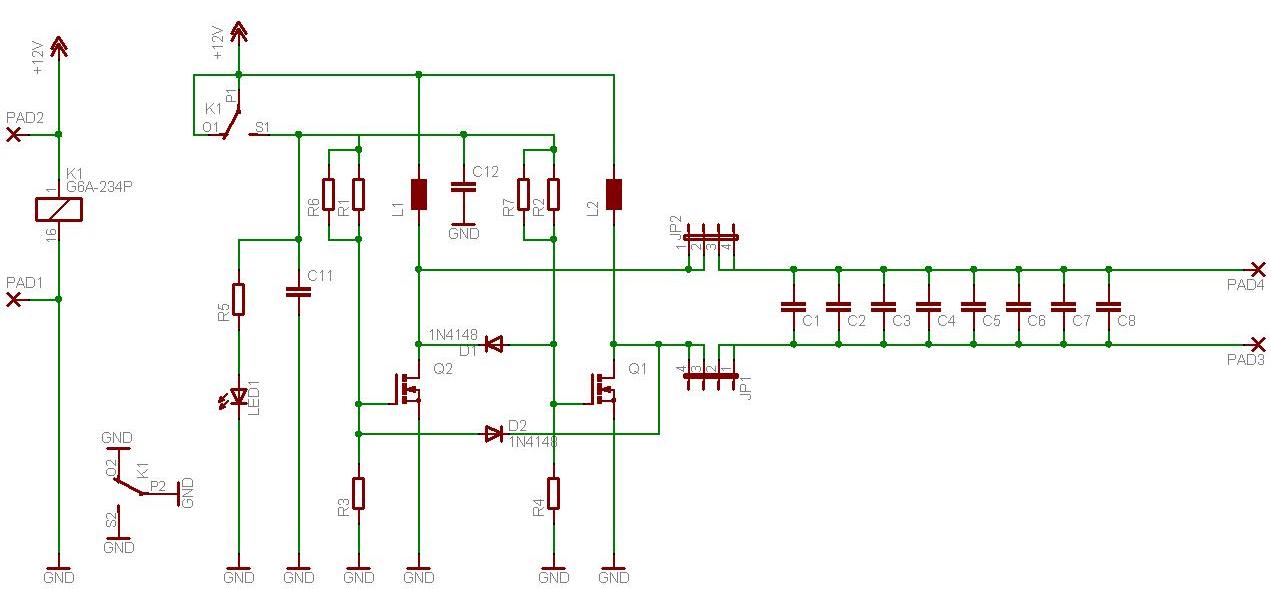
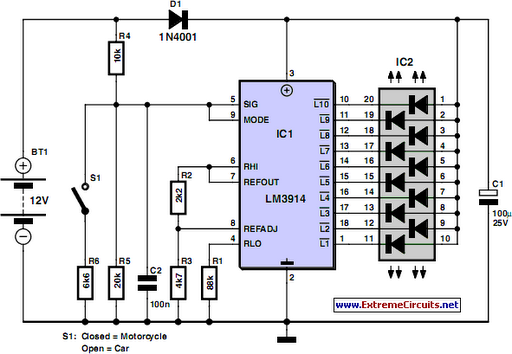
Battery Equality Monitor Circuit Schematic
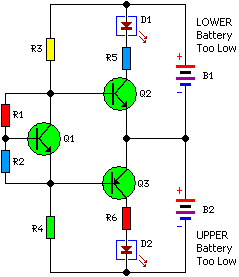
Most 24V power systems in trucks, 4WDs, RVs, boats, and similar applications utilize two series-connected 12V lead-acid batteries. The charging system is designed to maintain the total voltage of the two batteries. If one battery begins to fail, the circuit will activate an LED indicator, allowing for early detection of potential battery issues. The operation of the circuit is based on measuring the voltage difference between the two 12V batteries. The idle current is sufficiently low to permit continuous connection across the batteries.
The described circuit serves as a vital monitoring system for dual 12V lead-acid batteries arranged in series to form a 24V power supply. In such configurations, the reliability of both batteries is crucial for optimal performance. The circuit's primary function is to detect discrepancies in voltage levels between the two batteries, which may indicate a failing battery.
The circuit typically consists of a differential voltage sensor that continuously monitors the voltage across each battery. This sensor compares the voltage levels and identifies any significant variations. If the voltage difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, it triggers an LED indicator, providing a visual alert to the user regarding the health of the batteries.
The design of the circuit ensures that it operates with minimal idle current consumption, allowing it to remain connected to the battery system without draining the batteries themselves. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where the batteries are not frequently accessed or where constant monitoring is desired.
The inclusion of an LED indicator serves as a straightforward and effective means of communicating the status of the batteries. In practical terms, this circuit can help prevent unexpected failures and extend the lifespan of the battery system by allowing for timely maintenance or replacement of the failing battery. Overall, this monitoring solution enhances the reliability and safety of 24V power systems in various mobile and stationary applications.Almost all 24V power systems in trucks, 4WDs, RVs, boats, etc, employ two series-connected 12V lead-acid batteries. The charging system can only maintain the sum of the individual battery voltages. If one battery is failing, this circuit will light a LED. Hence impending battery problems can be forecast. The circuit works by detecting a voltage di fference between the two series connected 12V batteries. Idle current is low enough to allow the unit to be permanently left across the batteries. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a vital monitoring system for dual 12V lead-acid batteries arranged in series to form a 24V power supply. In such configurations, the reliability of both batteries is crucial for optimal performance. The circuit's primary function is to detect discrepancies in voltage levels between the two batteries, which may indicate a failing battery.
The circuit typically consists of a differential voltage sensor that continuously monitors the voltage across each battery. This sensor compares the voltage levels and identifies any significant variations. If the voltage difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, it triggers an LED indicator, providing a visual alert to the user regarding the health of the batteries.
The design of the circuit ensures that it operates with minimal idle current consumption, allowing it to remain connected to the battery system without draining the batteries themselves. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where the batteries are not frequently accessed or where constant monitoring is desired.
The inclusion of an LED indicator serves as a straightforward and effective means of communicating the status of the batteries. In practical terms, this circuit can help prevent unexpected failures and extend the lifespan of the battery system by allowing for timely maintenance or replacement of the failing battery. Overall, this monitoring solution enhances the reliability and safety of 24V power systems in various mobile and stationary applications.Almost all 24V power systems in trucks, 4WDs, RVs, boats, etc, employ two series-connected 12V lead-acid batteries. The charging system can only maintain the sum of the individual battery voltages. If one battery is failing, this circuit will light a LED. Hence impending battery problems can be forecast. The circuit works by detecting a voltage di fference between the two series connected 12V batteries. Idle current is low enough to allow the unit to be permanently left across the batteries. 🔗 External reference