block diagram of 8051
The 8051 microcontroller gained significant popularity after Intel permitted other manufacturers to produce and sell various versions of the 8051, provided these versions maintained code compatibility with the original 8051.
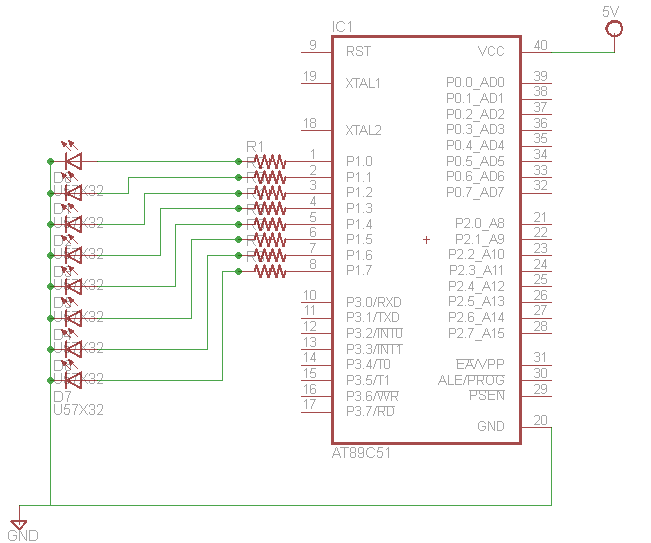
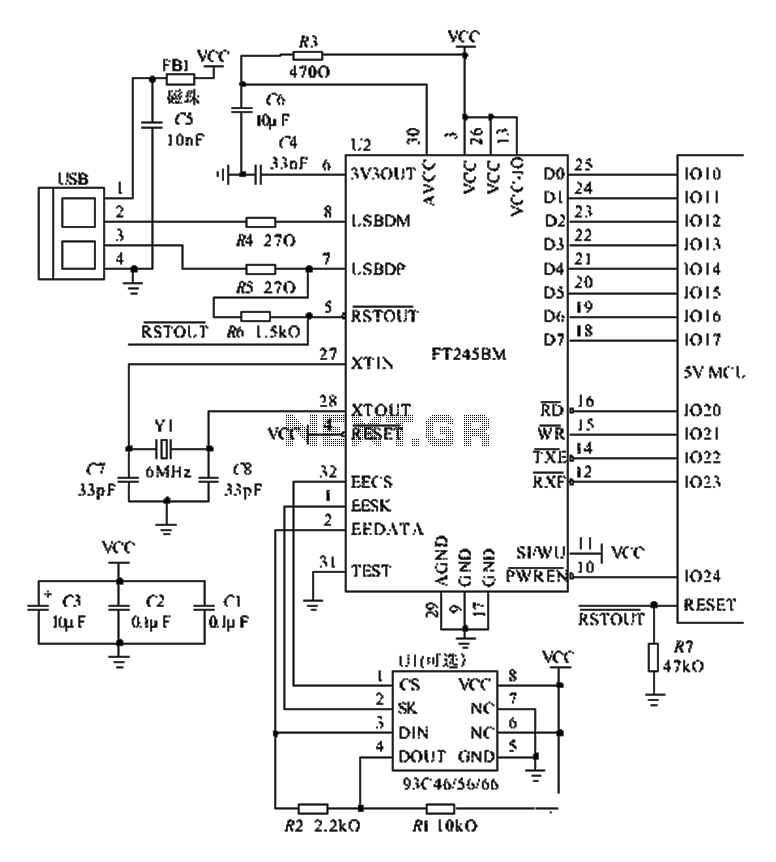
The 8051 microcontroller is an 8-bit processor that was developed by Intel in the 1980s. Its architecture is characterized by a 16-bit timer, a 16-bit program counter, and a 4 KB on-chip ROM, along with 128 bytes of RAM. The microcontroller features a 40-pin dual in-line package (DIP) and supports a variety of input/output operations, making it versatile for numerous applications in embedded systems.
The architecture of the 8051 includes several key components: the CPU, memory, and I/O ports. The CPU executes instructions fetched from memory and processes data. The on-chip memory consists of program memory (ROM) for storing the firmware and data memory (RAM) for temporary data storage during program execution. The I/O ports allow the microcontroller to interface with external devices, such as sensors, displays, and communication modules.
The introduction of the 8051 architecture to various manufacturers has led to the development of numerous variants, each with unique features while ensuring compatibility with the original instruction set. These variants often include enhancements such as increased memory capacity, additional I/O ports, and integrated peripherals like ADCs and DACs, which expand the microcontroller's functionality and application range.
The 8051 microcontroller is widely used in applications such as automation systems, consumer electronics, automotive controls, and communication devices. Its enduring popularity is attributed to its robust architecture, ease of programming, and the extensive resources available for developers, including libraries, development tools, and community support.The 8051 became widely popular after Intel allowed other manufacturers to make and market any flavors of the 8051 they please with the condition that they remain code-compatible with the 8051. 🔗 External reference
The 8051 microcontroller is an 8-bit processor that was developed by Intel in the 1980s. Its architecture is characterized by a 16-bit timer, a 16-bit program counter, and a 4 KB on-chip ROM, along with 128 bytes of RAM. The microcontroller features a 40-pin dual in-line package (DIP) and supports a variety of input/output operations, making it versatile for numerous applications in embedded systems.
The architecture of the 8051 includes several key components: the CPU, memory, and I/O ports. The CPU executes instructions fetched from memory and processes data. The on-chip memory consists of program memory (ROM) for storing the firmware and data memory (RAM) for temporary data storage during program execution. The I/O ports allow the microcontroller to interface with external devices, such as sensors, displays, and communication modules.
The introduction of the 8051 architecture to various manufacturers has led to the development of numerous variants, each with unique features while ensuring compatibility with the original instruction set. These variants often include enhancements such as increased memory capacity, additional I/O ports, and integrated peripherals like ADCs and DACs, which expand the microcontroller's functionality and application range.
The 8051 microcontroller is widely used in applications such as automation systems, consumer electronics, automotive controls, and communication devices. Its enduring popularity is attributed to its robust architecture, ease of programming, and the extensive resources available for developers, including libraries, development tools, and community support.The 8051 became widely popular after Intel allowed other manufacturers to make and market any flavors of the 8051 they please with the condition that they remain code-compatible with the 8051. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713