Car auto-dimmer
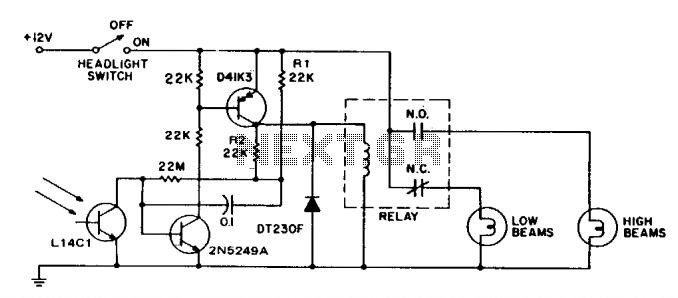
This circuit switches car headlights to the low beam state when it detects the lights of an oncoming vehicle. The received light is of low intensity and highly directional, indicating the use of a lens with the detector. A significant amount of hysteresis is incorporated into the circuit to prevent the headlights from "flashing."
Sensitivity is adjusted by a 22 megohm resistor, setting it to approximately 0.5 foot-candle at the transistor (0.01 at the lens), while hysteresis is defined by the resistor voltage divider formed by R1 and R2, which is connected in parallel with the collector-emitter of the D41K3 transistor. This configuration drives the 22 megohm resistor. The maximum switching rate is restricted by a 0.1 µF capacitor to 15 operations per minute.
The relay used in the circuit operates at 12V with a coil current of 0.3A, and it can handle a maximum load of 20A with form C contacts or solid-state switching rated for 16A in steady-state conditions, with a cold filament surge rating of 160A. The lens employed has a minimum diameter of 1 inch and is positioned to provide an approximate 10-degree view angle.
This circuit effectively enhances vehicle safety by automatically dimming headlights in response to oncoming traffic, thereby reducing glare for other drivers. The light detection mechanism relies on a lens system that focuses light onto a sensitive phototransistor, which is calibrated to respond at low ambient light levels. The hysteresis feature is crucial in ensuring that the system does not react to transient light changes, such as those caused by streetlights or reflective surfaces, which could lead to unnecessary switching of the headlights.
The choice of a 22 megohm resistor for sensitivity adjustment allows for fine-tuning of the light detection threshold, ensuring optimal performance under varying environmental conditions. The voltage divider formed by R1 and R2 plays a vital role in establishing the required hysteresis, which helps maintain stable operation and prevents rapid cycling of the headlights.
The relay component serves as a robust switching mechanism, capable of handling substantial current loads, which is essential for automotive applications. The specification of a 12V relay is standard in vehicle electrical systems, and the ability to manage cold filament surges ensures that the circuit can withstand the inrush current experienced when headlights are first activated.
The lens design, with its minimum diameter and specified view angle, is critical for accurate light detection. The 10-degree view angle allows the sensor to effectively capture the headlights of oncoming vehicles while minimizing interference from other light sources. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing automotive lighting systems, promoting safer driving conditions through intelligent headlight management.This circuit switches car headlights to the low beam state when it senses the lights of an on-coming car. The received light is very low level and highly directional, indicating the use of a lens with the detector.
A relatively large amount of hysteresis is built into the circuit to prevent "flashing lights." Sensitivity is set by the 22 megohm resistor to about 0.5 ft. candle at the transistor (0.01 at the lens), while hysteresis is determined by the Rl, R2 resistor voltage divider, parallel to the D41K3 collector emitter, which drives the 22 megohm resistor; maximum switching rate is limited by the 0.1 ?Â¥ capacitor to 15/minute. relay: 12v, 0.3a coil: 20a, form c. contacts or solid-state switching of 16a steady-state 160a cold filament surge. rating. lens; minimum 1" diameter. positioned for about 10? view angle. 🔗 External reference
Sensitivity is adjusted by a 22 megohm resistor, setting it to approximately 0.5 foot-candle at the transistor (0.01 at the lens), while hysteresis is defined by the resistor voltage divider formed by R1 and R2, which is connected in parallel with the collector-emitter of the D41K3 transistor. This configuration drives the 22 megohm resistor. The maximum switching rate is restricted by a 0.1 µF capacitor to 15 operations per minute.
The relay used in the circuit operates at 12V with a coil current of 0.3A, and it can handle a maximum load of 20A with form C contacts or solid-state switching rated for 16A in steady-state conditions, with a cold filament surge rating of 160A. The lens employed has a minimum diameter of 1 inch and is positioned to provide an approximate 10-degree view angle.
This circuit effectively enhances vehicle safety by automatically dimming headlights in response to oncoming traffic, thereby reducing glare for other drivers. The light detection mechanism relies on a lens system that focuses light onto a sensitive phototransistor, which is calibrated to respond at low ambient light levels. The hysteresis feature is crucial in ensuring that the system does not react to transient light changes, such as those caused by streetlights or reflective surfaces, which could lead to unnecessary switching of the headlights.
The choice of a 22 megohm resistor for sensitivity adjustment allows for fine-tuning of the light detection threshold, ensuring optimal performance under varying environmental conditions. The voltage divider formed by R1 and R2 plays a vital role in establishing the required hysteresis, which helps maintain stable operation and prevents rapid cycling of the headlights.
The relay component serves as a robust switching mechanism, capable of handling substantial current loads, which is essential for automotive applications. The specification of a 12V relay is standard in vehicle electrical systems, and the ability to manage cold filament surges ensures that the circuit can withstand the inrush current experienced when headlights are first activated.
The lens design, with its minimum diameter and specified view angle, is critical for accurate light detection. The 10-degree view angle allows the sensor to effectively capture the headlights of oncoming vehicles while minimizing interference from other light sources. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing automotive lighting systems, promoting safer driving conditions through intelligent headlight management.This circuit switches car headlights to the low beam state when it senses the lights of an on-coming car. The received light is very low level and highly directional, indicating the use of a lens with the detector.
A relatively large amount of hysteresis is built into the circuit to prevent "flashing lights." Sensitivity is set by the 22 megohm resistor to about 0.5 ft. candle at the transistor (0.01 at the lens), while hysteresis is determined by the Rl, R2 resistor voltage divider, parallel to the D41K3 collector emitter, which drives the 22 megohm resistor; maximum switching rate is limited by the 0.1 ?Â¥ capacitor to 15/minute. relay: 12v, 0.3a coil: 20a, form c. contacts or solid-state switching of 16a steady-state 160a cold filament surge. rating. lens; minimum 1" diameter. positioned for about 10? view angle. 🔗 External reference