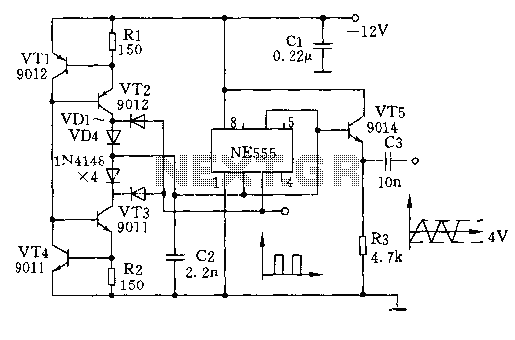
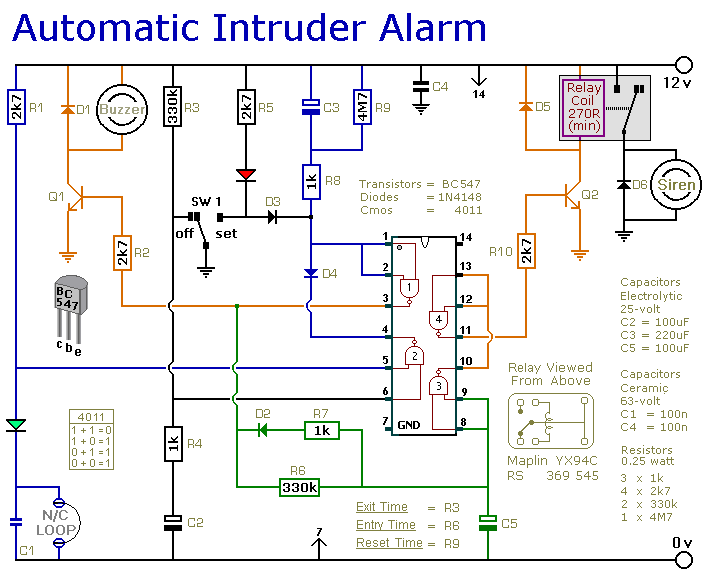
broken charger connection alarm circuit
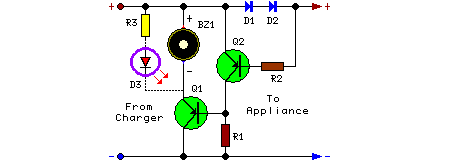
This circuit is designed to detect whether the load of a battery charger or plug-in adapter is properly connected. The load may consist of a set of batteries needing charging or any other device that operates on low DC voltage. The circuit can safely function within a voltage range of 3 to 15V and supports a maximum current of 1A, provided that the supply voltage is approximately one volt higher than the voltage needed by the load.
The circuit operates by monitoring the connection status of the load. It typically includes a voltage divider, a comparator, and an indicator, such as an LED, to signal the connection status. The voltage divider reduces the input voltage to a level suitable for the comparator, which compares the divided voltage against a reference voltage. If the load is properly connected, the voltage at the comparator's input will exceed the reference voltage, resulting in a high output signal. This signal can then be used to illuminate an LED, indicating that the load is connected correctly.
In cases where the load is disconnected or improperly connected, the voltage at the comparator will fall below the reference level, leading to a low output signal. This condition can also be used to turn off the LED, providing a clear visual indication of the issue. The circuit's design ensures that it can operate safely across a variety of battery types and low-voltage devices while maintaining a maximum current of 1A, making it versatile for different applications in battery management systems.
Overall, this circuit serves as a crucial safety feature in battery charging systems, preventing potential damage to the charger or load due to improper connections. Its ability to operate across a wide voltage range enhances its applicability in various electronic devices and systems, ensuring reliable performance and user feedback.This circuit can be useful to detect if the load of any battery charger or plug-in adapter supply is not properly connected. The load can be a set of batteries to be charged or any other type of battery or low dc voltage operated device.
The circuit can safely operate over a 3 to 15V range and 1A max. Current, provided the supply voltage is about one volt higher than the voltage required by the load.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by monitoring the connection status of the load. It typically includes a voltage divider, a comparator, and an indicator, such as an LED, to signal the connection status. The voltage divider reduces the input voltage to a level suitable for the comparator, which compares the divided voltage against a reference voltage. If the load is properly connected, the voltage at the comparator's input will exceed the reference voltage, resulting in a high output signal. This signal can then be used to illuminate an LED, indicating that the load is connected correctly.
In cases where the load is disconnected or improperly connected, the voltage at the comparator will fall below the reference level, leading to a low output signal. This condition can also be used to turn off the LED, providing a clear visual indication of the issue. The circuit's design ensures that it can operate safely across a variety of battery types and low-voltage devices while maintaining a maximum current of 1A, making it versatile for different applications in battery management systems.
Overall, this circuit serves as a crucial safety feature in battery charging systems, preventing potential damage to the charger or load due to improper connections. Its ability to operate across a wide voltage range enhances its applicability in various electronic devices and systems, ensuring reliable performance and user feedback.This circuit can be useful to detect if the load of any battery charger or plug-in adapter supply is not properly connected. The load can be a set of batteries to be charged or any other type of battery or low dc voltage operated device.
The circuit can safely operate over a 3 to 15V range and 1A max. Current, provided the supply voltage is about one volt higher than the voltage required by the load.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713