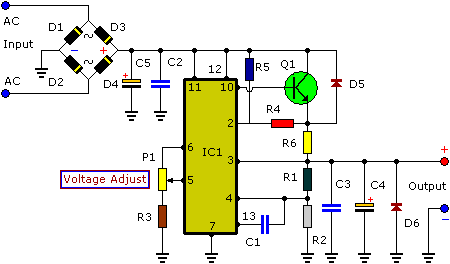
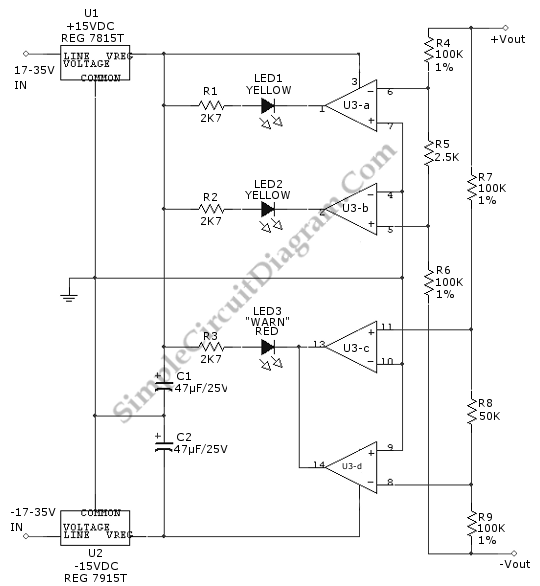
Car Cigar Lighter to USB Power Socket
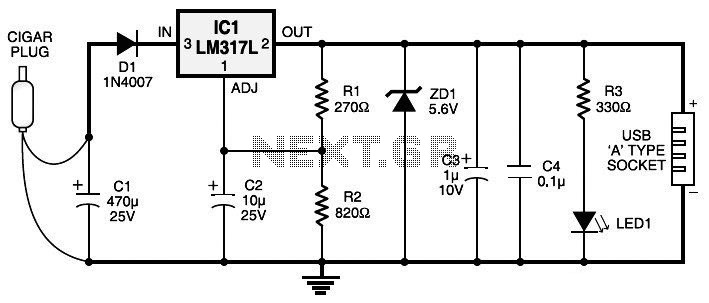
Currently, nearly all computer systems include logic blocks designed for interfacing with a USB port. In practical terms, a USB port can provide more than 100 mA of continuous electric current at 5V to the peripherals connected to the bus.
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) port serves as a crucial interface in modern computer systems, facilitating communication and power delivery between the host and various peripheral devices. The logic blocks associated with the USB port are typically integrated into the system's chipset or microcontroller, enabling the management of data transfer and power distribution.
A standard USB port operates at a nominal voltage of 5V, with the capability to supply a minimum of 100 mA of current. However, depending on the USB specification (such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or USB-C), the current capacity can be significantly higher, allowing for faster charging and powering of devices. For instance, USB 3.0 can provide up to 900 mA, while USB-C can deliver up to 3A or more, depending on the implementation.
The logic blocks typically include a USB controller, which handles the protocol for data communication, and power management circuitry that regulates the voltage and current supplied to the connected peripherals. This architecture ensures that devices such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage can operate effectively while maintaining safe power levels.
In addition to power delivery, USB ports support a variety of data transfer modes, including bulk, interrupt, isochronous, and control transfers, each serving different types of applications and requirements. The versatility of USB technology has made it a standard for connecting a wide range of devices in both consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Overall, the integration of USB logic blocks within computer systems enhances the functionality and user experience by providing a reliable and efficient means of connecting and powering peripheral devices.Nowadays, almost all computer systems have logic blocks for working with a USB port. A USB port, in practice, is capable of supplying more than 100 mA of continuous electric current at 5V to the peripherals which are hooked up with the bus.. 🔗 External reference
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) port serves as a crucial interface in modern computer systems, facilitating communication and power delivery between the host and various peripheral devices. The logic blocks associated with the USB port are typically integrated into the system's chipset or microcontroller, enabling the management of data transfer and power distribution.
A standard USB port operates at a nominal voltage of 5V, with the capability to supply a minimum of 100 mA of current. However, depending on the USB specification (such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or USB-C), the current capacity can be significantly higher, allowing for faster charging and powering of devices. For instance, USB 3.0 can provide up to 900 mA, while USB-C can deliver up to 3A or more, depending on the implementation.
The logic blocks typically include a USB controller, which handles the protocol for data communication, and power management circuitry that regulates the voltage and current supplied to the connected peripherals. This architecture ensures that devices such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage can operate effectively while maintaining safe power levels.
In addition to power delivery, USB ports support a variety of data transfer modes, including bulk, interrupt, isochronous, and control transfers, each serving different types of applications and requirements. The versatility of USB technology has made it a standard for connecting a wide range of devices in both consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Overall, the integration of USB logic blocks within computer systems enhances the functionality and user experience by providing a reliable and efficient means of connecting and powering peripheral devices.Nowadays, almost all computer systems have logic blocks for working with a USB port. A USB port, in practice, is capable of supplying more than 100 mA of continuous electric current at 5V to the peripherals which are hooked up with the bus.. 🔗 External reference