Buffer Amplifiers Circuit
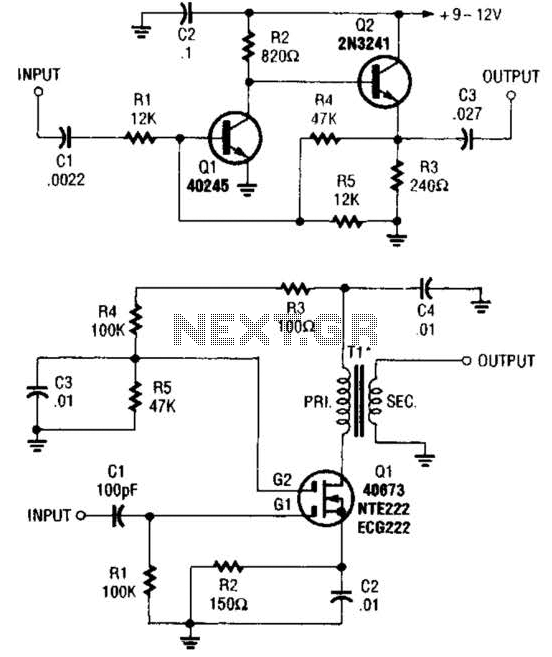
These two buffer/amplifiers have been effectively utilized with variable frequency oscillators (VFOs): one (depicted in A) is constructed using a pair of bipolar NPN transistors, while the other (illustrated in B) is designed around a dual-gate MOSFET.
The first buffer/amplifier, utilizing bipolar NPN transistors, operates by providing high input impedance and low output impedance, which is essential for interfacing with sensitive components like VFOs. The circuit typically includes two NPN transistors configured in a common emitter arrangement. The input signal is fed into the base of the first transistor, which amplifies the signal before passing it to the second transistor for further amplification. This configuration not only boosts the signal strength but also maintains signal integrity, minimizing distortion.
The second buffer/amplifier, based on a dual-gate MOSFET, offers advantages such as lower noise and higher bandwidth compared to its bipolar counterpart. The dual-gate configuration allows for enhanced control over the gain and frequency response of the amplifier. In this design, the input signal is applied to one gate of the MOSFET, while the second gate is used for gain control, allowing for fine-tuning of the amplifier's characteristics. This makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring precise signal manipulation, such as in VFO circuits.
Both designs are critical in ensuring that the output signals from VFOs remain stable and undistorted, which is vital for the performance of radio frequency systems and other applications where signal fidelity is paramount. The choice between the two configurations depends on specific application requirements, including desired frequency response, noise performance, and power consumption. These two buffer/amplifiers that have been successfully used with VFOs: one (shown in A) is based on a pair of bipolar npn transistors, and the other (shown in B) is built around a dual-gate MOSFET. 🔗 External reference
The first buffer/amplifier, utilizing bipolar NPN transistors, operates by providing high input impedance and low output impedance, which is essential for interfacing with sensitive components like VFOs. The circuit typically includes two NPN transistors configured in a common emitter arrangement. The input signal is fed into the base of the first transistor, which amplifies the signal before passing it to the second transistor for further amplification. This configuration not only boosts the signal strength but also maintains signal integrity, minimizing distortion.
The second buffer/amplifier, based on a dual-gate MOSFET, offers advantages such as lower noise and higher bandwidth compared to its bipolar counterpart. The dual-gate configuration allows for enhanced control over the gain and frequency response of the amplifier. In this design, the input signal is applied to one gate of the MOSFET, while the second gate is used for gain control, allowing for fine-tuning of the amplifier's characteristics. This makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring precise signal manipulation, such as in VFO circuits.
Both designs are critical in ensuring that the output signals from VFOs remain stable and undistorted, which is vital for the performance of radio frequency systems and other applications where signal fidelity is paramount. The choice between the two configurations depends on specific application requirements, including desired frequency response, noise performance, and power consumption. These two buffer/amplifiers that have been successfully used with VFOs: one (shown in A) is based on a pair of bipolar npn transistors, and the other (shown in B) is built around a dual-gate MOSFET. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713