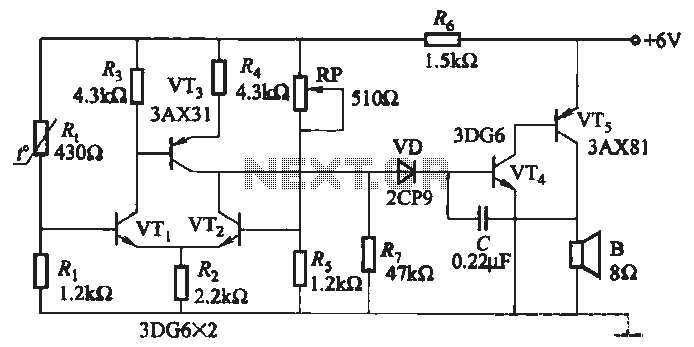
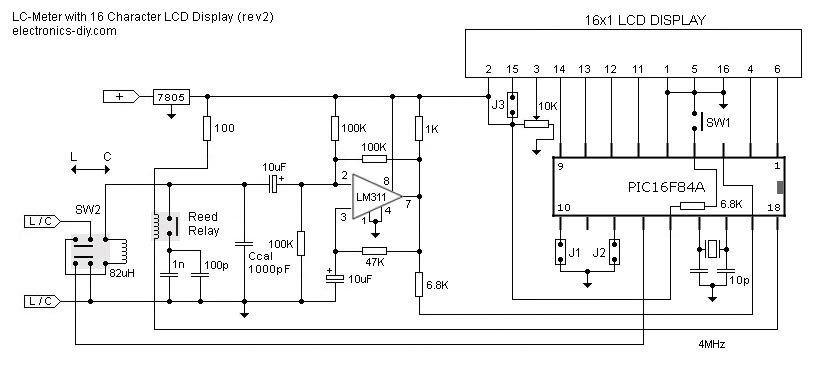
battery desulfator circuit
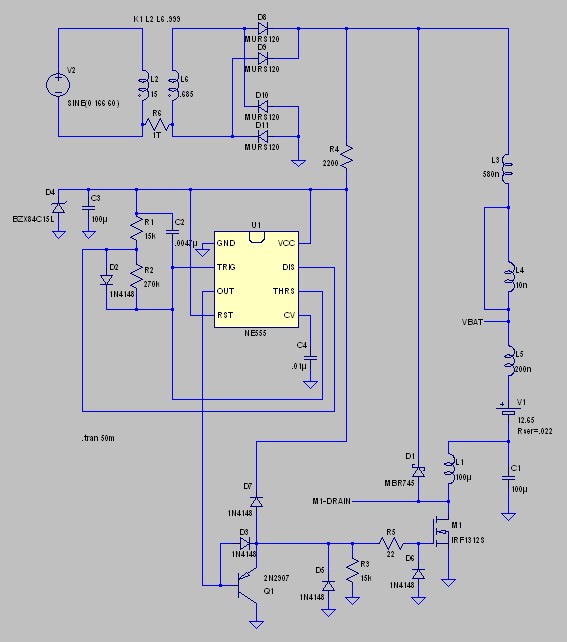
Desulfation is the process of reversing sulfation that occurs in a lead-acid battery over time. Desulfation partially restores the battery's ability to hold a charge, which is diminished due to sulfation.
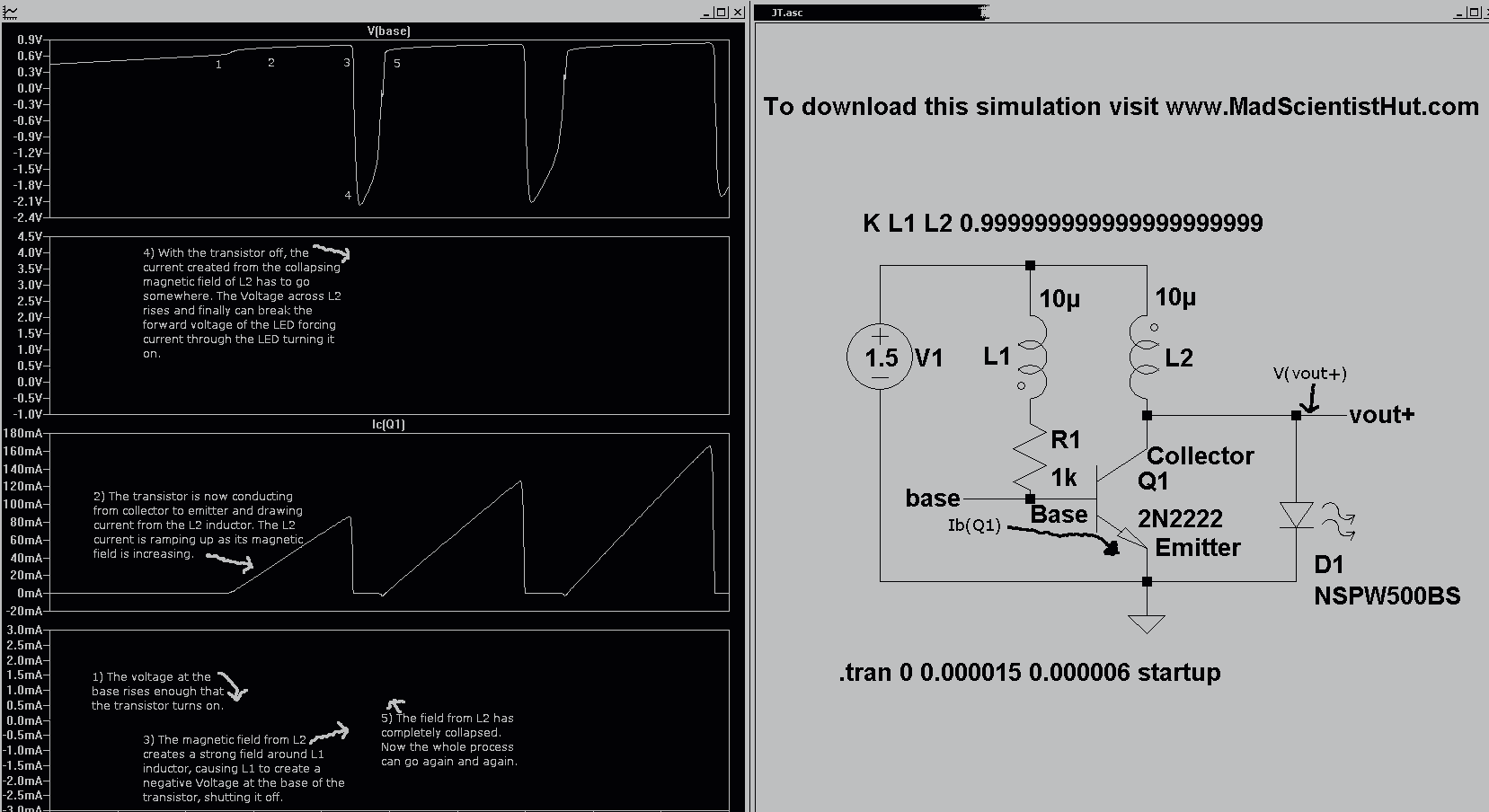
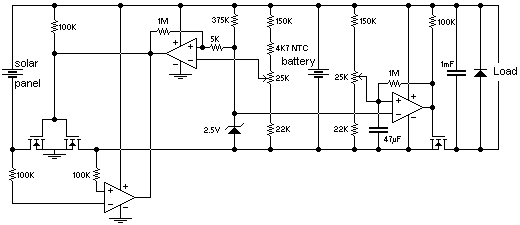
Desulfation is a critical maintenance procedure for lead-acid batteries, as sulfation leads to the formation of lead sulfate crystals on the battery plates. This accumulation impedes the chemical reactions necessary for the battery to function effectively, resulting in reduced capacity and shorter battery life. The desulfation process typically involves applying a controlled voltage and current to the battery, which can help dissolve the lead sulfate crystals and restore the active material on the plates.
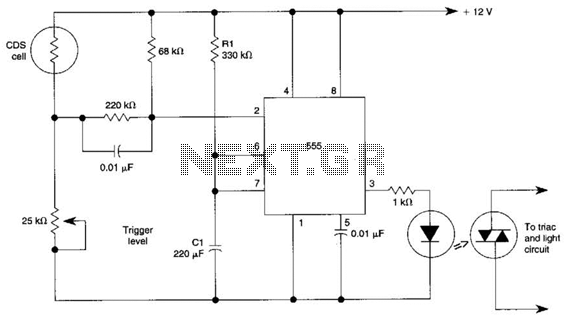
A common method for desulfation is the use of a specialized charger that employs high-frequency pulses or specific charging algorithms. These chargers can help break down the lead sulfate crystals without causing damage to the battery. In addition, some desulfation techniques may incorporate the use of additives that promote the dissolution of sulfate compounds.
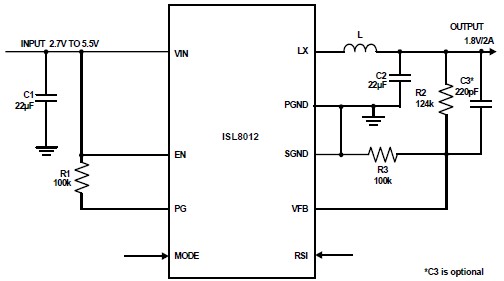
In a schematic design for a desulfation circuit, key components would typically include a microcontroller for monitoring and controlling the charging process, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) circuit to regulate the voltage and current, and a feedback mechanism to assess the battery's state of charge and health. The circuit may also feature safety mechanisms such as overcurrent protection and thermal management to ensure safe operation during the desulfation process.
The overall goal of a desulfation circuit is to extend the lifespan of lead-acid batteries, enhance performance, and reduce the frequency of replacement, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved reliability for applications relying on these batteries.Desulfation is the process of reversing the process of sulfation that occurs to a lead-acid battery over time. Desulfation restores, at least partially, the ability of the battery to hold a charge over the life of the battery originally caused by sulfation)..
