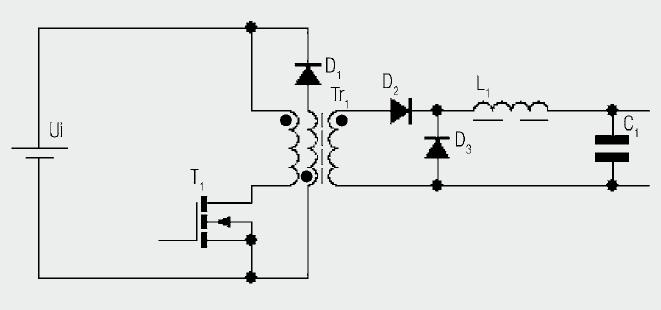
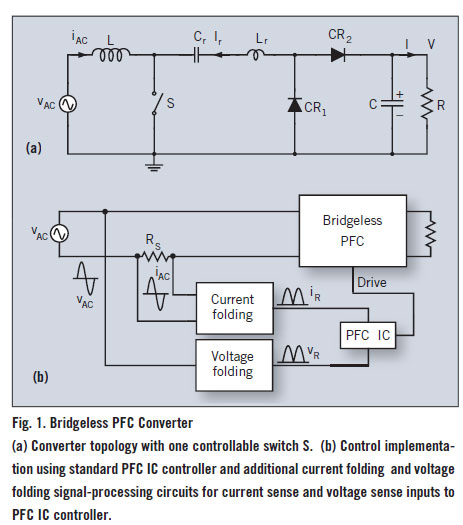
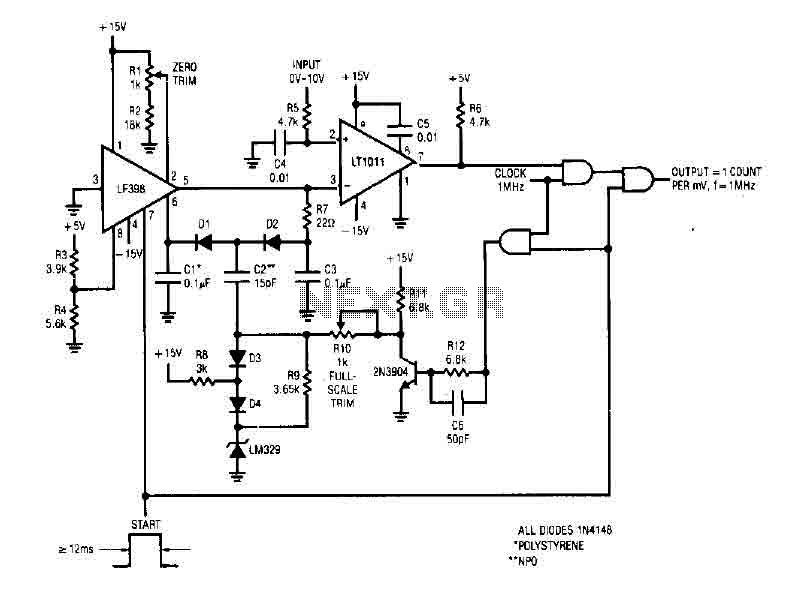
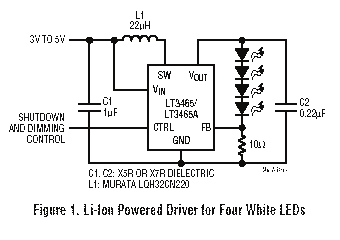
Calculator-to-stopwatch converter

This circuit can be connected to any existing calculator battery using a push-on automatic switch, allowing it to function as a stopwatch while the calculator is not in use.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in monostable mode to create a stopwatch function. When the push-on switch is activated, the timer begins to run, generating a pulse at a predetermined frequency. This frequency can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer, allowing for precise timing intervals.
The output from the 555 timer can be used to drive a display, such as an LED or an LCD, to visually indicate the elapsed time. In addition, the circuit can incorporate a second push-off switch that, when activated, will stop the timer and reset the display to zero.
To ensure compatibility with various calculator batteries, the circuit should include a voltage regulator to maintain a stable voltage supply to the 555 timer and any additional components. Proper filtering capacitors should also be included to reduce noise and improve the reliability of the circuit.
Overall, this stopwatch circuit enhances the functionality of standard calculators, providing an additional tool for users while maintaining simplicity and ease of use.This circuit can be fitted to any calculator existing calculator battery via the push-on with an automatic constant to enable it to be push-off switch and the existing calculator on-used as a stop-watch The 555 timer is set to off switch, run at a suitable frequency and connected to the. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in monostable mode to create a stopwatch function. When the push-on switch is activated, the timer begins to run, generating a pulse at a predetermined frequency. This frequency can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer, allowing for precise timing intervals.
The output from the 555 timer can be used to drive a display, such as an LED or an LCD, to visually indicate the elapsed time. In addition, the circuit can incorporate a second push-off switch that, when activated, will stop the timer and reset the display to zero.
To ensure compatibility with various calculator batteries, the circuit should include a voltage regulator to maintain a stable voltage supply to the 555 timer and any additional components. Proper filtering capacitors should also be included to reduce noise and improve the reliability of the circuit.
Overall, this stopwatch circuit enhances the functionality of standard calculators, providing an additional tool for users while maintaining simplicity and ease of use.This circuit can be fitted to any calculator existing calculator battery via the push-on with an automatic constant to enable it to be push-off switch and the existing calculator on-used as a stop-watch The 555 timer is set to off switch, run at a suitable frequency and connected to the. 🔗 External reference