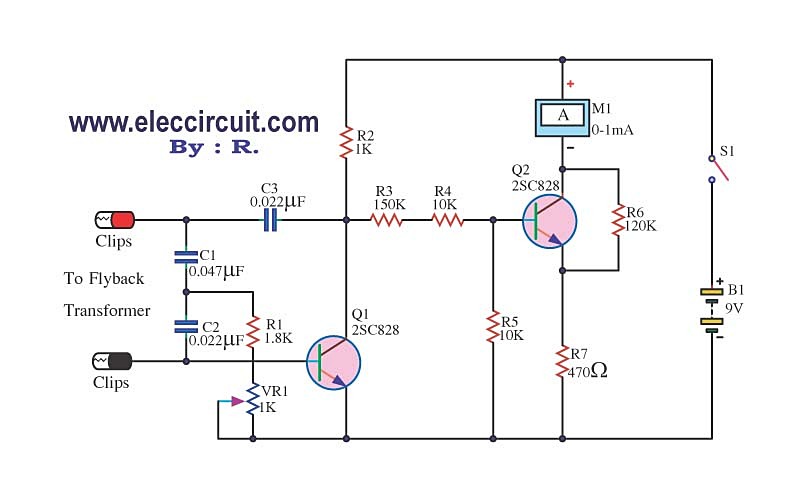
Build a Microphone Polarity Tester
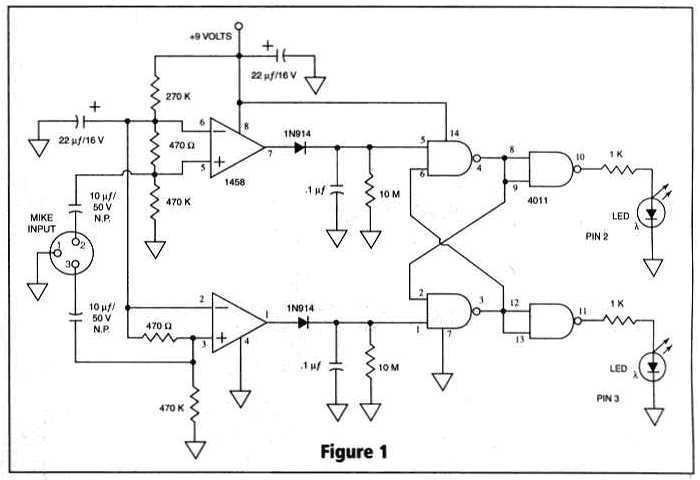
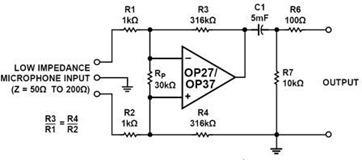
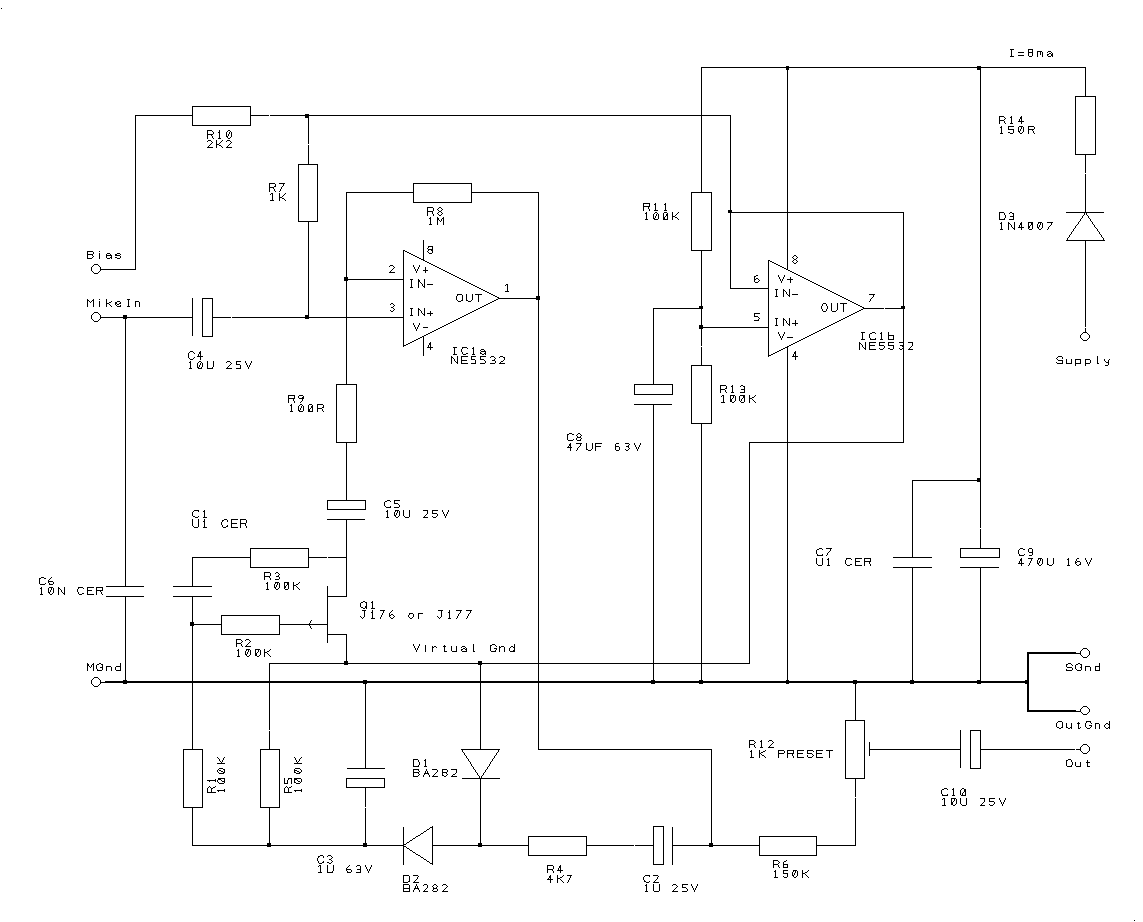
Many things can go wrong in a modern recording studio, but few are as difficult to track down as reversed microphone polarity. When a microphone is placed in front of a sound source, a positive pressure on its diaphragm caused by forward-moving air results in a positive voltage on one of its output pins and a negative voltage on the other. But which pin is positive? These days most microphones have XLR output connectors, with Pin 2 used for the positive voltage output and Pin 3 for the negative.
