Biomedical Monitoring circuit AT89C2051
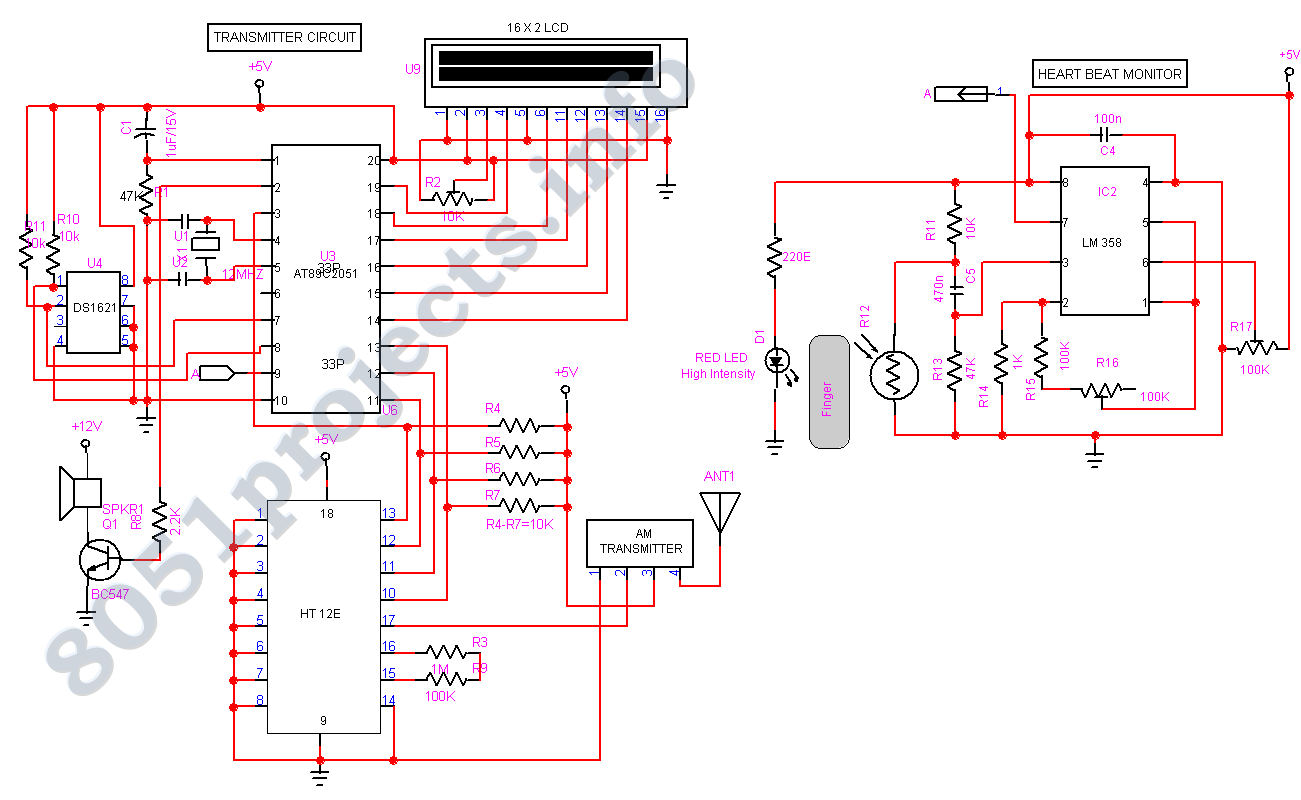
In spite of the improvement of communication link and despite all progress in advanced communication technologies, there are still very few functioning commercial wireless monitoring systems, which are most off-line, and there are still a number of issues to deal with. More: Therefore, there is a strong need for investigating the possibility of design and implementation of an interactive real-time wireless communication system. In our project, a generic real-time wireless communication system was designed and developed for sh
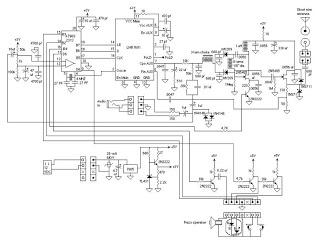
The described project focuses on the design and implementation of a generic real-time wireless communication system, addressing the limitations of existing commercial wireless monitoring systems. The circuit schematic for such a system typically includes several key components: a microcontroller, wireless transceiver modules, sensors, and a power supply.
