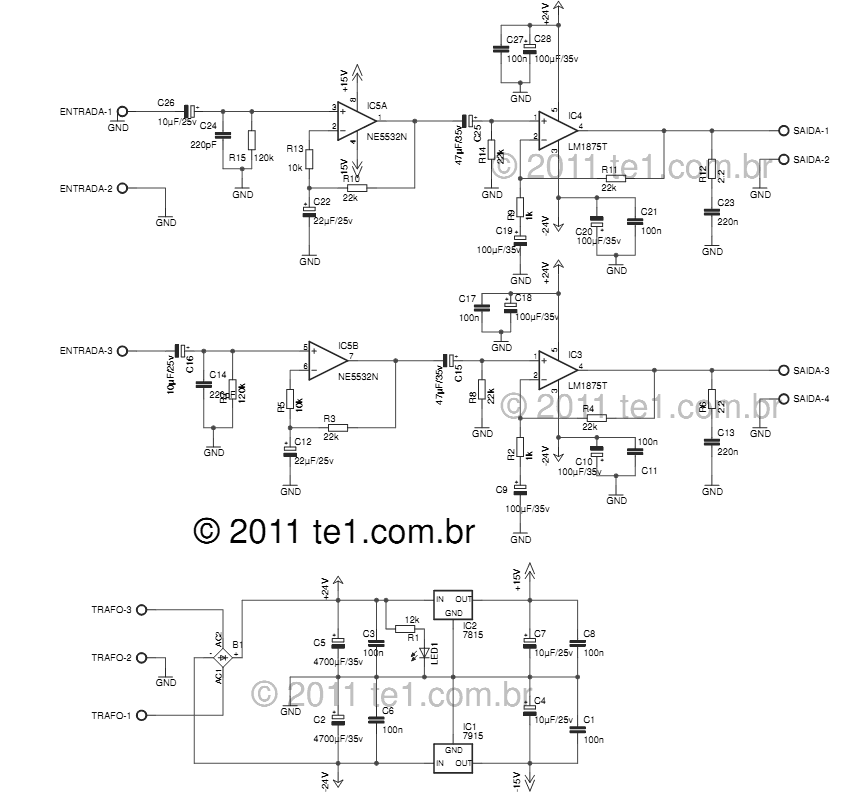
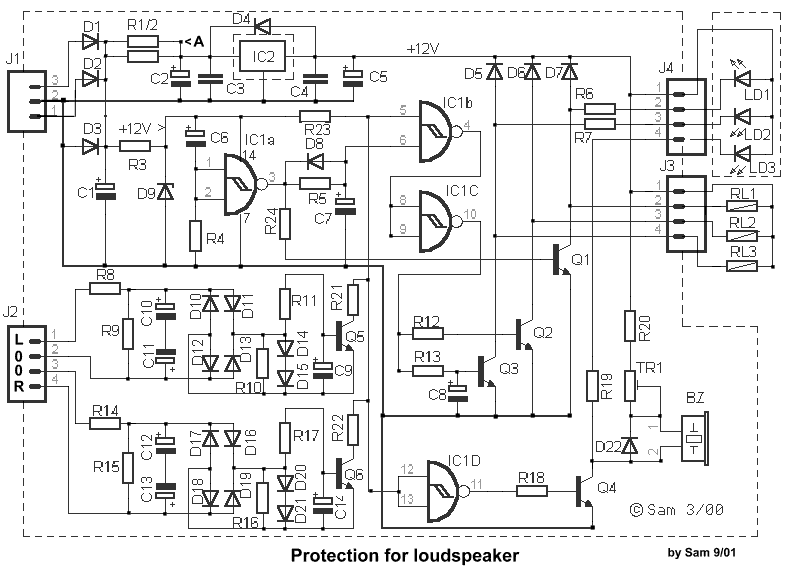
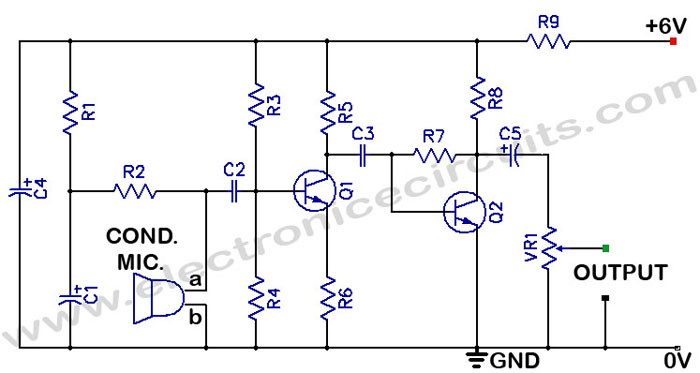
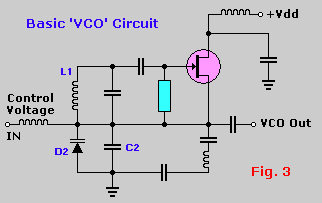
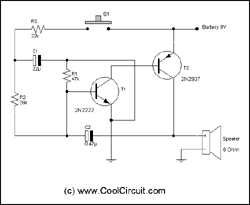
Capacitance compensation circuit diagram of a power protection
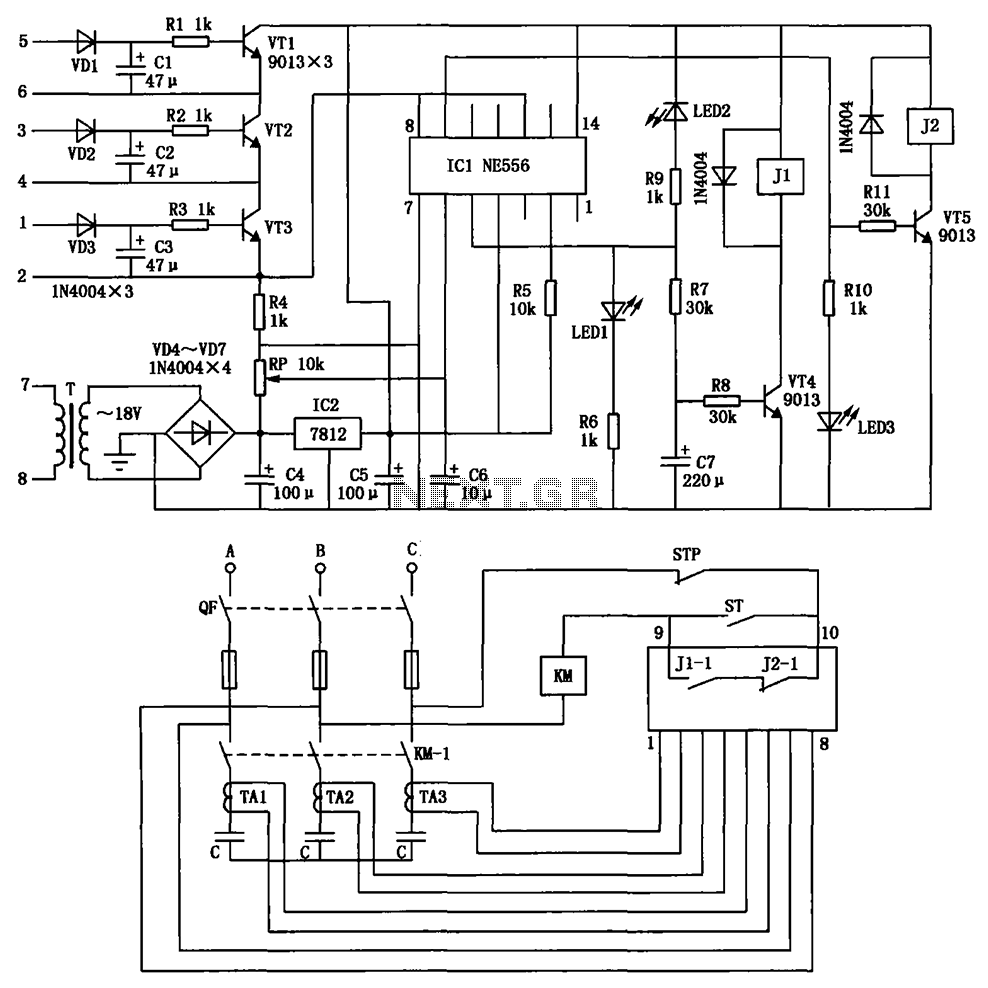
The circuit depicted is utilized in a power supply system to promptly disconnect the power supply in the event of an over-voltage condition during either the grid's on or off phase, thereby protecting the power capacitors.
This circuit serves a critical role in safeguarding electronic components by monitoring voltage levels and ensuring they remain within specified limits. It typically employs a voltage sensing mechanism, which may consist of a voltage divider and a comparator. The voltage divider scales down the input voltage to a manageable level, while the comparator compares this scaled voltage against a predetermined reference voltage.
When the input voltage exceeds the reference level, the comparator triggers a response, which may involve activating a relay or a solid-state switch to disconnect the load from the power supply. This disconnection occurs swiftly to prevent damage to sensitive components, particularly power capacitors, which can be adversely affected by excessive voltage.
In addition, the circuit may include transient voltage suppression devices, such as varistors or TVS diodes, to absorb voltage spikes and provide an additional layer of protection. The design should ensure that the components selected can handle the maximum expected voltage and current levels, while also considering thermal management to avoid overheating during operation.
Furthermore, the circuit layout should minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance to enhance response time and reliability. Proper grounding techniques and isolation methods should be employed to prevent noise interference and ensure stable operation. Overall, the implementation of this over-voltage protection circuit is essential for maintaining the longevity and reliability of power supply systems in various electronic applications. Circuit is shown, it is used in the power supply circuit can occur in the case of over-voltage grid on or off phase, promptly cut off the power supply to protect power capacito rs.
This circuit serves a critical role in safeguarding electronic components by monitoring voltage levels and ensuring they remain within specified limits. It typically employs a voltage sensing mechanism, which may consist of a voltage divider and a comparator. The voltage divider scales down the input voltage to a manageable level, while the comparator compares this scaled voltage against a predetermined reference voltage.
When the input voltage exceeds the reference level, the comparator triggers a response, which may involve activating a relay or a solid-state switch to disconnect the load from the power supply. This disconnection occurs swiftly to prevent damage to sensitive components, particularly power capacitors, which can be adversely affected by excessive voltage.
In addition, the circuit may include transient voltage suppression devices, such as varistors or TVS diodes, to absorb voltage spikes and provide an additional layer of protection. The design should ensure that the components selected can handle the maximum expected voltage and current levels, while also considering thermal management to avoid overheating during operation.
Furthermore, the circuit layout should minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance to enhance response time and reliability. Proper grounding techniques and isolation methods should be employed to prevent noise interference and ensure stable operation. Overall, the implementation of this over-voltage protection circuit is essential for maintaining the longevity and reliability of power supply systems in various electronic applications. Circuit is shown, it is used in the power supply circuit can occur in the case of over-voltage grid on or off phase, promptly cut off the power supply to protect power capacito rs.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713