Cellular Phone Calling Detector Circuit
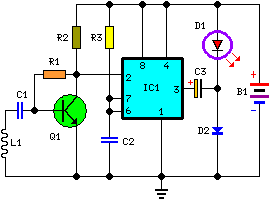
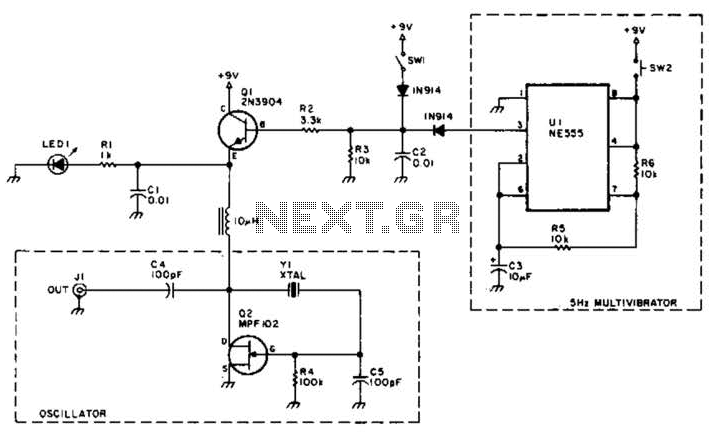
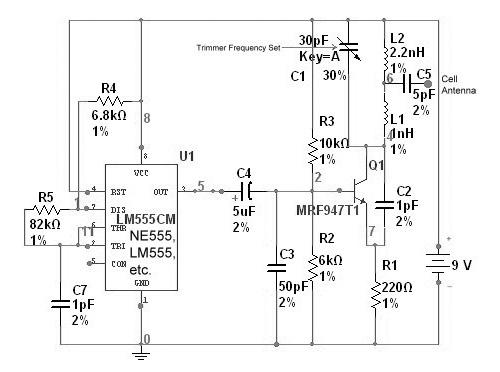
This circuit is designed to detect incoming calls on a cellular phone, even when the phone's ringer is turned off, by utilizing a flashing LED indicator. The device should be positioned a few centimeters away from the cellular phone, allowing its sensor coil L1 to sense the electromagnetic field generated by the phone's receiver during an incoming call.
The circuit operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the sensor coil L1 detects the electromagnetic field produced by the cellular phone when it receives a call. The coil is designed to be sensitive enough to pick up the field without requiring direct contact with the phone.
The main components of the circuit include the sensor coil L1, a rectifier circuit to convert the alternating current (AC) induced in the coil to direct current (DC), and a microcontroller or a simple transistor-based circuit to drive the LED. The LED serves as a visual indicator of an incoming call, flashing in response to the detected signal.
To enhance the circuit's performance, the sensor coil can be tuned to a specific frequency range that corresponds to the typical operating frequencies of cellular phones. This may involve adjusting the number of turns in the coil or incorporating capacitive elements to create a resonant circuit.
In terms of power supply, the circuit can be powered by a small battery or a low-voltage power source, ensuring that it remains portable and easy to use. The entire assembly can be housed in a small enclosure that allows for easy placement near the cellular phone without obstructing its normal operation.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for individuals who may need to be alerted to incoming calls discreetly, without relying on the phone's built-in ringer.This circuit was designed to detect when a call is incoming in a cellular phone (even when the calling tone of the device is switched-off) by means of a flashing LED. The device must be placed a few centimeters from the cellular phone, so its sensor coil L1 can detect the field emitted by the phone receiver during an incoming call..
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the sensor coil L1 detects the electromagnetic field produced by the cellular phone when it receives a call. The coil is designed to be sensitive enough to pick up the field without requiring direct contact with the phone.
The main components of the circuit include the sensor coil L1, a rectifier circuit to convert the alternating current (AC) induced in the coil to direct current (DC), and a microcontroller or a simple transistor-based circuit to drive the LED. The LED serves as a visual indicator of an incoming call, flashing in response to the detected signal.
To enhance the circuit's performance, the sensor coil can be tuned to a specific frequency range that corresponds to the typical operating frequencies of cellular phones. This may involve adjusting the number of turns in the coil or incorporating capacitive elements to create a resonant circuit.
In terms of power supply, the circuit can be powered by a small battery or a low-voltage power source, ensuring that it remains portable and easy to use. The entire assembly can be housed in a small enclosure that allows for easy placement near the cellular phone without obstructing its normal operation.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for individuals who may need to be alerted to incoming calls discreetly, without relying on the phone's built-in ringer.This circuit was designed to detect when a call is incoming in a cellular phone (even when the calling tone of the device is switched-off) by means of a flashing LED. The device must be placed a few centimeters from the cellular phone, so its sensor coil L1 can detect the field emitted by the phone receiver during an incoming call..
🔗 External reference