🔗 External reference
Desulfation is a critical maintenance procedure for lead-acid batteries, as sulfation leads to the formation of lead sulfate crystals on the battery plates. This accumulation impedes the chemical reactions necessary for the battery to function effectively, resulting in reduced capacity and shorter battery life. The desulfation process typically involves applying a controlled voltage and current to the battery, which can help dissolve the lead sulfate crystals and restore the active material on the plates.
A common method for desulfation is the use of a specialized charger that employs high-frequency pulses or specific charging algorithms. These chargers can help break down the lead sulfate crystals without causing damage to the battery. In addition, some desulfation techniques may incorporate the use of additives that promote the dissolution of sulfate compounds.
In a schematic design for a desulfation circuit, key components would typically include a microcontroller for monitoring and controlling the charging process, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) circuit to regulate the voltage and current, and a feedback mechanism to assess the battery's state of charge and health. The circuit may also feature safety mechanisms such as overcurrent protection and thermal management to ensure safe operation during the desulfation process.
The overall goal of a desulfation circuit is to extend the lifespan of lead-acid batteries, enhance performance, and reduce the frequency of replacement, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved reliability for applications relying on these batteries.Desulfation is the process of reversing the process of sulfation that occurs to a lead-acid battery over time. Desulfation restores, at least partially, the ability of the battery to hold a charge over the life of the battery originally caused by sulfation)..
🔗 External reference