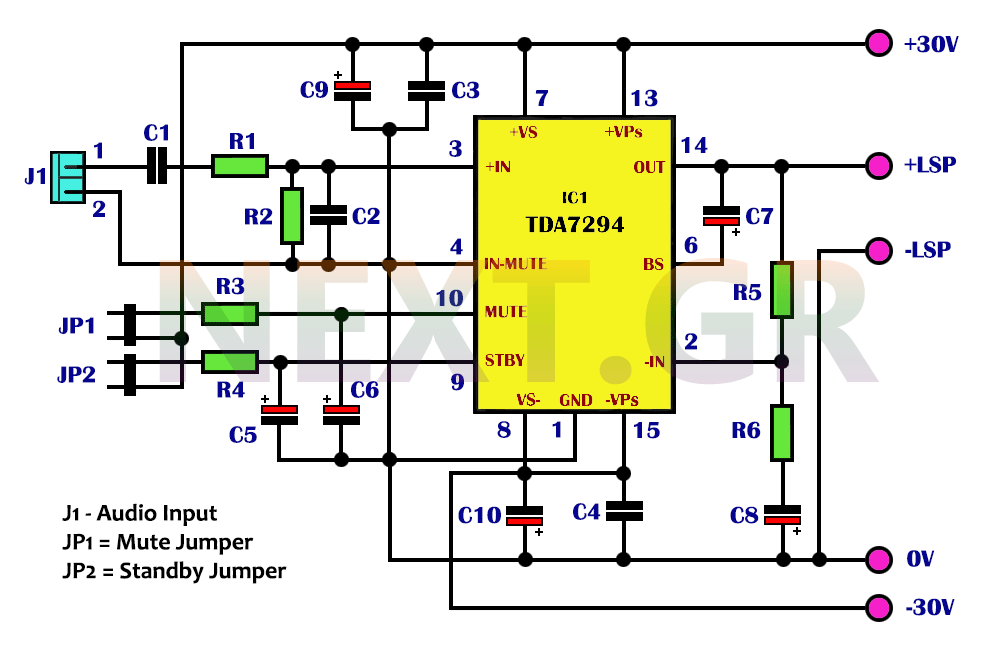
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, managing data acquisition from various sensors and controlling the wireless communication. Common choices for microcontrollers include the Arduino family or Raspberry Pi, which offer sufficient processing power and flexibility for real-time applications.
Wireless transceiver modules, such as those based on Wi-Fi (e.g., ESP8266/ESP32) or Bluetooth (e.g., HC-05), facilitate the transmission of data between the monitoring system and a remote user interface. These modules should be selected based on the required range, data rate, and power consumption.
Sensors play a critical role in the system, providing real-time data relevant to the monitoring application. Depending on the intended use, this could include environmental sensors (temperature, humidity), motion sensors, or specific industrial sensors. Each sensor must be connected to the microcontroller via appropriate interfacing circuitry, which may include analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for analog sensors.
