Mosfet Buffer Amplifier Circuit
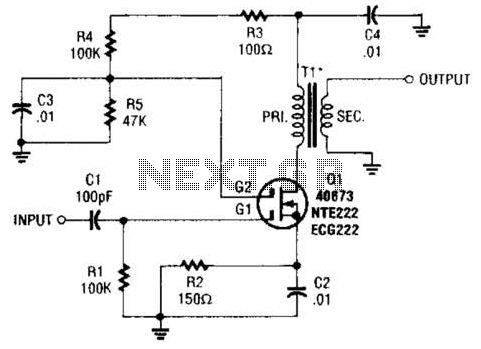
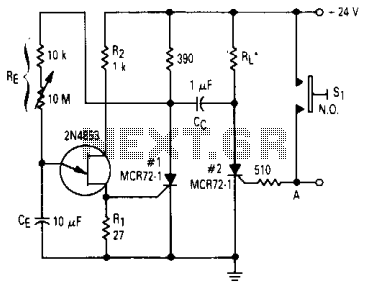
A MOSFET is utilized as a wideband buffer amplifier. T1 is wound on a toroid of approximately specified diameter, using material suitable for the frequency range, typically between 1 MHz and 20 MHz. The turns ratio should be approximately 4:1, depending on the load impedance. At a frequency of 4 MHz, the primary winding consists of 18 turns, while the secondary has 4 turns, resulting in a stage gain of about 14 dB (with a load impedance of 50 ohms).
The circuit employs a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) configured as a buffer amplifier to achieve high input impedance and low output impedance, which is essential for effective signal transmission without distortion. The choice of a toroidal transformer (T1) is crucial for maintaining efficiency and minimizing electromagnetic interference, as toroidal cores provide a compact and effective magnetic path.
The transformer’s primary winding is designed with 18 turns, which is optimized for the specified frequency of 4 MHz. The secondary winding, with 4 turns, maintains the desired turns ratio of 4:1. This ratio is vital for impedance matching to the load, ensuring that maximum power transfer occurs. The load impedance of 50 ohms is standard for many RF applications, making this configuration suitable for integration into various systems.
The gain of approximately 14 dB indicates that the output voltage is significantly amplified relative to the input, providing the necessary signal strength for further processing or transmission. This design is particularly advantageous in applications requiring wide bandwidth and minimal signal degradation, such as in RF amplifiers and communication systems. The careful selection of materials and winding configurations contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the buffer amplifier circuit. A MOSFET is used as a wideband buffer amplifier. T1 is wound on a toroid of approximately /f diameter, with material suitable for frequency (usually 1- to 20-MHz range). The turns ratio should be about 4:1 depending on load impedance. Typically, at 4 MHz, there are 18 turns on the primary, 4 turns on the secondary, and the stage gain is about 14-dB voltage (ZL - 50 ).
The circuit employs a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) configured as a buffer amplifier to achieve high input impedance and low output impedance, which is essential for effective signal transmission without distortion. The choice of a toroidal transformer (T1) is crucial for maintaining efficiency and minimizing electromagnetic interference, as toroidal cores provide a compact and effective magnetic path.
The transformer’s primary winding is designed with 18 turns, which is optimized for the specified frequency of 4 MHz. The secondary winding, with 4 turns, maintains the desired turns ratio of 4:1. This ratio is vital for impedance matching to the load, ensuring that maximum power transfer occurs. The load impedance of 50 ohms is standard for many RF applications, making this configuration suitable for integration into various systems.
The gain of approximately 14 dB indicates that the output voltage is significantly amplified relative to the input, providing the necessary signal strength for further processing or transmission. This design is particularly advantageous in applications requiring wide bandwidth and minimal signal degradation, such as in RF amplifiers and communication systems. The careful selection of materials and winding configurations contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the buffer amplifier circuit. A MOSFET is used as a wideband buffer amplifier. T1 is wound on a toroid of approximately /f diameter, with material suitable for frequency (usually 1- to 20-MHz range). The turns ratio should be about 4:1 depending on load impedance. Typically, at 4 MHz, there are 18 turns on the primary, 4 turns on the secondary, and the stage gain is about 14-dB voltage (ZL - 50 ).