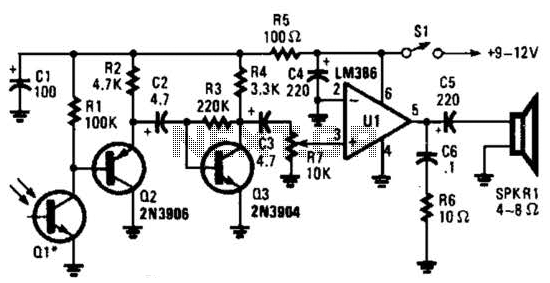
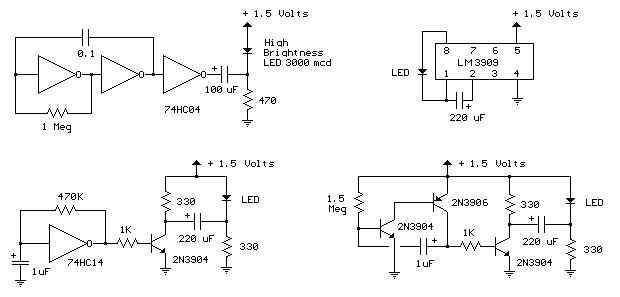
By a clock with a calendar Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027 a circuit diagram of an ultrasonic range finder
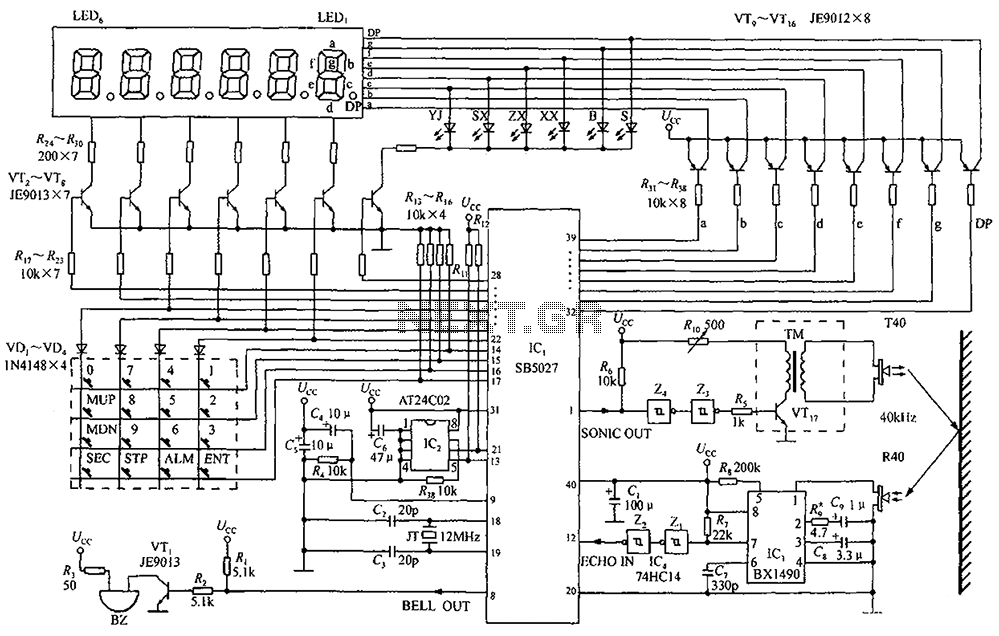
A circuit diagram of an ultrasonic range finder is constructed using a clock with a calendar and the Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027.
The ultrasonic range finder circuit utilizes the Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027, which is designed to measure distances by emitting ultrasonic waves and calculating the time taken for the waves to return after reflecting off an object. This IC integrates various functionalities, including a clock with a calendar, which can be employed to timestamp measurements or synchronize operations.
The circuit typically includes a transmitter and receiver pair, where the transmitter emits ultrasonic pulses at a specific frequency. The SB5027 manages the timing of these emissions and listens for the echoes. Upon receiving the reflected signal, the IC calculates the distance based on the speed of sound in air, utilizing the time delay between emission and reception.
Additional components in the circuit may include a microcontroller for processing the distance data, a display module for visual output, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger measurements at regular intervals, utilizing the calendar feature to log data over time, which can be useful for applications requiring historical distance tracking.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design, as the circuit should operate efficiently within the specified voltage range of the SB5027. The layout should minimize interference and optimize the positioning of the transmitter and receiver for accurate measurements. Overall, this ultrasonic range finder circuit is a versatile tool for various applications, including automation, robotics, and obstacle detection. By a clock with a calendar Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027 constitute a circuit diagram of an ultrasonic range finder
The ultrasonic range finder circuit utilizes the Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027, which is designed to measure distances by emitting ultrasonic waves and calculating the time taken for the waves to return after reflecting off an object. This IC integrates various functionalities, including a clock with a calendar, which can be employed to timestamp measurements or synchronize operations.
The circuit typically includes a transmitter and receiver pair, where the transmitter emits ultrasonic pulses at a specific frequency. The SB5027 manages the timing of these emissions and listens for the echoes. Upon receiving the reflected signal, the IC calculates the distance based on the speed of sound in air, utilizing the time delay between emission and reception.
Additional components in the circuit may include a microcontroller for processing the distance data, a display module for visual output, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger measurements at regular intervals, utilizing the calendar feature to log data over time, which can be useful for applications requiring historical distance tracking.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design, as the circuit should operate efficiently within the specified voltage range of the SB5027. The layout should minimize interference and optimize the positioning of the transmitter and receiver for accurate measurements. Overall, this ultrasonic range finder circuit is a versatile tool for various applications, including automation, robotics, and obstacle detection. By a clock with a calendar Ultrasonic Ranging IC SB5027 constitute a circuit diagram of an ultrasonic range finder