In a typical recording studio setup, the correct polarity of the microphone signal is crucial for achieving optimal audio quality. Reversed polarity can lead to phase cancellation, resulting in a thin or hollow sound, particularly when multiple microphones are used simultaneously. This phenomenon occurs because when one microphone's diaphragm moves in response to a sound wave, the corresponding voltage output may be inverted if the wiring is incorrect or if the microphone is connected in reverse.
To ensure proper polarity, an XLR connector's pinout must be understood. The standard configuration for an XLR connector is as follows: Pin 1 is ground (shield), Pin 2 is the positive signal (hot), and Pin 3 is the negative signal (cold). When wiring or troubleshooting, it is essential to verify that the output of the microphone corresponds to this standard. A common method to check polarity is by using an oscilloscope to visualize the waveform. By applying a known sound source, such as a clap or a tone generator, the oscilloscope can display the waveform's phase relationship, allowing for easy identification of any polarity issues.
In addition to the wiring of the microphone, the input stage of the audio interface or mixing console must also be considered. Many modern devices feature a polarity reverse switch, which allows users to quickly correct any phase issues without needing to rewire connections. This feature is particularly useful in complex setups where multiple microphones are used, such as in a drum kit recording.
To mitigate reversed polarity issues, it is advisable to implement a consistent wiring protocol and to educate all personnel involved in the recording process about the importance of microphone polarity. Regular maintenance checks of cables and connectors can also prevent accidental reversals due to wear or damage. Understanding and addressing microphone polarity is essential for achieving high-quality recordings and ensuring that sound sources are accurately captured in the studio environment.Many things can go wrong in a modern recording studio, but few are as difficult to track down as reversed microphone polarity. When a microphone is placed in front of a sound source, a positive pressure on its diaphragm caused by forward-moving air results in a positive voltage on one of its output pins and a negative voltage on the other.
But which pin is positive? These days most microphones have XLR output connectors, with Pin 2 used for the positive voltage output and Pin 3 for the negative. 🔗 External reference
In a typical recording studio setup, the correct polarity of the microphone signal is crucial for achieving optimal audio quality. Reversed polarity can lead to phase cancellation, resulting in a thin or hollow sound, particularly when multiple microphones are used simultaneously. This phenomenon occurs because when one microphone's diaphragm moves in response to a sound wave, the corresponding voltage output may be inverted if the wiring is incorrect or if the microphone is connected in reverse.
To ensure proper polarity, an XLR connector's pinout must be understood. The standard configuration for an XLR connector is as follows: Pin 1 is ground (shield), Pin 2 is the positive signal (hot), and Pin 3 is the negative signal (cold). When wiring or troubleshooting, it is essential to verify that the output of the microphone corresponds to this standard. A common method to check polarity is by using an oscilloscope to visualize the waveform. By applying a known sound source, such as a clap or a tone generator, the oscilloscope can display the waveform's phase relationship, allowing for easy identification of any polarity issues.
In addition to the wiring of the microphone, the input stage of the audio interface or mixing console must also be considered. Many modern devices feature a polarity reverse switch, which allows users to quickly correct any phase issues without needing to rewire connections. This feature is particularly useful in complex setups where multiple microphones are used, such as in a drum kit recording.
To mitigate reversed polarity issues, it is advisable to implement a consistent wiring protocol and to educate all personnel involved in the recording process about the importance of microphone polarity. Regular maintenance checks of cables and connectors can also prevent accidental reversals due to wear or damage. Understanding and addressing microphone polarity is essential for achieving high-quality recordings and ensuring that sound sources are accurately captured in the studio environment.Many things can go wrong in a modern recording studio, but few are as difficult to track down as reversed microphone polarity. When a microphone is placed in front of a sound source, a positive pressure on its diaphragm caused by forward-moving air results in a positive voltage on one of its output pins and a negative voltage on the other.
But which pin is positive? These days most microphones have XLR output connectors, with Pin 2 used for the positive voltage output and Pin 3 for the negative. 🔗 External reference