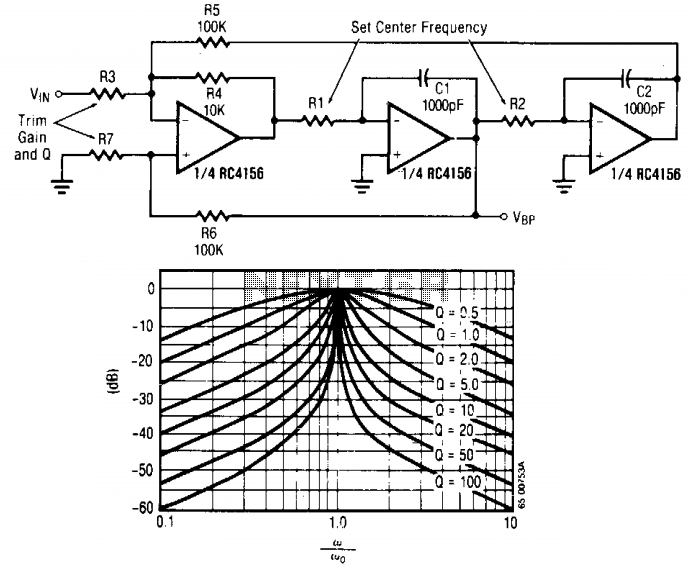
Biquad filter
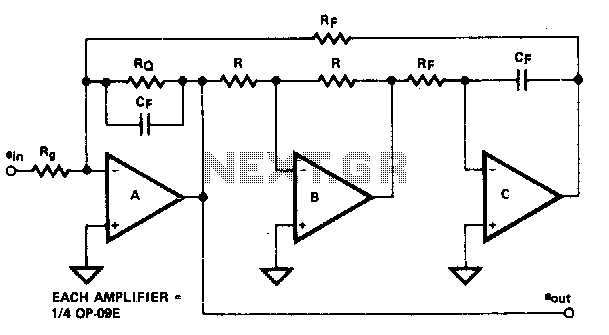
The biquad filter, although resembling the state-variable filter, maintains a fixed bandwidth that does not vary with the center frequency. This type of filter is particularly beneficial in applications like spectrum analyzers, which necessitate a filter with a constant bandwidth.
The biquad filter is a versatile and widely used analog filter topology characterized by its ability to provide second-order filtering effects. It can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) and passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The fixed bandwidth feature of the biquad filter makes it particularly suitable for applications where consistent frequency response is critical, such as in audio processing, signal conditioning, and spectrum analysis.
In a typical biquad filter circuit, the configuration may include a combination of feedback and feedforward paths that determine the filter's transfer function. The transfer function can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitors, allowing for fine-tuning of the center frequency and gain while keeping the bandwidth constant. The filter can be designed as a low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop filter, depending on the desired application.
For implementation in a spectrum analyzer, the biquad filter can be cascaded with multiple stages to achieve a higher order filter response, enhancing selectivity and improving the ability to discern closely spaced frequency components. The fixed bandwidth is particularly advantageous in such scenarios, as it ensures that the filter's performance remains stable across a range of center frequencies, providing reliable and repeatable measurements.
In summary, the biquad filter's unique characteristics, including its fixed bandwidth and adaptability for various applications, make it an essential component in electronic filter design, particularly in precision measurement tools like spectrum analyzers.The biquad filter, while appearing very similar to the state-variable filter, has a bandwidth that is fixed regardless of center frequency This type of filter is useful in applications such as spectrum analyzers, which require a filter with a fixed bandwidth. 🔗 External reference
The biquad filter is a versatile and widely used analog filter topology characterized by its ability to provide second-order filtering effects. It can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) and passive components such as resistors and capacitors. The fixed bandwidth feature of the biquad filter makes it particularly suitable for applications where consistent frequency response is critical, such as in audio processing, signal conditioning, and spectrum analysis.
In a typical biquad filter circuit, the configuration may include a combination of feedback and feedforward paths that determine the filter's transfer function. The transfer function can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitors, allowing for fine-tuning of the center frequency and gain while keeping the bandwidth constant. The filter can be designed as a low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop filter, depending on the desired application.
For implementation in a spectrum analyzer, the biquad filter can be cascaded with multiple stages to achieve a higher order filter response, enhancing selectivity and improving the ability to discern closely spaced frequency components. The fixed bandwidth is particularly advantageous in such scenarios, as it ensures that the filter's performance remains stable across a range of center frequencies, providing reliable and repeatable measurements.
In summary, the biquad filter's unique characteristics, including its fixed bandwidth and adaptability for various applications, make it an essential component in electronic filter design, particularly in precision measurement tools like spectrum analyzers.The biquad filter, while appearing very similar to the state-variable filter, has a bandwidth that is fixed regardless of center frequency This type of filter is useful in applications such as spectrum analyzers, which require a filter with a fixed bandwidth. 🔗 External reference