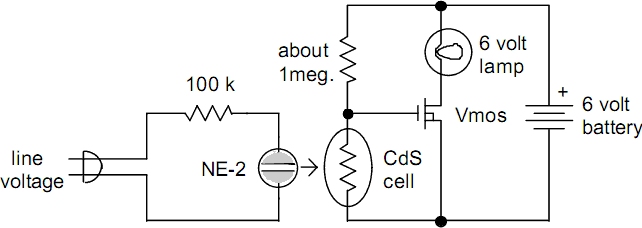
Bearing fault detector circuit diagram 2
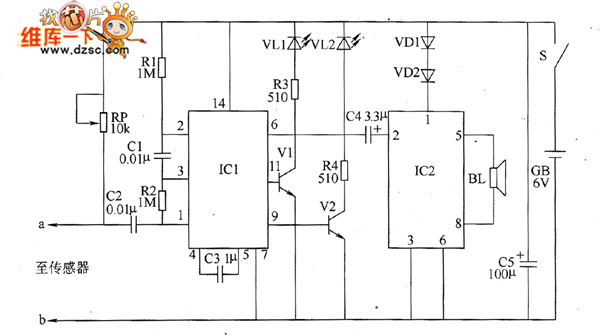
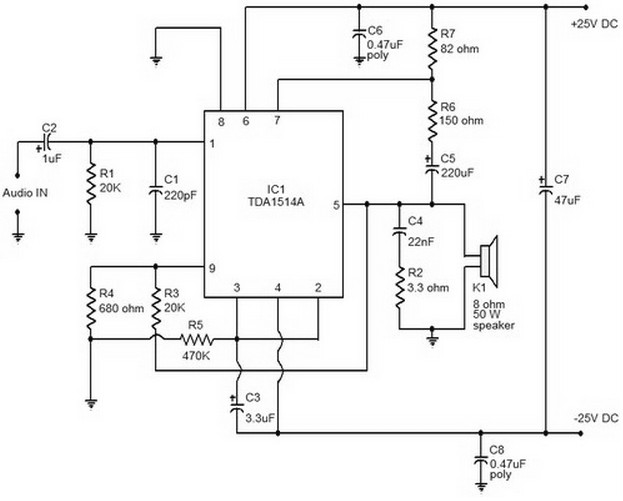
The bearing fault detection circuit comprises bearing detection sensors, a signal processing circuit, and a sound and light circuit. The signal processing circuit includes the input socket XS, a voice integrated circuit IC1, capacitors C1 to C3, resistors R1, R2, and a potentiometer RP. The sound and light circuit consists of transistors V1 and V2, LEDs VL1 and VL2, an audio power amplifier integrated circuit IC2, resistors R3 and R4, capacitor C4, diodes VD1 and VD2, and a speaker BL. Resistors R1 to R4 should be selected as 1/4W or 1/8W metal film resistors, while RP is a small synthetic membrane potentiometer or variable resistor.
The bearing fault detection circuit is designed to monitor the operational integrity of bearings by detecting faults through various components that work in unison. The circuit begins with the bearing detection sensors that capture data regarding the condition of the bearings. These sensors are critical for identifying anomalies such as vibrations or temperature changes that may indicate wear or failure.
The signal processing circuit serves as the central hub for interpreting the data from the sensors. It includes an input socket (XS) for receiving signals, a voice integrated circuit (IC1) that processes audio signals, and several passive components like capacitors (C1, C2, C3) and resistors (R1, R2). The potentiometer (RP) allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response characteristics, ensuring accurate detection thresholds.
The sound and light circuit is responsible for providing feedback to the user regarding the status of the bearings. It utilizes transistors (V1, V2) to control the activation of visual indicators (LEDs VL1, VL2) and auditory signals through an audio power amplifier (IC2). The use of resistors (R3, R4) and a capacitor (C4) in this circuit helps to manage current flow and signal clarity. Diodes (VD1, VD2) are included to protect the circuit from potential back EMF generated by the speaker (BL), ensuring longevity and reliability.
Overall, this circuit is a comprehensive system for real-time monitoring of bearing health, employing a combination of sensor technology, signal processing, and user feedback mechanisms to ensure operational safety and efficiency. Proper selection of components, such as metal film resistors and a synthetic membrane potentiometer, contributes to the circuit's performance and durability.The bearing fault detection circuit is composed of the bearing detection sensors, signal processing circuit and sound and light circuit, and it is shown as the chart. Signal processing circuit consists of the input socket XS, voice integrated circuit IC1, capacitors C1 ~ C3, resistors R1, R2 and potentiometer RP.
Sound and light is composed of the transistors V1, V2, LEDs VL1, VL2, audio power amplifier integrated circuit IC2, resistors R3, R4, capacitor C4, diodes VD1, VD2, and speaker BL. R1 ~ M select the 1/4W or 1/8W metal film resistors. RP uses the small synthetic membrane potentiometer or variable resistor. 🔗 External reference
The bearing fault detection circuit is designed to monitor the operational integrity of bearings by detecting faults through various components that work in unison. The circuit begins with the bearing detection sensors that capture data regarding the condition of the bearings. These sensors are critical for identifying anomalies such as vibrations or temperature changes that may indicate wear or failure.
The signal processing circuit serves as the central hub for interpreting the data from the sensors. It includes an input socket (XS) for receiving signals, a voice integrated circuit (IC1) that processes audio signals, and several passive components like capacitors (C1, C2, C3) and resistors (R1, R2). The potentiometer (RP) allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response characteristics, ensuring accurate detection thresholds.
The sound and light circuit is responsible for providing feedback to the user regarding the status of the bearings. It utilizes transistors (V1, V2) to control the activation of visual indicators (LEDs VL1, VL2) and auditory signals through an audio power amplifier (IC2). The use of resistors (R3, R4) and a capacitor (C4) in this circuit helps to manage current flow and signal clarity. Diodes (VD1, VD2) are included to protect the circuit from potential back EMF generated by the speaker (BL), ensuring longevity and reliability.
Overall, this circuit is a comprehensive system for real-time monitoring of bearing health, employing a combination of sensor technology, signal processing, and user feedback mechanisms to ensure operational safety and efficiency. Proper selection of components, such as metal film resistors and a synthetic membrane potentiometer, contributes to the circuit's performance and durability.The bearing fault detection circuit is composed of the bearing detection sensors, signal processing circuit and sound and light circuit, and it is shown as the chart. Signal processing circuit consists of the input socket XS, voice integrated circuit IC1, capacitors C1 ~ C3, resistors R1, R2 and potentiometer RP.
Sound and light is composed of the transistors V1, V2, LEDs VL1, VL2, audio power amplifier integrated circuit IC2, resistors R3, R4, capacitor C4, diodes VD1, VD2, and speaker BL. R1 ~ M select the 1/4W or 1/8W metal film resistors. RP uses the small synthetic membrane potentiometer or variable resistor. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713