Car Headlights Timer Circuit Schematic
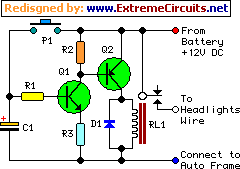
This device is a simple timer that keeps the headlights of a vehicle on for approximately 1 minute and 30 seconds, allowing for illumination when accessing dark areas without the need to return to switch off the lights. Pressing P1 charges capacitor C1 from the vehicle's 12V battery supply. This action turns on transistor Q1, which subsequently activates transistor Q2 and its associated relay load. The headlights are thus controlled through the relay contacts wired in parallel with the vehicle's headlight switch. Relay RL1 remains engaged until C1 is nearly fully discharged, specifically when its voltage drops below approximately 0.7V. The timing delay of the circuit is determined by the values of C1 and resistor R1, and is calibrated to around 1 minute and 30 seconds. However, due to the wide tolerance of electrolytic capacitors, this delay may vary from about 1 minute and 30 seconds to 1 minute and 50 seconds. An interesting modification allows the vehicle's interior lamp to serve as the trigger for the timer. In this configuration, when the door is opened, C1 charges, but it will only begin to discharge when the door is closed, effectively replacing the pushbutton operation. To implement this feature, the cathode of a 1N4002 diode should be connected to the junction of R1 and C1, while the anode connects to the "live" wire of the interior lamp. This wire can be identified using a voltmeter, as it will show a 12V voltage relative to the vehicle frame when the lamp is illuminated.
The timer circuit operates on a straightforward principle utilizing a capacitor, resistors, and transistors to control the relay that activates the headlights. Initially, when the button P1 is pressed, capacitor C1 begins to charge from the 12V supply of the vehicle's battery. The charging process allows Q1, a switching transistor, to enter saturation, which in turn drives Q2, another transistor that controls the relay RL1. This relay, when energized, connects the vehicle's headlights to the power supply, allowing them to remain illuminated.
The timing mechanism relies on the RC (resistor-capacitor) time constant, where the product of R1 and C1 determines the duration for which the headlights will stay on. The voltage across C1 decreases as it discharges through R1, and once it drops below 0.7V, Q1 turns off, deactivating Q2 and consequently the relay RL1, which turns off the headlights.
In the alternative configuration using the interior lamp, the circuit becomes even more user-friendly. The diode 1N4002 ensures that the capacitor charges only when the door is open. When the door closes, the discharge path is established, allowing the circuit to function without manual intervention. This modification enhances the convenience of the timer, making it a practical addition to any vehicle for improved safety and ease of use in dark environments. Proper selection of component values is crucial to achieving the desired timing interval and ensuring reliable operation of the circuit under various conditions.This device is a simple timer, allowing to keep on the headlights of your vehicle for about 1min. and 30sec. , e. g. when accessing some dark place, without the necessity of coming back to switch-off the lights. Pushing on P1 allows C1 charging to full 12V battery supply. Therefore Q1 is driven hard-on, driving in turn Q2 and its Relay load. The hea dlights are thus activated by means of the Relay contact wired in parallel to the vehicle`s headlights switch. RL1 remains activated until C1 is almost fully discharged, i. e. When its voltage falls below about 0. 7V. The timing delay of the circuit depends by C1 and R1 values and was set to about 1min. and 30sec. In practice, due to electrolytic capacitors wide tolerance value, this delay will vary from about 1min.
and 30sec. to 1min. and 50sec. An interesting variation is to use the inside lamp as a command source for the timer. In this way, when the door is opened C1 is charged, but it will start to discharge only when the door will be closed, substituting pushbutton operation. To enable the circuit acting in this way, simply connect the cathode of a 1N4002 diode to R1-C1 junction and the anode to the "live" lead of the inside lamp.
This lead can be singled-out using a voltmeter, as it is the lead where a 12V voltage can be measured in respect to the vehicle frame when the lamp is on. 🔗 External reference
The timer circuit operates on a straightforward principle utilizing a capacitor, resistors, and transistors to control the relay that activates the headlights. Initially, when the button P1 is pressed, capacitor C1 begins to charge from the 12V supply of the vehicle's battery. The charging process allows Q1, a switching transistor, to enter saturation, which in turn drives Q2, another transistor that controls the relay RL1. This relay, when energized, connects the vehicle's headlights to the power supply, allowing them to remain illuminated.
The timing mechanism relies on the RC (resistor-capacitor) time constant, where the product of R1 and C1 determines the duration for which the headlights will stay on. The voltage across C1 decreases as it discharges through R1, and once it drops below 0.7V, Q1 turns off, deactivating Q2 and consequently the relay RL1, which turns off the headlights.
In the alternative configuration using the interior lamp, the circuit becomes even more user-friendly. The diode 1N4002 ensures that the capacitor charges only when the door is open. When the door closes, the discharge path is established, allowing the circuit to function without manual intervention. This modification enhances the convenience of the timer, making it a practical addition to any vehicle for improved safety and ease of use in dark environments. Proper selection of component values is crucial to achieving the desired timing interval and ensuring reliable operation of the circuit under various conditions.This device is a simple timer, allowing to keep on the headlights of your vehicle for about 1min. and 30sec. , e. g. when accessing some dark place, without the necessity of coming back to switch-off the lights. Pushing on P1 allows C1 charging to full 12V battery supply. Therefore Q1 is driven hard-on, driving in turn Q2 and its Relay load. The hea dlights are thus activated by means of the Relay contact wired in parallel to the vehicle`s headlights switch. RL1 remains activated until C1 is almost fully discharged, i. e. When its voltage falls below about 0. 7V. The timing delay of the circuit depends by C1 and R1 values and was set to about 1min. and 30sec. In practice, due to electrolytic capacitors wide tolerance value, this delay will vary from about 1min.
and 30sec. to 1min. and 50sec. An interesting variation is to use the inside lamp as a command source for the timer. In this way, when the door is opened C1 is charged, but it will start to discharge only when the door will be closed, substituting pushbutton operation. To enable the circuit acting in this way, simply connect the cathode of a 1N4002 diode to R1-C1 junction and the anode to the "live" lead of the inside lamp.
This lead can be singled-out using a voltmeter, as it is the lead where a 12V voltage can be measured in respect to the vehicle frame when the lamp is on. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713