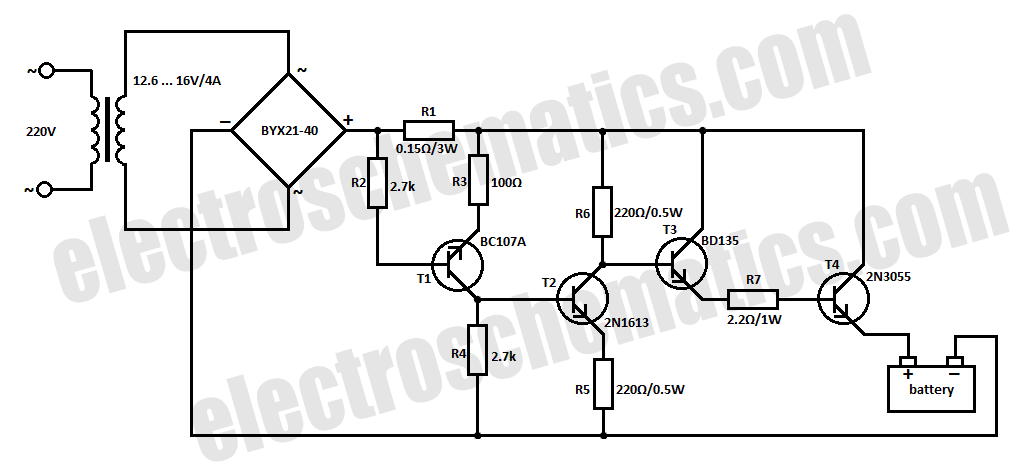
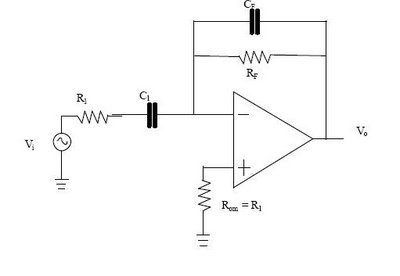
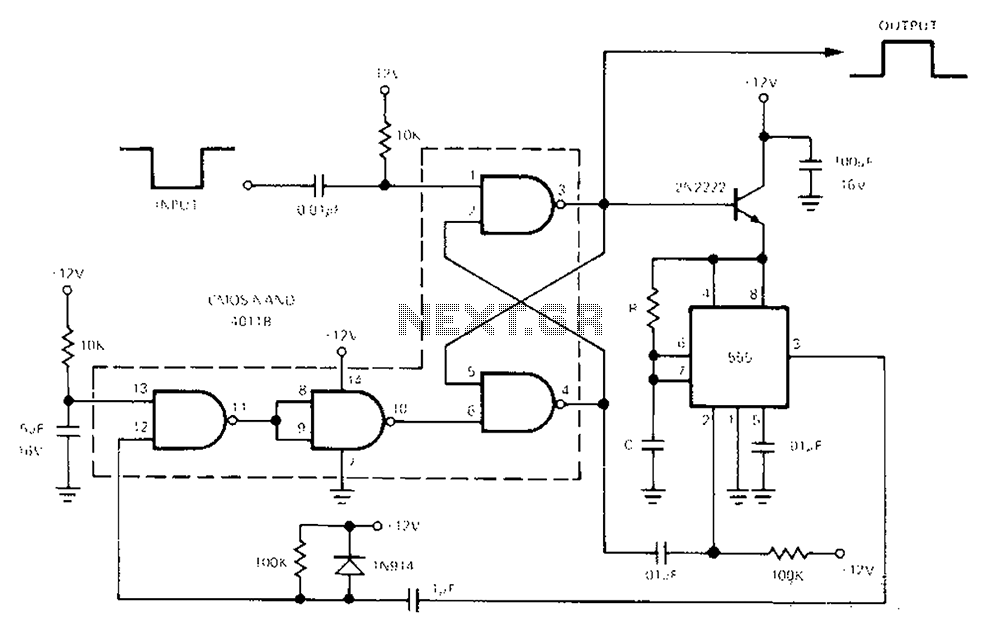
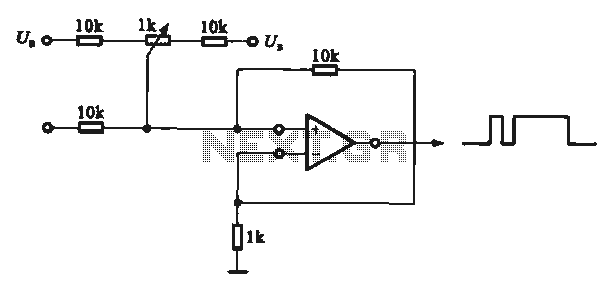
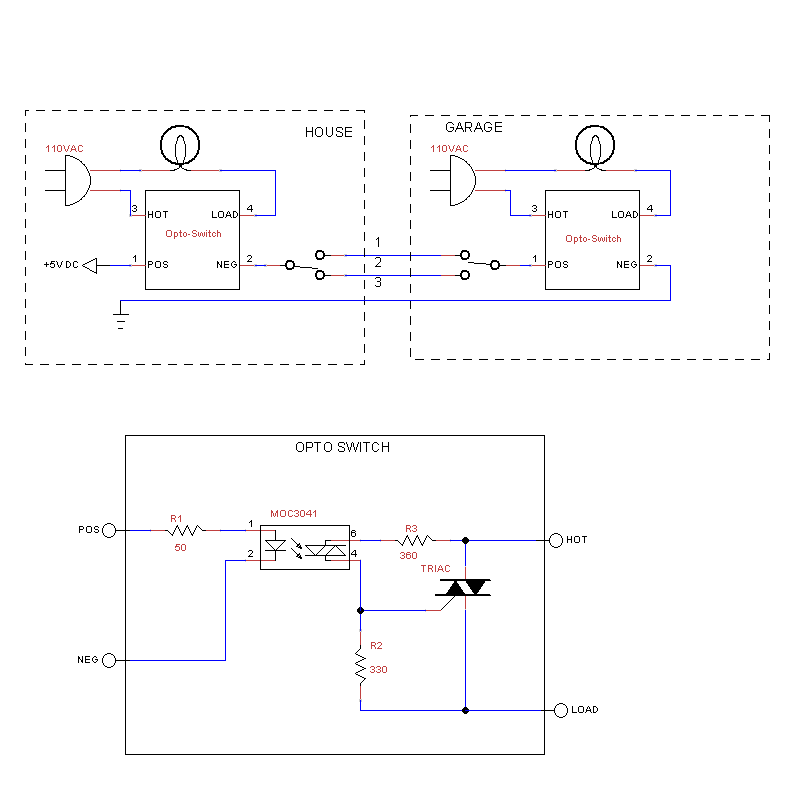
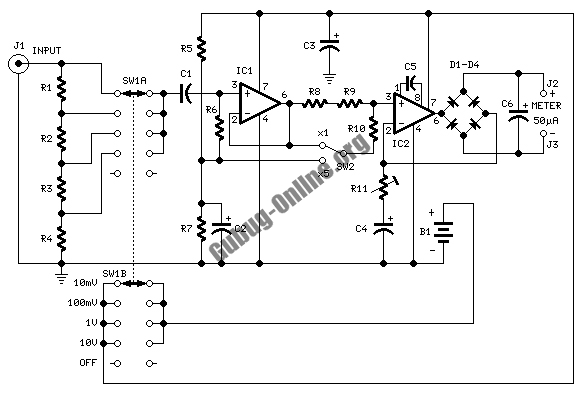
Circuit Diagram Of Simple Infrared Sensor Modules
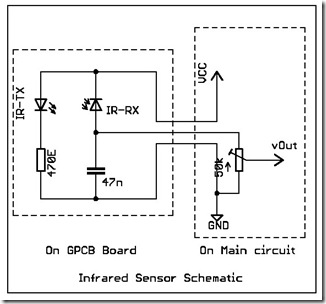
The following circuit illustrates a simple infrared sensor module circuit diagram. Features include a simple infrared sensor module and flame detection.
The simple infrared sensor module circuit operates by utilizing an infrared (IR) transmitter and receiver pair. The IR transmitter emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye. The IR receiver detects the reflected light from objects, allowing the circuit to sense the presence of nearby objects or flames.
In the schematic, the circuit typically includes a power supply, which can be a battery or a DC power source, providing the necessary voltage for the sensor module. The infrared LED serves as the transmitter, while a photodiode or phototransistor acts as the receiver. When the infrared light emitted by the LED hits an object, such as a flame, it reflects back to the receiver, generating a signal.
The output from the infrared sensor can be connected to a microcontroller or an alert system, such as an LED or a buzzer, to indicate the detection of a flame or an object. Additional components may include resistors to limit current and capacitors for filtering noise in the signal.
This circuit design is widely used in various applications, including fire detection systems, automatic lighting systems, and proximity sensors, due to its simplicity and effectiveness in detecting infrared signals. Proper calibration and positioning of the sensor are crucial to maximize its sensitivity and accuracy in detecting flames or nearby objects.The following circuit shows about Simple Infrared Sensor Modules Circuit Diagram. Feature: simple infrared sensor module, flame detection, .. 🔗 External reference
The simple infrared sensor module circuit operates by utilizing an infrared (IR) transmitter and receiver pair. The IR transmitter emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye. The IR receiver detects the reflected light from objects, allowing the circuit to sense the presence of nearby objects or flames.
In the schematic, the circuit typically includes a power supply, which can be a battery or a DC power source, providing the necessary voltage for the sensor module. The infrared LED serves as the transmitter, while a photodiode or phototransistor acts as the receiver. When the infrared light emitted by the LED hits an object, such as a flame, it reflects back to the receiver, generating a signal.
The output from the infrared sensor can be connected to a microcontroller or an alert system, such as an LED or a buzzer, to indicate the detection of a flame or an object. Additional components may include resistors to limit current and capacitors for filtering noise in the signal.
This circuit design is widely used in various applications, including fire detection systems, automatic lighting systems, and proximity sensors, due to its simplicity and effectiveness in detecting infrared signals. Proper calibration and positioning of the sensor are crucial to maximize its sensitivity and accuracy in detecting flames or nearby objects.The following circuit shows about Simple Infrared Sensor Modules Circuit Diagram. Feature: simple infrared sensor module, flame detection, .. 🔗 External reference