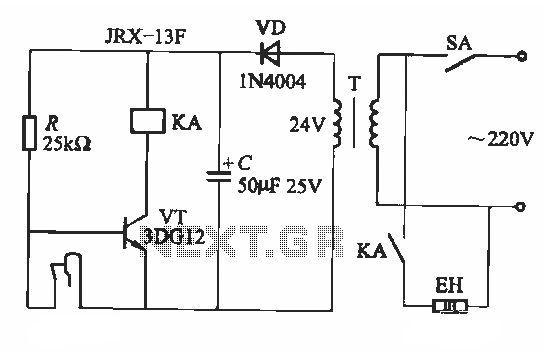
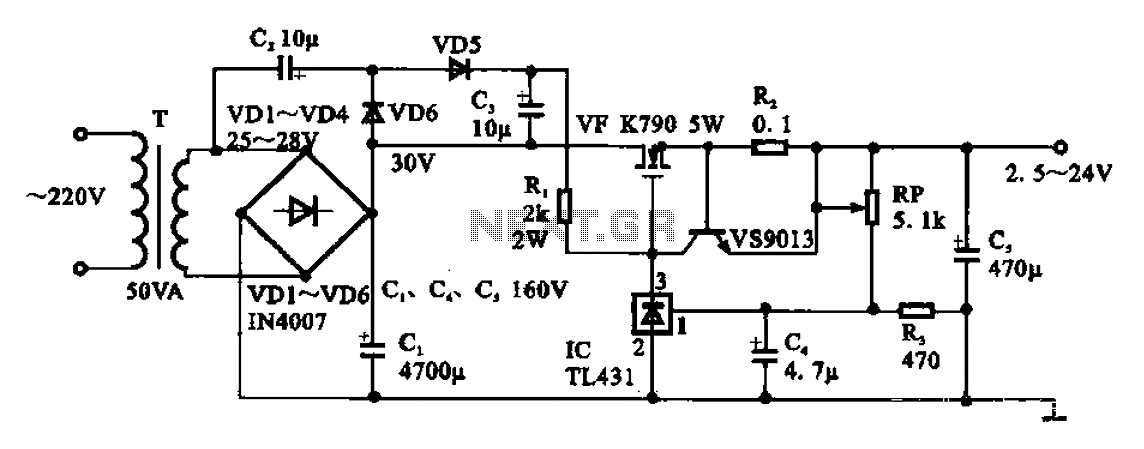
The power supply circuit is essential to ensure reliable operation of the system. It may include batteries or a power adapter, along with voltage regulators to provide stable power to the microcontroller and peripherals.
In addition to the hardware components, software development is crucial for the system's functionality. This involves programming the microcontroller to handle data collection, processing, and communication tasks, as well as developing an interface for users to interact with the system remotely.
Overall, the design and implementation of a real-time wireless communication system require careful consideration of hardware selection, circuit design, and software integration to create an effective monitoring solution.In spite of the improvement of communication link and despite all progress in advanced communication technologies, there are still very few functioning commercial wireless monitoring systems, which are most off-line, and there are still a number of issues to deal with. Therefore, there is a strong need for investigating the possibility of design and implementation of an interactive real-time wireless communication system. In our project, a generic real-time wireless communication system was designed and developed for sh 🔗 External reference
The described project focuses on the design and implementation of a generic real-time wireless communication system, addressing the limitations of existing commercial wireless monitoring systems. The circuit schematic for such a system typically includes several key components: a microcontroller, wireless transceiver modules, sensors, and a power supply.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, managing data acquisition from various sensors and controlling the wireless communication. Common choices for microcontrollers include the Arduino family or Raspberry Pi, which offer sufficient processing power and flexibility for real-time applications.
Wireless transceiver modules, such as those based on Wi-Fi (e.g., ESP8266/ESP32) or Bluetooth (e.g., HC-05), facilitate the transmission of data between the monitoring system and a remote user interface. These modules should be selected based on the required range, data rate, and power consumption.
Sensors play a critical role in the system, providing real-time data relevant to the monitoring application. Depending on the intended use, this could include environmental sensors (temperature, humidity), motion sensors, or specific industrial sensors. Each sensor must be connected to the microcontroller via appropriate interfacing circuitry, which may include analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for analog sensors.
The power supply circuit is essential to ensure reliable operation of the system. It may include batteries or a power adapter, along with voltage regulators to provide stable power to the microcontroller and peripherals.
In addition to the hardware components, software development is crucial for the system's functionality. This involves programming the microcontroller to handle data collection, processing, and communication tasks, as well as developing an interface for users to interact with the system remotely.
Overall, the design and implementation of a real-time wireless communication system require careful consideration of hardware selection, circuit design, and software integration to create an effective monitoring solution.In spite of the improvement of communication link and despite all progress in advanced communication technologies, there are still very few functioning commercial wireless monitoring systems, which are most off-line, and there are still a number of issues to deal with. Therefore, there is a strong need for investigating the possibility of design and implementation of an interactive real-time wireless communication system. In our project, a generic real-time wireless communication system was designed and developed for sh 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713