Block Diagram of the CT Scanner
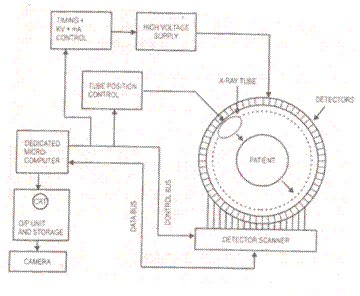
The CT Scanner, short for computed tomography scanner, was invented in 1970, building on prior advancements in dedicated minicomputers. A high DC voltage is applied to the capacitors as X-rays enter the system. The chamber ionizes the xenon gas, causing it to migrate to the capacitor plates, which generates a current in the high voltage load. This current is proportional to the radiation and is sent to the computer as data for image computation.
The CT Scanner operates based on the principles of X-ray imaging and advanced computational algorithms. The system consists of several key components, including an X-ray tube, detector array, high-voltage power supply, and a data acquisition system.
When the CT Scanner is activated, the X-ray tube emits a controlled beam of X-rays that passes through the object being scanned, typically a human body. As the X-rays pass through different tissues, they are attenuated to varying degrees, depending on the density and composition of the tissues. The remaining X-rays are detected by the detector array positioned opposite the X-ray source.
The detector array often consists of numerous individual detectors that convert incoming X-ray photons into electrical signals. The ionization of xenon gas within the chamber plays a crucial role in this process. When X-rays interact with the xenon gas, they ionize it, causing electrons to be released. These electrons migrate towards the capacitor plates, generating a measurable current. The current produced is proportional to the intensity of the radiation, thereby providing vital information about the internal structure of the scanned object.
This electrical signal is then processed by the data acquisition system, which digitizes the information and sends it to the computer. The computer uses sophisticated algorithms to reconstruct the data into cross-sectional images, or slices, of the scanned object. These images can then be displayed on a monitor for analysis by medical professionals, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
In summary, the CT Scanner represents a significant advancement in medical imaging technology, combining the principles of physics, electronics, and computer science to produce detailed images of internal structures with high precision and clarity.The CT Scanner is the abbreviation of computer tomography scanner. The invention of CT Scanner in 1970 was made possible by a previously established insight and development of the dedicated minicomputers. A high DC voltage is applied to the capacitors an x-rays entry. The chamber ionizes the xenon item causing it to migrate to capacitor plate and causing a current in the high voltage load. This current is proportional to the radiation and is fed to the computer as data for computing the image. 🔗 External reference
The CT Scanner operates based on the principles of X-ray imaging and advanced computational algorithms. The system consists of several key components, including an X-ray tube, detector array, high-voltage power supply, and a data acquisition system.
When the CT Scanner is activated, the X-ray tube emits a controlled beam of X-rays that passes through the object being scanned, typically a human body. As the X-rays pass through different tissues, they are attenuated to varying degrees, depending on the density and composition of the tissues. The remaining X-rays are detected by the detector array positioned opposite the X-ray source.
The detector array often consists of numerous individual detectors that convert incoming X-ray photons into electrical signals. The ionization of xenon gas within the chamber plays a crucial role in this process. When X-rays interact with the xenon gas, they ionize it, causing electrons to be released. These electrons migrate towards the capacitor plates, generating a measurable current. The current produced is proportional to the intensity of the radiation, thereby providing vital information about the internal structure of the scanned object.
This electrical signal is then processed by the data acquisition system, which digitizes the information and sends it to the computer. The computer uses sophisticated algorithms to reconstruct the data into cross-sectional images, or slices, of the scanned object. These images can then be displayed on a monitor for analysis by medical professionals, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
In summary, the CT Scanner represents a significant advancement in medical imaging technology, combining the principles of physics, electronics, and computer science to produce detailed images of internal structures with high precision and clarity.The CT Scanner is the abbreviation of computer tomography scanner. The invention of CT Scanner in 1970 was made possible by a previously established insight and development of the dedicated minicomputers. A high DC voltage is applied to the capacitors an x-rays entry. The chamber ionizes the xenon item causing it to migrate to capacitor plate and causing a current in the high voltage load. This current is proportional to the radiation and is fed to the computer as data for computing the image. 🔗 External reference