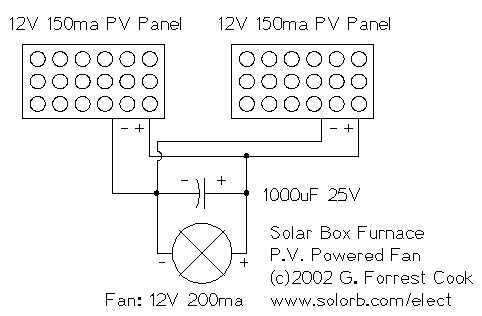
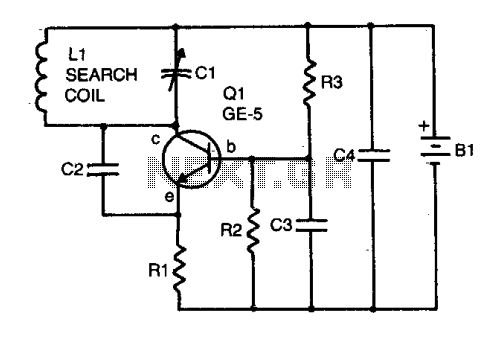
Bridge circuit
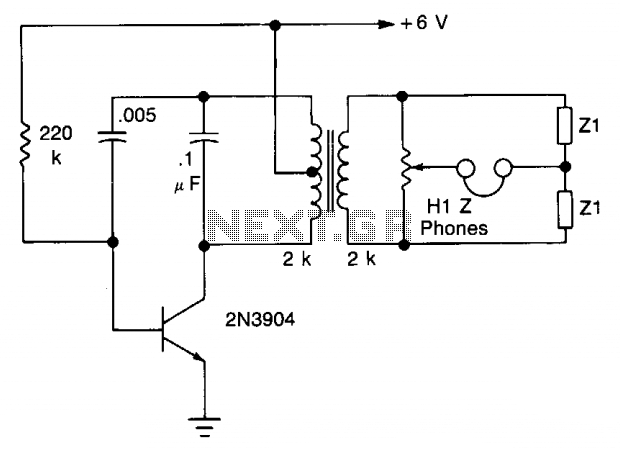
The transistor is configured as an audio oscillator, utilizing an audio transformer in the collector. The secondary winding is connected to a linear potentiometer. The ratio between the two sections of the potentiometer from the slider is proportional to the values of Z1 and Z2 when no signal is heard in the headphones.
The described circuit employs a transistor configured as an audio oscillator, which generates audio frequency signals. The audio transformer in the collector serves to couple the oscillator's output to the load, which in this case is the secondary winding of the transformer. This transformer plays a critical role in impedance matching and signal transfer between the oscillator and the audio output.
The linear potentiometer, connected to the secondary winding, allows for adjustable output levels. The slider of the potentiometer provides a variable resistance that can be manipulated to control the amplitude of the audio signal reaching the headphones. The relationship between the two sections of the potentiometer is determined by the values of Z1 and Z2, which represent the impedance values in the circuit. When no audio signal is present in the headphones, the ratio of the potentiometer's sections reflects these impedance values, ensuring that the circuit maintains a balanced output.
For practical implementation, the transistor should be selected based on its frequency response characteristics to ensure optimal performance as an audio oscillator. The audio transformer should also be chosen to match the frequency range of interest and the desired output impedance. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to maintain its operation in the active region, thus allowing for consistent oscillation and audio signal generation. Additionally, consideration should be given to the power supply voltage and the overall circuit layout to minimize noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio output.The transistor is connected as an audio oscillator, using an audio transformer in the collector. The secondary goes to a linear pot. The ratio between the two parts of the pot from the slider is proportional to the values of Z1 and Z2 when no signal is heard in the phones.
The described circuit employs a transistor configured as an audio oscillator, which generates audio frequency signals. The audio transformer in the collector serves to couple the oscillator's output to the load, which in this case is the secondary winding of the transformer. This transformer plays a critical role in impedance matching and signal transfer between the oscillator and the audio output.
The linear potentiometer, connected to the secondary winding, allows for adjustable output levels. The slider of the potentiometer provides a variable resistance that can be manipulated to control the amplitude of the audio signal reaching the headphones. The relationship between the two sections of the potentiometer is determined by the values of Z1 and Z2, which represent the impedance values in the circuit. When no audio signal is present in the headphones, the ratio of the potentiometer's sections reflects these impedance values, ensuring that the circuit maintains a balanced output.
For practical implementation, the transistor should be selected based on its frequency response characteristics to ensure optimal performance as an audio oscillator. The audio transformer should also be chosen to match the frequency range of interest and the desired output impedance. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to maintain its operation in the active region, thus allowing for consistent oscillation and audio signal generation. Additionally, consideration should be given to the power supply voltage and the overall circuit layout to minimize noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio output.The transistor is connected as an audio oscillator, using an audio transformer in the collector. The secondary goes to a linear pot. The ratio between the two parts of the pot from the slider is proportional to the values of Z1 and Z2 when no signal is heard in the phones.